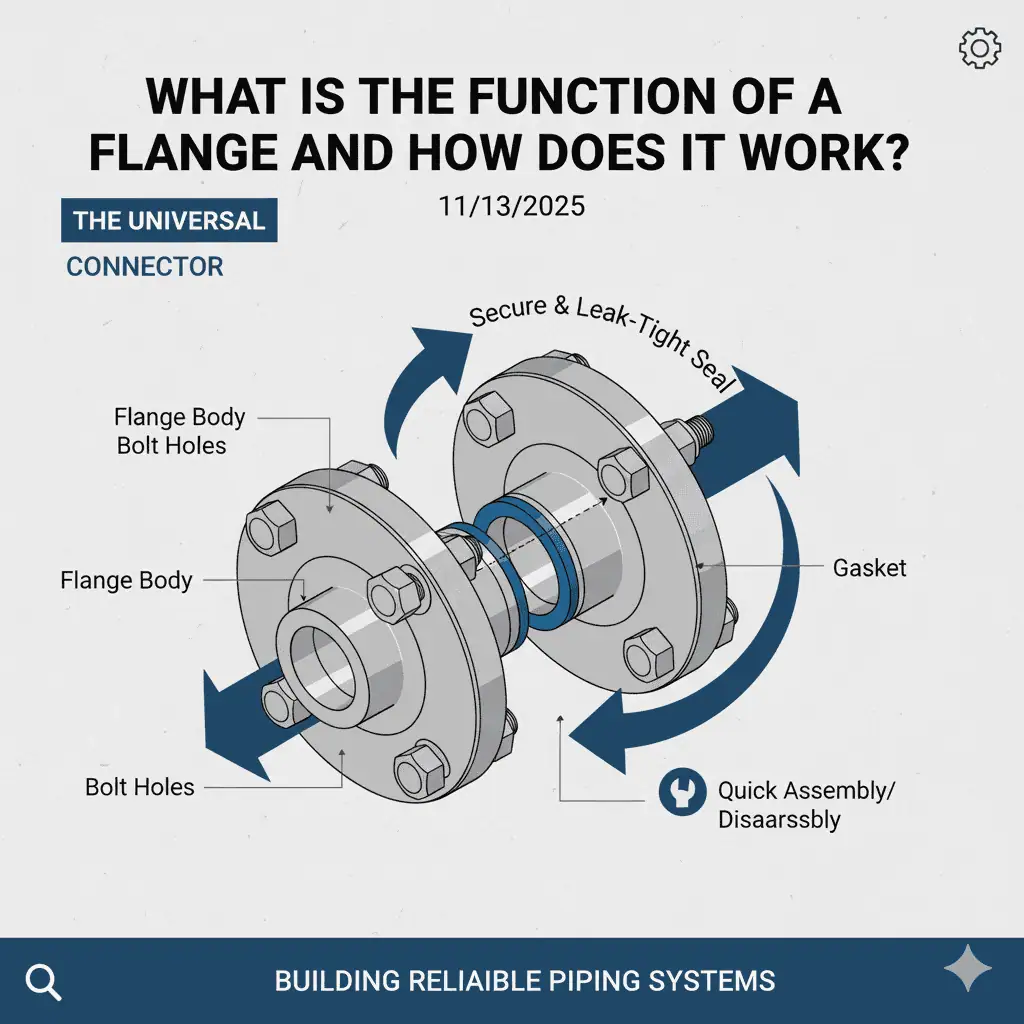
A flange is used to create a reliable, detachable joint between pipes and equipment. A typical flanged joint is secured with bolts and sealed by a gasket, helping the system withstand pressure, temperature, and vibration. In engineering terms, the seal is achieved by bolt preload compressing the gasket to a target stress level. Internal pressure then tries to separate the joint (end force), so the connection must keep enough residual gasket stress after relaxation, thermal cycling, and vibration. For buyers and inspectors, clear flange markings and matching MTCs are essential for confirming material grade, rating, and traceability—especially when the service is corrosive, high-temperature, or safety-critical.
