DIN 931 hex bolts feature a partially threaded shaft with an unthreaded shank, while DIN 933 hex bolts are fully threaded. This distinction plays a vital role in selecting the right fasteners for structural integrity and application. The Hex Bolt Dimensions Guide highlights that partially threaded bolts offer enhanced shear strength, making them ideal for high-load and precise alignment situations.
Sunhy supplies industrial hex fasteners engineered for demanding environments, supporting both DIN and ISO standards (ISO 4014 and ISO 4017).
- Partially threaded bolts deliver increased shear resistance.
- Structural joints and machinery assemblies benefit from the unthreaded shank.
DIN 931 and DIN 933 Overview
What Is DIN 931?
DIN 931 hex bolts are partially threaded fasteners designed for structural applications requiring high shear strength and precise alignment.
DIN 931 bolts feature an unthreaded shank between the head and the threaded portion. This design allows the bolt to withstand shear forces and maintain alignment in assemblies. Manufacturers produce DIN 931 bolts according to strict standards, ensuring consistent dimensions and tolerances.
The tolerances for diameter, length, and thread pitch guarantee compatibility with nuts and threaded holes, even with minor manufacturing variations.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Nominal Dimensions | M5 to M36, with defined thread, pitch, head height, width across flats, radius |
| Tolerances | Specified for thread, head height, width across flats, shank length, overall length |
What Is DIN 933?
DIN 933 hex bolts are fully threaded fasteners ideal for clamping and precision assembly tasks.
DIN 933 bolts have threads running from the tip to the underside of the hex head. This threading style enables secure clamping and easy adjustment in applications where full engagement is necessary. DIN 933 bolts follow the same standards for dimensions and tolerances as DIN 931, ensuring reliable performance and interchangeability in many industrial settings.
- DIN 933 bolts suit assemblies that require maximum grip and flexibility.
- The fully threaded design allows for precise tensioning and easy length adjustment.
Key Differences in Threading
The main differences between DIN 931 and DIN 933 hex bolts lie in their threading and application suitability.
DIN 931 bolts have a partially threaded shaft, while DIN 933 bolts are fully threaded. These differences affect how each bolt performs in specific environments.
| Bolt Type | Threading Type | Application Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| DIN 933 | Fully threaded | Ideal for clamping and precision assembly |
| DIN 931 | Partially threaded | More suitable for applications requiring shear strength and alignment |
Both DIN 931 and DIN 933 share similarities in head design, material options, and compliance with DIN standards. However, their threading differences determine their best use cases. Selecting the correct bolt type ensures optimal performance and safety in industrial applications.
Hex Bolt Dimensions Guide: DIN 931 vs. DIN 933
DIN 931 and DIN 933 hex bolts differ in their threading and available sizes, which directly impact mechanical performance and application suitability.
This hex bolt dimensions guide provides a clear comparison of standard dimensions, shank and thread lengths, and typical diameter and length options for both standards.
Standard Dimensions and Ranges
Manufacturers produce DIN 931 and DIN 933 hex bolts in a wide range of sizes to meet diverse industrial needs. The hex bolt dimensions guide below summarizes the standard diameter and length ranges:
| Diameter Range | Length Range |
|---|---|
| M3 to M64 | 25mm to 640mm |
Sunhy aligns its product offering with industry standards, providing a comprehensive selection of hex bolt dimensions guide options. The company supports both catalog-standard and custom sizes, ensuring compatibility with various engineering requirements.
Shank Length vs. Full Thread Length
The difference in shank and thread length defines the mechanical properties of DIN 931 and DIN 933 bolts. The hex bolt dimensions guide highlights these distinctions:
- DIN 931 bolts feature a partially threaded shaft. The unthreaded shank offers a smooth bearing surface, which increases shear strength and reduces stress concentration.
- DIN 933 bolts have threads running the entire length. This design maximizes clamping force and ensures even load distribution across the bolt.
- The unthreaded shank in DIN 931 bolts has a larger cross-sectional area than the threaded section. This feature enhances resistance to shear loads and improves alignment in structural joints.
