Hex head bolts serve as essential fasteners in industrial settings, providing secure connections for machinery, structural steel, and heavy equipment. The global market for hex bolts continues to expand, with projections reaching USD 173.8 billion by 2034. Selecting the correct type, grade, and material impacts safety and reliability in applications such as bridge construction, power plants, and offshore platforms. Quality, traceability, and customization support demanding environments, ensuring each bolt performs under high stress and corrosive conditions.
Technical Overview: Hex Head Bolts and Standards
Definition and Load-Bearing Functions
Hex head bolts play a critical role in industrial assembly. Engineers use these bolts to join structural steel, secure machinery, and anchor heavy equipment. The hexagon head design allows for high torque application, which ensures a tight and secure fit. Hex bolts distribute load evenly across the bearing surface, reducing the risk of joint failure. Hexagon head bolts provide reliable performance in both static and dynamic load conditions.
The load-bearing capacity of hex bolts depends on material composition and manufacturing standards. For example, ASTM A325 bolts use medium carbon steel and serve in bridges and buildings. ASTM A490 bolts, made from alloy steel, offer higher strength for heavy construction. ASTM A193 B7 bolts withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for petrochemical and power generation industries. ASTM A307 bolts, produced from low-carbon steel, fit non-critical applications.
Tip: Always select hex bolts based on the required load, environment, and compliance with engineering standards.
Global Standards Guide (ASME B18.2.1, DIN 931/933, ISO 4014/4017)
Manufacturers and engineers rely on international standards to ensure compatibility and safety. The most recognized standards for hex head bolts include ASME B18.2.1, DIN 931/933, and ISO 4014/4017. Each standard defines dimensions, tolerances, and thread specifications for hexagon head bolts.
| Description | DIN Standard | ISO Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Hex Head Bolts (Fully Threaded), Metric Coarse | DIN 933 | ISO 4017 |
| Hex Head Bolts (Partially Threaded), Metric Coarse | DIN 931 | ISO 4014 |
| Hex Head Bolts (Fully Threaded), Metric Fine | DIN 961 | ISO 8676 |
| Hex Head Bolts (Partially Threaded), Metric Fine | DIN 960 | ISO 8765 |
ISO standards often specify tighter tolerances than DIN standards. For instance, an M10 hex bolt under DIN 933 requires a 17 mm wrench, while ISO 4017 specifies a 16 mm wrench. This difference affects tool selection and assembly practices. ISO 4014 and ISO 4017 classify hexagon head fasteners for global use, supporting standardization across supply chains.
| Standard | Bolt Size | Wrench Size | Tolerance Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIN 933 | M10 | 17 mm | Generally wider tolerances |
| ISO 4017 | M10 | 16 mm | Tighter tolerances specified |
| DIN 931/933 | Various | Varies | Transition to ISO for harmonization |
Engineers should verify which standard applies to their project to ensure proper fit and performance. Hex bolts produced to these standards guarantee interchangeability and reliability in critical applications.
Hex Bolt vs. Hex Cap Screw: An Engineering Distinction
Tolerance Differences under ASME B18.2.1
Engineers often compare hex bolts and hex cap screws when selecting fasteners for industrial projects. The main difference lies in their tolerance requirements under ASME B18.2.1. Hex cap screws feature tighter tolerances, which make them ideal for applications demanding precise alignment. These screws fit directly into tapped holes, ensuring a secure and accurate connection. Hex bolts, on the other hand, have looser tolerances. They work best in general applications where high precision is not critical.
| Feature | Hex Bolt | Hex Cap Screw |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerances | Higher maximum tolerance on body diameter | Tighter tolerances for precise installation |
| Installation | Requires a nut, passes through unthreaded holes | Threads directly into a tapped hole |
| Body Diameter | Typically undersized for easier passage | Full-sized, precise diameter for alignment |
Hex cap screws provide a minimum body diameter of 0.245” and a maximum of 0.250” for a ¼” nominal size, which demonstrates their strict dimensional control. Using the wrong fastener in high-stress or precision-required applications can lead to improper fit and reduced performance.
Note: Engineers should always verify tolerance requirements before selecting hex head bolts or hex cap screws for critical assemblies.
When to Use Washer Faces vs. Flat Bearing Surfaces
The design of the fastener head affects load distribution and installation. Hex cap screws include a washer face under the head, which helps distribute clamping force evenly and protects the mating surface. This feature is essential in assemblies where surface integrity and even load are priorities. Hex bolts typically have a flat bearing surface without a washer face, making them suitable for general-purpose connections.