Practical inspection reality: many “mystery leaks” are not caused by the flange type. They come from one of four controllable items: (1) wrong gasket for the media/temperature, (2) uneven bolt load, (3) dirty/damaged flange faces, or (4) misalignment/pipe strain that bends the joint after tightening.
| Buyer/Inspector Check | What to Verify | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Marking/Stamp | Standard (ASME/EN), size (NPS/DN), rating (Class/PN), material grade (ASTM/EN), heat number | Confirms compatibility, pressure-temperature limits, and traceability |
| MTC / EN 10204 document | Chemistry, mechanical properties, heat number match, heat treatment if required | Reduces risk of wrong grade in corrosive or high-temperature service |
| Facing and finish | RF/FF/RTJ, serration condition, dents, corrosion, coating contamination | Facing mismatch or surface damage is a common root cause of leakage |
| Bolting | Stud/bolt grade, nut grade, lubrication plan, torque/tension method | Incorrect bolting practice is a leading contributor to gasket failure |
High-quality stainless steel flanges from Sunhy are designed for demanding industrial service:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Handles water, chemicals, and harsh pipe environments (material selection must still match chloride level, temperature, and media). |
| High Strength | Supports pressure boundary joints when correctly specified (standard, class/PN, and bolting method remain decisive). |
| Passive Film Self-Repair | Helps maintain corrosion protection after minor surface damage, provided the alloy is suitable for the environment. |
| Reduced Maintenance | Stable material performance can reduce unplanned shutdowns when assembly and inspection are controlled. |
What is a Flange?
Definition
A flange is a protruded rim or ridge that connects pipes, valves, or equipment in a piping system.
In practice, a flange provides a rigid, alignable surface for bolting and gasket sealing. It strengthens the joint, stabilizes movement at connection points, and helps prevent fluid or gas leakage. Because flanged joints are removable, they also simplify inspection, cleaning, and component replacement. For a broader overview of designs and applications, see what is a flange. For a basic engineering definition, see Wikipedia’s flange definition.
Engineering note (what makes it “work”): the joint seals when the gasket is compressed to the right stress and stays there. If bolt preload drops (relaxation, embedding, thermal cycling), gasket stress falls and leakage starts—often at the lowest-loaded bolt sector.
Sunhy supplies stainless steel flanges manufactured to international standards with clear material identification and traceability for project and inspection needs.
Main Function
The main function of a flange is to securely join pipes and equipment while allowing easy disassembly for maintenance.
A bolted, gasketed flange joint supports system expansion, modification, and routine service without cutting or re-welding the pipeline. When properly selected and installed, flanges provide reliable sealing performance and mechanical strength across a wide range of operating conditions.
Two functions happen at the same time: (1) the flange carries mechanical load and keeps alignment; (2) the gasket provides the seal. If you over-focus on “strong flange” but ignore bolting and gasket selection, leakage risk stays high.
Here are the key roles of flanges in piping systems:
- Serve as the protruding rim that allows pipes, valves, and equipment to connect.
- Enhance the strength of the joint.
- Enable easy disassembly for inspection and maintenance.
- Allow system flexibility for expansion and modification.
- Provide a tight seal to prevent leaks.
| Flange Function | Benefit to You |
|---|---|
| Secure Connection | Keeps pipes and equipment joined safely |
| Leak-Proof Seal | Prevents fluid or gas loss (when gasket stress is maintained) |
| Easy Maintenance | Simplifies inspection and repair |
| System Flexibility | Supports expansion and upgrades |
Sunhy stainless steel flanges are produced with precision machining and controlled manufacturing processes to support consistent fit-up, sealing, and long-term reliability in demanding environments.
Field case (selection error): a maintenance team installed an RF gasket set between an RF flange and a flat-face mating surface on a pump skid. The gasket compressed unevenly, and seepage appeared after warm-up. Corrective action was not “more torque”; it was restoring correct facing compatibility and checking flange parallelism before reassembly.