- Fully threaded DIN 933 bolts provide uniform pressure and exceptional grip strength, making them ideal for applications that require strong clamping.
Engineers select the appropriate bolt type based on the required mechanical performance. The hex bolt dimensions guide helps users match the right shank or thread length to their application.
Typical Diameter and Length Options
The hex bolt dimensions guide also compares the most common sizes available for DIN 931 and DIN 933 bolts:
| Bolt Type | Diameter Range | Length Range |
|---|---|---|
| DIN 931 | M4 to M48 | Up to 125 mm, 200 mm, and over 200 mm |
| DIN 933 | M3 to M42 | Various lengths available |
Sunhy offers hex bolts in sizes from M3 to M64, exceeding typical market ranges. Customers can choose from a wide selection of materials, coatings, and strength classes. The table below summarizes Sunhy’s capabilities:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Size Range | M3 to M64 |
| Customization Options | Various materials, coatings, strength classes |
| Industry Standard Alignment | Yes |
Sunhy’s hex bolt dimensions guide ensures that engineers and procurement specialists can select the exact sizes and specifications needed for their projects. The company’s support for custom and OEM fasteners allows for tailored solutions in demanding environments.
Structural Integrity and Shear Strength
Shear Applications and Unthreaded Shank
DIN 931 partially threaded bolts deliver superior strength in shear applications due to their unthreaded shank.
The unthreaded shank in these hex bolts creates a smooth bearing surface that resists shear forces more effectively than fully threaded designs. Engineers rely on partially threaded bolts for structural joints where alignment and joint strength are critical. The design reduces stress concentration, which increases the overall strength of the connection. Stainless steel options further enhance durability in corrosive environments, making these bolts suitable for bridges, machinery frames, and pressure equipment.
The differences in shank design directly impact the performance of bolts under load. Partially threaded bolts maintain joint integrity and prevent premature failure in high-shear scenarios.
Risks of Full Thread Engagement
Fully threaded hex bolts, such as DIN 933, present specific risks in structural applications.
When engineers select bolts for load-bearing joints, they must consider the following risks associated with full thread engagement:
- Not suitable for applications requiring shank support due to the absence of an unthreaded portion to resist shear forces.
- Stainless steel variants may experience galling during installation if not properly lubricated.
- Risk of encountering counterfeit or substandard products in non-specialist markets.
These differences highlight the importance of choosing the correct bolt type for each application. Stainless steel bolts offer corrosion resistance but require careful handling to avoid installation issues. Strength and reliability depend on proper selection and sourcing.
Tension vs. Shear Loads
Engineers must match bolt type to the primary load—tension or shear—to ensure optimal strength and safety.
Hex bolts experience two main types of loads: tension and shear. DIN 931 partially threaded bolts excel in shear applications, where the unthreaded shank absorbs lateral forces. DIN 933 bolts perform best in tension scenarios, where full thread engagement distributes axial loads evenly. Stainless steel construction provides added strength and resistance to environmental damage in both cases.
| Load Type | Recommended Bolt | Key Strength Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Shear | DIN 931 partially threaded bolts | Unthreaded shank resists lateral force |
| Tension | DIN 933 hex bolts | Full thread distributes axial load |
Understanding the differences between bolt designs allows engineers to maximize joint strength and longevity. Stainless steel options and proper bolt selection ensure reliable performance in demanding environments.
DIN Standards and ISO Equivalents
DIN 931 and ISO 4014 Comparison
DIN 931 and ISO 4014 both define partially threaded hex bolts, but ISO 4014 has replaced DIN 931 as the current international standard.
DIN 931 standards set the foundation for metric fastener standards comparison in structural applications. ISO 4014 bolts feature an unthreaded shank beneath the head, which improves shear strength for demanding assemblies. The main points of comparison include:
- ISO 4014 now serves as the global reference for partially threaded hex bolts, taking over from DIN 931.
- Both standards specify similar dimensions for partially threaded bolts, ensuring compatibility in most applications.
- The unthreaded shank in both DIN 931 and ISO 4014 enhances performance in structural joints.