- Hex cap screws are preferred for:
- Precision machinery
- Equipment requiring even load distribution
- Applications with tapped holes
- Hex bolts are chosen for:
- Structural steel connections
- Assemblies using nuts
- Projects where tolerances are less critical
Hex head bolts remain a staple in industrial fastening, but understanding the distinction between hex bolts and hex cap screws ensures optimal performance and reliability in every application.
Structural Types and Thread Configurations
Full Thread (Tap Bolts) vs. Partial Thread (Structural Strength)
Engineers select hex bolts based on thread configuration to match the demands of each application. Fully threaded hex bolts, also known as tap bolts, provide consistent grip strength along their entire length. This design distributes pressure evenly, making these bolts less likely to loosen under vibration or dynamic loads. Fully threaded hex bolts excel in structural settings where grip strength is critical, such as securing metal frameworks or heavy machinery.
Partial thread hex bolts feature an unthreaded shank near the head. This section improves alignment and increases shear strength, which is essential for connections that experience lateral forces. The unthreaded portion allows for precise positioning, making these bolts ideal for structural steel assemblies and bridge construction. Engineers often choose partial thread bolts when alignment and shear resistance outweigh the need for maximum grip.
| Bolt Type | Thread Coverage | Mechanical Advantage | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fully Threaded Hex Bolts | Full length | Even pressure, strong grip | Metal frameworks, machinery |
| Partial Thread Hex Bolts | Partial length | Precise alignment, shear strength | Structural steel, bridges |
Standard Hex vs. Heavy Hex (Structural Connections)
Hex head bolts come in standard and heavy hex variations. Heavy hex bolts, such as A325 Type 1, feature a larger head and increased bearing surface. This design enables higher clamping force and improved torque control. Heavy hex bolts provide reliable performance in structural connections, including steel columns and beams. The larger head reduces the risk of bolt pull-through and enhances joint integrity.
Standard hex bolts suit general-purpose fastening tasks. They offer versatility for machinery assembly and non-critical connections. Heavy hex bolts remain the preferred choice for demanding structural applications due to their superior load-bearing capacity.
Flange Bolts and Specialized Heads
Specialized hexagon head bolts, including flange bolts, serve unique roles in industrial sectors. Flange bolts incorporate a built-in washer under the head, which distributes load and protects the mating surface. Engineers use these bolts to simplify assembly and improve clamping efficiency.
- Automotive industry – Engine assemblies, exhaust systems, chassis components
- Piping systems – Secure pipe connections in oil, gas, and chemical industries
- Heavy machinery – Stability in industrial equipment and construction machinery
- Structural applications – Bridges, buildings, metal frameworks
Selecting the right types of hexagon head bolts ensures optimal performance and safety in every project. Hex head bolts, hexagonal head bolt designs, and fully threaded hex bolts offer solutions for a wide range of industrial needs.
Mechanical Properties: Bolt Grades and Strength
Metric Grades Explained (Class 8.8, 10.9, 12.9 Tensile Strength)
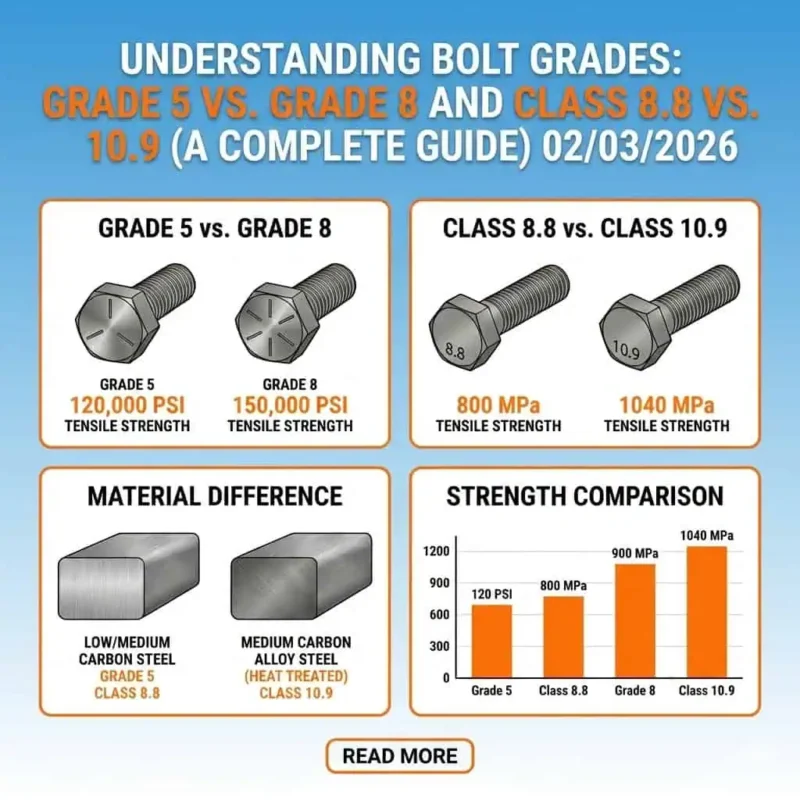
Engineers rely on metric hex head bolts for their consistent strength and grade classification. Manufacturers mark each bolt with a class number that indicates its mechanical properties. Class 8.8, 10.9, and 12.9 metric hex head bolts represent the most common grades in industrial applications. These grades provide high strength and durability for demanding environments.