What Are Flanges Used For?
Applications in Piping Systems
Flanges are used to connect, seal, and support pipe systems across many industries.
They are a common joining method for pipes, valves, pumps, and equipment where a strong and removable connection is required. The ability to assemble and disassemble sections efficiently makes flanges especially practical for maintenance-intensive systems.
Typical flange-heavy packages include heat exchangers, pump suction/discharge spools, valve skids, filters/strainers, and pressure vessel nozzles. These locations see frequent inspection because they combine pressure boundary duty with vibration, temperature cycling, and maintenance access requirements.
ASME B16.5 is a commonly referenced standard for pipe flanges and flanged fittings in many industrial projects. The table below summarizes common industries where flanges are widely used and the practical benefits they provide:
| Industry | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Oil and Gas | Pipeline systems, refineries, offshore platforms | High pressure and temperature tolerance, durability |
| Chemical Processing | Chemical reactors, piping systems, storage tanks | Corrosion resistance, leak prevention |
| Power Generation | Boiler systems, turbine systems, cooling systems | High-temperature performance, reliability |
| Water and Wastewater Treatment | Water distribution, treatment plants, pumping stations | Versatility, leak-free connections |
| Food and Beverage | Processing equipment, packaging systems | Hygienic design, durability |
You often see Sunhy stainless steel flanges in petrochemical, marine, and pressure vessel applications. These flanges are selected for corrosion resistance, strength, and compliance with commonly required international standards.
Benefits in Industrial Use
Flanged joints improve serviceability, safety, and system flexibility.
They allow sections to be opened for inspection or cleaning without cutting the pipe, which reduces downtime and supports efficient upgrades over the life of the installation.
From an operations perspective, flanges also support isolation for hydrotesting, temporary blinds/spades, and rapid replacement of valves or instruments—tasks that would be slow or risky if every connection required welding.
- Flanged joints provide secure, gasketed connections suitable for pressure- and temperature-driven service.
- They allow different pipe materials and sizes to be integrated within the same system when properly specified.
- Customizing flanges for special projects helps meet unique media, space, or standard requirements.
- Quick assembly and disassembly supports efficient maintenance planning and reduces shutdown time.
- Stainless steel options offer strong resistance to corrosion and surface damage in aggressive service environments.
Note: Material selection, correct gasket choice, and controlled bolt tightening are key to achieving reliable long-term performance in any flanged joint.
In most industrial systems, flanges remain a practical choice for building safe, reliable, and maintainable piping networks.
Field case (maintenance-driven design): on a utility heat exchanger, adding flanged spool pieces near the unit allowed faster bundle pulls and gasket changes during shutdowns. The improvement was not theoretical—maintenance duration dropped because lifting points, clearance, and bolt access were engineered in.
Pipe Flanges: Types and Components
Common Flange Types
Many common types of flanges are used in industrial piping systems.
Pipe flanges connect pipes, valves, and equipment to form strong, serviceable joints. Understanding the common flange types helps engineers and buyers select designs that match pressure class, temperature range, and maintenance needs.
Selection shortcut (engineering logic): if the line is high-cycle temperature, high pressure, or high consequence, prioritize joint rigidity (weld neck / long weld neck) and a gasket system that maintains stress. If the service is low pressure and maintenance-heavy, slip-on or lap joint may be acceptable—provided alignment control is good.
- Weld Neck Flange – Typically used for high-pressure and high-temperature pipelines; better stress distribution at the hub.
- Slip-On Flange – Common in low- to moderate-pressure piping systems; easier fit-up but lower fatigue strength than weld neck.
- Socket Weld Flange – Used for small-diameter, higher-pressure lines; avoid crevice issues where corrosion is a concern.
- Blind Flange – Used to seal off pipe ends or valves; often used for isolation during testing/maintenance.
- Lap Joint Flange – Suitable for systems requiring frequent dismantling; rotates for bolt alignment (with stub end).
- Threaded Flange – Used in lower-pressure applications where welding is not preferred; limit use where vibration and thermal cycling are severe.
- Long Weld Neck Flange – Often specified for pressure vessels and heat exchangers; provides extra rigidity at nozzles.
Sunhy offers a wide range of pipe flanges, including blind, lap joint, slip-on, socket weld, threaded, and weld neck flanges. Precision forging and machining help ensure consistent dimensions and reliable sealing performance.
| Flange Type | Joint Integrity | Weld Type | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weld Neck | High | Butt weld | High-pressure systems |
| Slip-On | Medium | Fillet weld | Low-pressure systems |
| Socket Weld | Medium | Fillet weld | Small-diameter, high-pressure |
| Lap Joint | NA | None | Frequent dismantling |
| Threaded | Low | None | Non-welded, low-pressure |
| Blind | NA | None | Sealing ends |
Field case (bolt material mistake): stainless studs assembled dry on a stainless flange (no lubricant, no anti-galling plan) seized during tightening. The team could not reach target preload and later saw weeping. The fix was controlled lubrication + proper tightening method + replacing damaged studs/nuts, not “tighten harder.”
Key Components
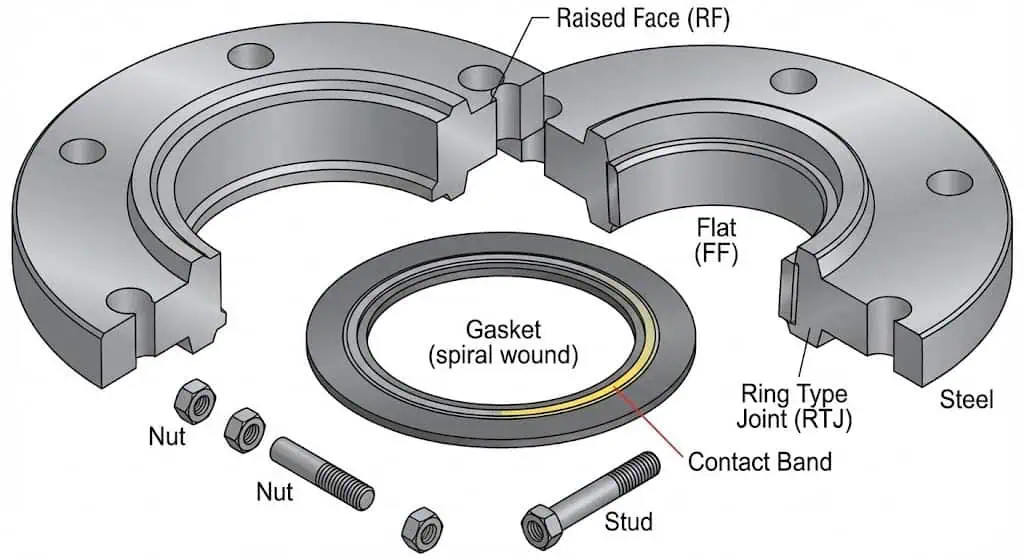
A standard flanged joint includes several key components.
The flange, gasket, bolts, and nuts work together to ensure alignment, load transfer, and sealing performance.
What engineers actually look at: face condition (nicks, corrosion, waviness), flange parallelism, bolt grade/length engagement, lubrication plan, and gasket compatibility with the media and temperature. These details decide whether the joint holds preload after startup.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Flange Body | A thick round disc that withstands pressure and connects pipe sections. |
| Sealing Surface | The area that touches the gasket and ensures a tight seal (facing type matters: RF/FF/RTJ). |
| Bolt Holes | Holes for bolts that hold flanges together securely (hole alignment reduces assembly stress). |
| Gasket | A material placed between flanges to fill gaps and prevent leaks (must match media/temperature). |
You can rely on Sunhy’s manufacturing capabilities for both standard and custom pipe flanges. Sunhy produces flanges with a maximum machining diameter of 3200 mm and can handle workpieces up to 10 tons, meeting demanding project requirements.