| Grade | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (psi) |
|---|---|---|
| 8.8 | 800 | — |
| 10.9 | 1700 | 170,000 |
| 12.9 | 1900 | 190,000 |
Class 8.8 metric hex head bolts offer reliable strength and grade for general machinery. Class 10.9 and 12.9 bolts deliver high tensile strength for heavy construction, mining, and pressure equipment. These grades ensure that hex bolts maintain integrity under high stress.
Imperial Grades Explained (SAE J429 Grade 2, 5, 8)
Imperial hex bolts follow the SAE J429 standard, which defines strength and grade for American fasteners. Grade 2, 5, and 8 bolts serve different roles in industrial settings. Grade 2 bolts fit non-critical applications, while Grade 5 bolts provide higher strength for automotive and machinery use. Grade 8 bolts deliver high strength for heavy machinery and aerospace projects.
| Bolt Grade | Tensile Strength (psi) | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 2 | 60,000–74,000 | Non-critical applications |
| Grade 5 | 105,000–120,000 | Automotive, machinery |
| Grade 8 | Up to 150,000 | Heavy machinery, aerospace |
Selecting the correct strength and grade ensures that hex head bolts meet the demands of each project.
Understanding Proof Load, Yield Strength, and Tensile Strength
Engineers evaluate hex bolts using three key mechanical properties:
- Proof load measures the minimum load a bolt can withstand without permanent deformation. This property ensures hex bolts perform reliably in critical applications.
- Yield strength indicates the load at which a bolt will deform permanently. Understanding yield strength helps engineers prevent structural failures.
- Tensile strength defines the maximum load a bolt can handle before breaking. High tensile strength is essential for hex head bolts used in extreme conditions.
Choosing the right metric hex head bolts and imperial hex bolts based on strength and grade guarantees quality and safety in industrial fasteners.
Material Selection for Environmental Durability
Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for High-Stress Applications
Engineers select materials for hex bolts based on mechanical demands and environmental exposure. Carbon steel offers a balance of strength, affordability, and versatility. It serves well in general construction and machinery. Alloy steel provides enhanced strength, hardness, and improved corrosion resistance. This material supports high-stress environments such as aerospace and heavy machinery.
| Material | Mechanical Properties |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Strength, affordability, versatility; grades 2, 5, and 8 commonly used |
| Alloy Steel | Increased strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance; ideal for demanding settings |
| Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance; grades 304 and 316 for marine and outdoor use |
Stainless Steel Solutions (304 vs. 316 for Corrosion Resistance)
Stainless steel remains the preferred choice for environments where corrosion resistance is critical. Grade 304 provides good general protection but can be vulnerable to chlorides, such as salt. Grade 316 contains molybdenum, which boosts resistance to harsh chemicals and saltwater. This feature makes 316 ideal for marine and chemical processing applications.
- 304 stainless steel: Good general corrosion resistance; less effective against salt.
- 316 stainless steel: Superior corrosion resistance in chemical and marine environments due to molybdenum content.
Surface Treatments (Zinc Plating, Hot-Dip Galvanizing, Black Oxide)
Surface treatments extend the life of bolts and improve performance in challenging conditions. Zinc plating uses electroplating to create a thin protective layer, suitable for indoor or light outdoor use. Hot-dip galvanizing applies a thicker coating, offering robust protection for outdoor and industrial settings. Black oxide provides minimal dimensional change and low corrosion resistance unless oiled, making it suitable for interior hardware.
| Feature | Zinc Plated Steel | Galvanized Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Method | Electroplating | Hot-dip or electro-galvanizing |
| Coating Thickness | ~5–10 microns | 45–100+ microns (hot-dip) |
| Durability | Moderate (indoor use) | High (outdoor/industrial use) |
| Finish Type | Key Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc or Hot-Dip Galvanizing | Economic cathodic protection | Structural bolts, outdoor gear |
| Black Oxide | Minimal dimensional impact; low corrosion if oiled | Interior hardware, mil-spec connectors |
Engineers match material and finish to the environment, ensuring hex bolts deliver reliable performance and corrosion resistance in every application.