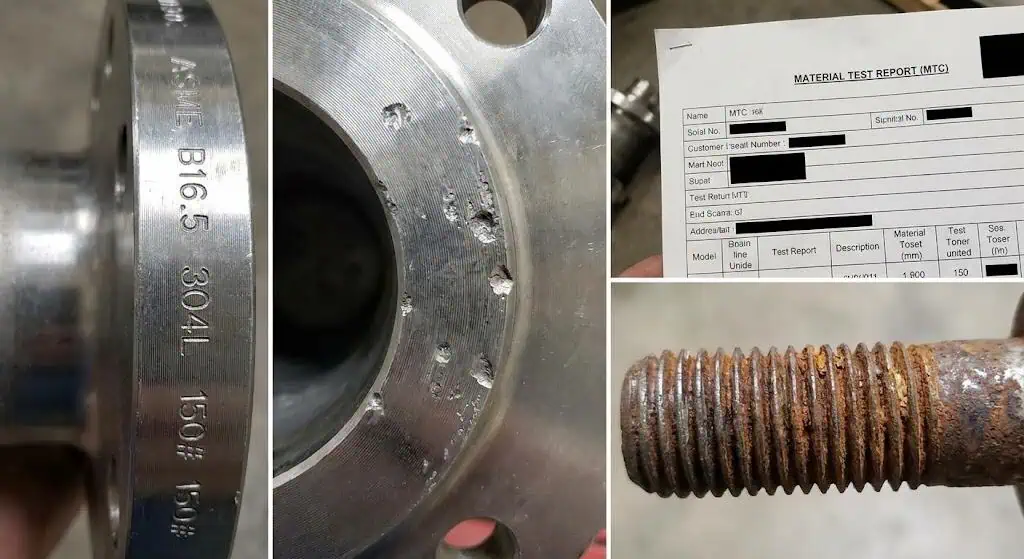

| Receiving Inspection Checklist | Pass/Fail Notes |
|---|---|
| Confirm standard and rating (ASME Class / EN PN) match the drawing | Check stamping vs purchase order |
| Verify material grade and heat number (stamp ↔ MTC) | Critical service: consider PMI sampling |
| Inspect facing for dents, corrosion, coating, and gasket imprinting | Reject/repair if sealing surface is damaged |
| Check bolt hole alignment and overall dimensions | Misalignment drives assembly stress and leaks |
Understanding flange types and joint components helps support correct selection, installation, and long-term maintenance planning.
How Does Flange Connection Work?
Connection Process
A flanged connection is assembled using flanges, bolts, and a gasket.
This method creates a strong, serviceable joint that can be disassembled for inspection, modification, or replacement as needed.
Here is how does flange connection work:
- Gather the right tools and materials:
- Flanges (confirm standard and rating)
- Gaskets (select based on pressure, temperature, and fluid)
- Bolts and nuts (ensure proper size and grade)
- Torque wrench (calibrated)
- Lubricant/anti-seize plan for bolts (especially stainless bolting)
- Align the pipe ends:
Place the flanges on the pipe ends and confirm face alignment and parallelism. Poor alignment creates uneven gasket loading and leakage. If the pipe “springs” into place when you loosen bolts, you have pipe strain that must be corrected before final tightening. - Inspect and clean the facing:
Remove dirt, paint, oil, old gasket residue, and corrosion. Verify there are no dents or raised burrs across the sealing surface. - Insert the gasket:
Center the gasket between the flange faces to ensure uniform sealing contact. Do not use gasket adhesive unless the procedure allows it; many adhesives contaminate faces and change friction behavior. - Install bolts and nuts:
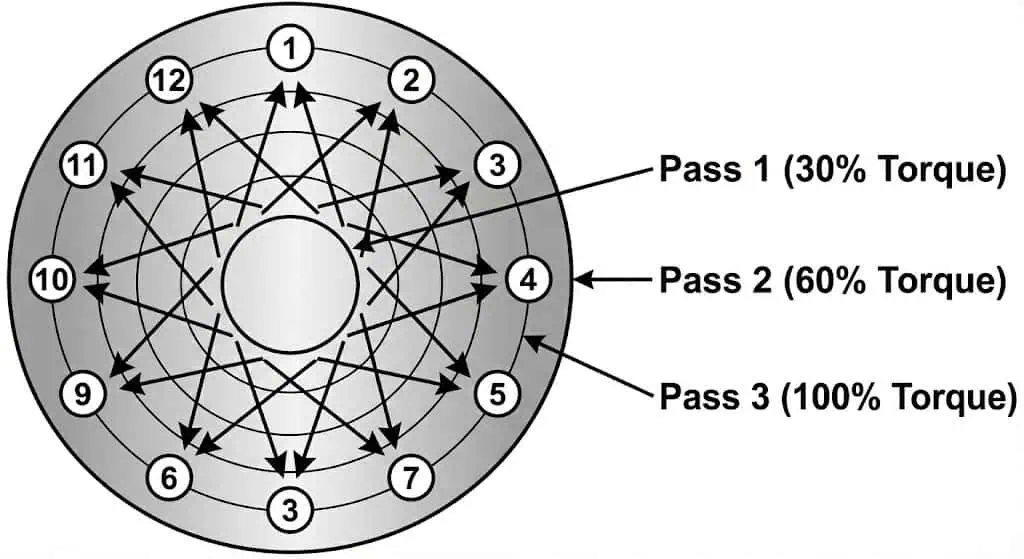
Insert bolts through the flange holes, lubricate as required, and hand-tighten nuts for initial positioning. Ensure full thread engagement and correct washer use if specified. - Tighten bolts in a star pattern (multiple passes):
Use a torque wrench and follow a crisscross (star) tightening sequence to apply even gasket stress. Apply torque in controlled stages (for example: 30% → 60% → 100%), then perform a final circular pass at target torque to equalize load. Follow the recommended torque values for the flange size and bolt grade. - Check the connection:
Inspect alignment and gap uniformity, and re-check for leakage after startup. Re-torque only if your procedure calls for it; some gasket types are not intended for hot re-torque.
Tip: A controlled star-pattern tightening method with staged passes helps avoid uneven bolt load and improves sealing reliability.
Sunhy’s precision manufacturing supports consistent bolt-hole alignment, sealing surface finish, and dimensional tolerances, which helps simplify assembly and improve joint reliability.
Ensuring Leak-Proof Seals
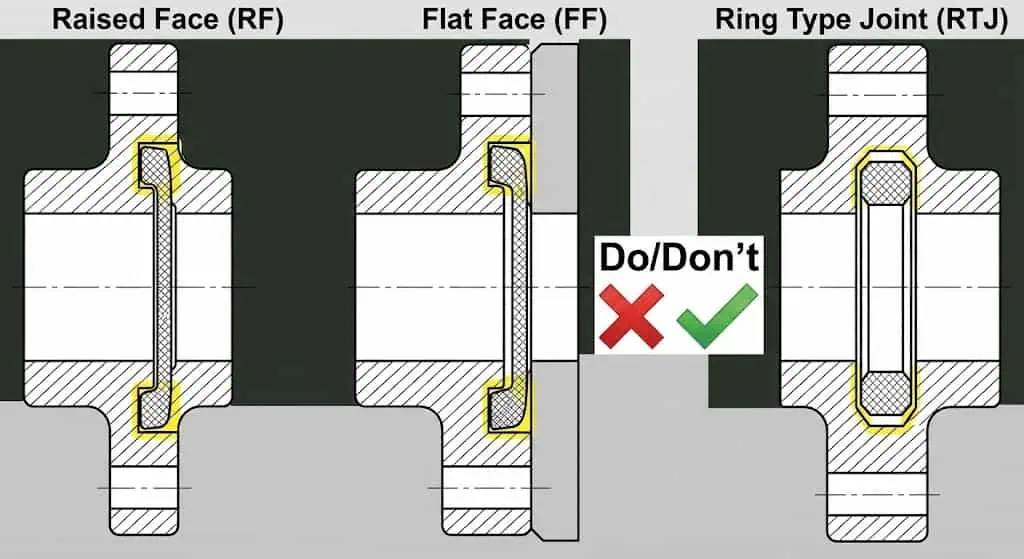
Leak prevention depends on correct alignment, gasket selection, and controlled bolt tightening.