Technical Specifications and Sizing
Accurate Measurement: Diameter, Length, and Thread Pitch
Selecting the correct size and length for hex head bolts ensures reliable performance in any application. Engineers must know how to measure a hex head bolt accurately. The diameter is the first critical dimension, as it determines both the bolt’s strength and the hole size needed for installation. Measure the diameter across the bolt’s shank, not including the threads. The length is measured from the flat bearing surface under the head to the tip of the bolt, following standards such as ASME B18.2.1. Thread pitch refers to the distance between two adjacent thread crests, measured in millimeters for metric bolts. For Unified Thread Standard (UTS) bolts, threads per inch (TPI) indicate the density of threads along the shank. Choosing the correct size and length prevents installation errors and ensures the bolt can handle the required load.
Thread Fit Classes (2A/2B vs. 6g/6H)
Thread fit classes define the tolerance and compatibility between bolts and nuts. The most common classes for UTS bolts are 2A (external) and 2B (internal), which provide a balance between ease of assembly and load-bearing capacity. Metric bolts use 6g (external) and 6H (internal) classes, offering a similar fit to 2A. These classes ensure that bolts and nuts fit together smoothly, reducing the risk of thread damage or loosening.
| Thread Fit Class | Description | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2A/2B | Standard for UTS bolts, suitable for most uses | Good load-bearing, reliable assembly |
| 6g/6H | Metric threads, interchangeable with 2A/2B | Positive impact on performance and compatibility |
Selecting the right thread fit class helps maintain joint integrity and simplifies maintenance.
Identifying Head Markings for Verification
Head markings on hex head bolts provide essential information about grade and manufacturer. These markings help users verify that the bolt meets the required strength and application standards. For example, SAE Grade 2 bolts have no markings, Grade 5 bolts display three radial lines, and Grade 8 bolts show six radial lines. These symbols indicate the bolt’s material and tensile strength, ensuring the right bolt is used for each job.
| Bolt Head Marking | SAE Grade | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| No Marking | Grade 2 | Light-duty, furniture, general applications |
| 3 Radial Lines | Grade 5 | Automotive, machinery, structural |
| 6 Radial Lines | Grade 8 | Heavy-duty, aerospace, industrial |
Manufacturers also include unique letters or numbers to identify the source and traceability of each bolt. This practice supports quality control and compliance in critical industries.
Critical Applications in B2B Sectors
Heavy Construction and Structural Steel
Hex bolts play a vital role in the construction industry. Engineers use hex head bolts to secure structural connections in buildings and bridges. These bolts also support various infrastructure projects, providing reliable fastening for steel frameworks. Industrial machinery relies on hex bolts for operational safety and efficiency.
- Structural connections for buildings
- Bridge assembly
- Infrastructure projects
- Machinery fastening
Automotive OEM and Aftermarket Repair
The automotive industry demands precision and reliability in every assembly. Hex bolts are specified by thread diameter and length, such as M8 × 20, to ensure a perfect fit. Standards like GB/T 5780-2016, DIN 601, and ISO 4014 guide the selection process. Hex head bolts secure engine components and chassis fasteners, maintaining stability under high vibrations. Hex cap screws offer superior manufacturing tolerances, allowing high torque transfer without slippage.
- Securing drivetrain assemblies
- Suspension brackets
- Engine mounts
- Chassis fasteners
Tip: The hex design allows easy use with standard wrenches and sockets, streamlining assembly and maintenance.
Water Treatment and Chemical Processing Equipment
Hex bolts must withstand harsh environments in water treatment and chemical processing. B8 bolts provide high strength and corrosion resistance, performing well under extreme temperatures and chemical exposure. 17-4 stainless steel hex bolts offer increased strength and durability, making them suitable for high-temperature chemical processing.
- Chemical processing equipment
- Water treatment plants
- Applications requiring durability against oxidation and chemical exposure
Heavy Machinery and Mining Operations
Hex bolts contribute to the reliability of heavy machinery and mining operations. Their high tensile strength ensures joints withstand significant tension and pressure. Standardized sizes simplify maintenance and replacement. The hexagonal shape provides stable tightening, preventing loosening under dynamic loads.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High Tensile Strength | Withstands significant tension and pressure |
| Standardized Sizes | Facilitates easy maintenance and replacement |
| Hexagonal Shape | Prevents loosening under dynamic loads |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Balances performance and affordability |
Heavy hex nuts, constructed from high-grade steel, resist mechanical wear and fatigue. Their robust design maintains structural integrity across varying temperatures, which is essential for dynamic applications.