Common leak causes include uneven bolt load, damaged gasket materials, or contaminated sealing surfaces. You can prevent these issues by following standardized installation practices and documenting the bolting method used.
Leak troubleshooting workflow (field-proven): (1) confirm the leak location and fluid, (2) verify bolt load method and lubrication, (3) inspect gasket type/size and facing compatibility, (4) check for pipe strain/misalignment, (5) inspect facing damage or corrosion pitting, (6) correct root cause and rebuild with controlled procedure.
Follow these steps to achieve a leak-proof seal:
- Clean the flange faces:
Remove dirt, oil, and debris from the flange surfaces before assembly. - Select the correct gasket:
Choose a gasket based on the system’s pressure, temperature, and the media being handled. In general, spiral wound gaskets are widely used for higher-pressure and higher-temperature service, while PTFE gaskets are often specified for chemical and hygiene-sensitive applications. The table below summarizes common gasket types, typical use cases, and material options.
| Gasket Type | Typical Use Case | Material Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Spiral Wound | High temperature / high pressure | SS316 with graphite or PTFE |
| Compressed Fiber | Low pressure, general service | Non-asbestos, aramid fiber |
| PTFE Sheet | Food, chemical, non-metal piping | Virgin PTFE or filled PTFE |
| Metal Ring (RTJ) | High-pressure pipelines | Soft iron, stainless steel, Inconel |
| Graphite | High heat, aggressive media | Flexible graphite, stainless steel inserts |
- Center the gasket:
Ensure the gasket sits evenly between the flange faces. - Tighten bolts evenly:
Use a torque wrench and tighten bolts in a star pattern. Lubricate bolts for uniform tension where required. - Inspect and maintain:
Check the joint for leakage, corrosion, or bolt loosening. Re-check after initial thermal cycling if specified by procedure.
Note: Routine inspection and torque verification help catch early issues and extend gasket and joint life.
Sunhy’s quality control includes dimensional inspection, bolt-hole alignment checks, and sealing surface verification. The company follows commonly required standards such as ASME, ASTM, DIN, and ISO 9001 to support consistent fit-up and reliable sealing performance.
| Sunhy Quality Control Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Compatibility Checks | Ensure flange faces and materials match your system requirements. |
| Torque Specifications | Use controlled tightening methods to reduce uneven bolt load and gasket stress loss. |
| Regular Inspections | Inspect and maintain flanged connections to avoid leaks. |
| Compliance Assurance | Meet global standards with high-precision CNC machining and testing. |
Summary:
A reliable flanged connection depends on correct component selection, proper assembly practices, and routine maintenance. Precision manufacturing and consistent inspection help improve long-term sealing and safety performance.
Advantages of Using Flanges
Easy Maintenance
Flanges make maintenance and inspection simple and fast.
Flanged joints can be opened without cutting the pipe, which reduces labor time and helps shorten shutdown windows. This is especially valuable in systems that require regular inspection, cleaning, or component replacement.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Easy Disassembly | You can quickly separate sections for cleaning or inspection. |
| Excellent Sealing | Flanges use gaskets to provide reliable seals, even under high pressure. |
| Reliable Access | You get straightforward access for repairs or upgrades when bolt access and clearance are engineered in. |
- Flanges can be assembled in tight spaces where welding is less practical.
- They support efficient system modifications during plant upgrades.
- Inspection and replacement can be carried out with standard tools and controlled procedures.
Sunhy’s stainless steel flanges meet ISO 9001 and PED standards to support consistent performance in maintenance-critical environments.
Strength and Safety
Flanges deliver strong joint integrity for demanding service conditions.
In higher-pressure and higher-temperature systems, properly specified flanges help distribute loads evenly and maintain gasket compression. This reduces the risk of leakage and supports safe operation across long service cycles. Project specifications typically reference recognized flange standards (for example, ASME Class-rated flanges or EN PN-rated flanges) to control dimensions and pressure-temperature performance.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Pressure Design | Flanges are widely used in refineries, process plants, and pipeline systems where pressure boundary integrity matters. |
| Thick Flange Body | You get better load distribution and joint stability (when mating faces are parallel and bolting is controlled). |
| Leak-Proof Performance | Gaskets and precise machining support a secure seal when correct stress is maintained. |
| Certified Quality | Controlled manufacturing and traceability support safety and reliability targets. |
- Well-designed transitions can help reduce turbulence and local stress concentration.
- Robust joint design contributes to predictable inspection intervals and maintenance planning.
- Standardized flange systems can help simplify inventory for large-scale projects.
Note: Correct selection of flange type, material, gasket, and bolt grade is essential for meeting project safety and reliability targets.
Choose the right flange to keep your pipe system safe and efficient.
You need to match flange type, material, and standards to your application. The table below shows what to consider:
| Factor | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Operating Conditions | Controls pressure/temperature limits and gasket selection |
| Material Compatibility | Prevents corrosion, galling, and premature facing damage |
| Proper Installation | Maintains gasket stress and reduces leak risk |
Sunhy stainless steel flanges are designed to support long service life and stable sealing performance when correctly specified and installed.
FAQ
What materials can you use for flanges?
Stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel are common choices.
Material selection should match the system’s pressure, temperature, and corrosion environment. Stainless steel flanges are often specified where moisture, aggressive media, or cleaning chemicals are present. In chloride-containing service, confirm the alloy selection and temperature limits rather than assuming “stainless = corrosion proof.”
How do you choose the right flange type?
Match the flange type to your system’s pressure, temperature, and maintenance needs.
Weld neck flanges are commonly used for higher pressure and thermal cycling. Slip-on flanges are used for lower pressure service with good alignment control. Lap joint flanges are common where frequent dismantling is required. Always confirm the project’s required standard and rating (Class/PN) before final selection.
Tip: Confirm project standards and dimensional requirements before final selection.
Can you reuse gaskets when reconnecting flanges?
No, you should always use a new gasket.
A new gasket helps ensure proper compression and sealing reliability. Reusing old gaskets increases leak risk because the gasket has already been crushed, heat-aged, or chemically attacked.
What standards do Sunhy flanges meet?
Sunhy flanges meet ASME, ASTM, DIN, and EN1092-1 standards.
Products are supplied with documentation aligned with commonly required certifications such as ISO 9001 and PED where applicable. Always verify the exact standard edition, pressure rating (Class/PN), and material grade on the purchase order and MTC.
How do you prevent leaks in flange connections?
Use the correct gasket, tighten bolts evenly, and inspect regularly.
Good results depend on clean sealing faces, controlled torque application, and correct alignment. If leaks repeat, investigate bolt load method, lubrication, gasket type, and pipe strain rather than only increasing torque.
- Clean flange faces
- Use proper torque in staged star-pattern passes
- Inspect after installation and after initial thermal cycling (if required)
What do flange markings and MTCs tell you during inspection?
They confirm rating, material grade, and traceability.
Check that the flange stamp (standard + size + Class/PN + material grade + heat number) matches the MTC heat number and chemistry/mechanical values. For critical service, add PMI spot checks and ensure the inspection document type matches project requirements (for example, EN 10204 3.1 when specified).
Why do flanges sometimes leak after startup even if they were tight during assembly?
Because bolt preload and gasket stress can drop after heating and pressurization.
Common causes include gasket creep/relaxation, embedding of rough surfaces, thermal expansion mismatch, and pipe strain that changes flange parallelism. The corrective action is a controlled rebuild with alignment correction and the correct gasket/bolting procedure—not uncontrolled over-torque.