Procurement and Quality Assurance Strategies
Verifying Manufacturer Certifications and Material Test Reports (MTRs)
Manufacturers must provide certifications and material test reports to guarantee the quality of hex bolts. These documents confirm that fasteners meet industry standards and perform reliably in critical applications.
- ISO 9001:2015 certification ensures consistent manufacturing processes.
- Material test reports include chemical composition, tensile strength, and dimensional accuracy.
- Initial appearance inspection checks for surface defects.
- Dimension inspection verifies tolerances.
- Chemical composition analysis confirms material specifications.
- Tensile strength testing assesses load capacity.
- Corrosion resistance testing evaluates surface treatments.
Quality assurance guidelines help maintain safety and regulatory compliance. Many industries require ASTM-compliant hex head bolts for secure fastening and traceability.
Installation Torque Guidelines and Anti-Seize Practices
Proper installation and maintenance of hex bolts depend on following recommended torque values and anti-seize practices. Correct torque ensures secure fastening and prevents joint failure.
| Bolt Size | Torque Value (lb-ft) | Load with Anti-Seize (lbs) |
|---|---|---|
| 8mm | 18.5 | 32,000 |
| 5/8″ | 220 | 32,000 |
Technicians should apply anti-seize compounds to prevent galling and facilitate easy installation. These practices support ease of installation and extend the service life of fasteners.
Preventing Failures: Galling, Fatigue, and Hydrogen Embrittlement
Hex bolts may fail due to fatigue, galling, or hydrogen embrittlement.
| Failure Mode | Description | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue Failure | Cracks from repeated loading cycles | Dynamic loading, poor design, improper preload |
| Hydrogen Embrittlement | Brittle fracture from hydrogen absorption | Hydrogen-rich environments, electroplating |
| Galling and Seizing | Parts lock together under pressure | Over-tightening, insufficient lubrication |
Engineers prevent these issues by selecting proper materials, maintaining consistent preload, and applying corrosion-resistant coatings. Regular inspections and anti-fatigue measures, such as lock washers, support proper installation and maintenance.
Customization Options for OEM Requirements
OEMs often require customized hex bolts for specialized applications.
| Customization Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Material Options | Carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, Monel, Super Duplex 2507 |
| Surface Treatments | Zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, black oxide, zinc-flake coating |
| Size Range | Standard sizes from M6 to M48; custom dimensions available |
| Special Features | Special thread requirements, customized lengths, private-label packaging |
Packaging options include polybags, plastic boxes, color boxes, and branded cartons. These choices ensure fasteners meet project specifications and support secure fastening in diverse environments.
Proper installation and maintenance, combined with best practices for using hex bolts, guarantee quality and reliability in every application.
Understanding hex head bolts, their grades, materials, and measurements ensures engineers and contractors achieve safe, reliable connections in industrial projects. These bolts serve as critical components for structural integrity and safety. Selecting the right fastener type and material prevents failures in load-bearing structures.
| Selection Factor | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Quality | Enhanced reliability |
| Traceability | Improved supply chain control |
| Customization | Meets specific requirements |
- Quality, traceability, and customization in fastener selection lead to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- This guide empowers professionals to make informed choices for every application.
FAQ
What is the difference between a hex bolt and a hex cap screw?
A hex cap screw has tighter tolerances and a washer face under the head. A hex bolt has looser tolerances and a flat bearing surface.
| Feature | Hex Bolt | Hex Cap Screw |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | Loose | Tight |
| Washer Face | No | Yes |
How can you identify the grade of a hex head bolt?
Check the head markings. Each grade uses a unique symbol or number.
- Grade 2: No markings
- Grade 5: Three radial lines
- Grade 8: Six radial lines
Which materials offer the best corrosion resistance for hex bolts?
Stainless steel, especially 316 grade, provides the best corrosion resistance.
316 stainless steel resists saltwater and chemicals. 304 stainless steel works well for general use.
What standards should engineers reference for hex head bolts?
Engineers should reference ASME B18.2.1, DIN 931/933, and ISO 4014/4017.
These standards define dimensions, tolerances, and thread specifications for hex head bolts.
How do you measure the length of a hex head bolt?
Measure from the flat bearing surface under the head to the tip of the bolt.
Do not include the head height in the measurement.