DIN 933 and ISO 4017 Comparison
DIN 933 and ISO 4017 both describe fully threaded hex bolts, with ISO 4017 serving as the updated international standard.
DIN 933 bolts remain widely used in industry, even after the introduction of ISO 4017. Both standards share similar dimensional requirements for fully threaded bolts, making them suitable for clamping and precision assembly. The transition to ISO 4017 ensures global consistency in manufacturing and application.
- DIN 933 bolts have threads running from tip to head, matching the ISO 4017 design.
- Both standards support a wide range of sizes and materials for industrial use.
- Manufacturers and distributors continue to supply DIN 933 bolts due to ongoing demand.
Interchangeability in Practice
DIN and ISO hex bolts often interchange in practice, but small differences can affect fit and procurement.
Many industrial users rely on both DIN and ISO bolts, but subtle differences sometimes impact compatibility. For example, the width across flats (WAF) may differ:
| Standard | Width Across Flats (WAF) |
|---|---|
| DIN 933 | 17mm |
| ISO 4017 | 16mm |
- Despite the formal withdrawal of DIN standards, DIN 931 and DIN 933 bolts remain popular in the market.
- Major distributors frequently stock DIN 933 hex heads, reflecting their continued relevance.
- The ISO version of a fastener is not always easier to source, and sometimes the DIN version presents procurement challenges.
Engineers should always check dimensional details before substituting between DIN and ISO bolts. Careful comparison ensures proper fit and compliance in critical applications.
Application Guide: Choosing the Right Hex Bolt
When to Use DIN 931
Engineers select DIN 931 hex bolts for applications that demand superior shear strength and precise alignment.
The partially threaded design provides an unthreaded shank, which increases resistance to lateral forces. This feature makes DIN 931 bolts suitable for structural connections, machinery frames, and assemblies where joint integrity is critical. The unthreaded section helps maintain alignment and reduces stress concentration. Stainless steel bolt head markings help identify grade and compliance, supporting safety in high-load environments. ISO standards ensure compatibility with global engineering practices.
| Application Criteria | DIN 931 Suitability |
|---|---|
| Shear strength required | Excellent |
| Alignment critical | High |
| Structural joints | Preferred |
When to Use DIN 933
DIN 933 hex bolts are the preferred choice for clamping, tensioning, and assemblies requiring full thread engagement.
The fully threaded shaft allows for maximum grip and flexibility in length adjustment. DIN 933 bolts excel in situations where axial loads dominate, such as securing panels, mounting equipment, or joining components with variable thickness. ISO 4017 standards match DIN 933 specifications, ensuring interchangeability. Common stainless steel bolt markings indicate material and grade, supporting traceability. DIN 933 hexagon set screws and fully threaded set screws provide reliable performance in dynamic assemblies.
Tip: Use DIN 933 bolts when the application requires strong clamping force and easy adjustment. ISO standards guarantee consistent quality and fit.
Common Industrial Use Cases
DIN and ISO hex bolts serve a wide range of industries, each with specific requirements for performance and reliability.
Market data highlights several sectors where DIN 931 and DIN 933 bolts play a vital role:
- Petrochemical industry
- Automobile manufacturing
- Construction
- Pressure piping
- Rail transit
- Steel structure engineering
- Large-scale power generation machinery facilities
- Infrastructure
Engineers rely on DIN and ISO bolts for their proven strength and versatility. The hex design supports efficient installation and removal. Manufacturers use common stainless steel bolt markings to ensure compliance and traceability. These bolts meet the demands of high-load, high-temperature, and corrosive environments.
Procurement and Quality Considerations
Material and Strength Classes
DIN 931 and DIN 933 hex bolts are available in a wide range of materials and strength classes, which directly impact performance and reliability.
Manufacturers produce fasteners using carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel grades such as 304 and 316. Sunhy offers advanced alloys like Duplex 2205, Titanium Grade 5, and Inconel 625 for demanding environments. Engineers select stainless options for corrosion resistance in chemical plants, marine structures, and food processing. The choice of material affects the bolt’s ability to withstand high loads, temperature extremes, and aggressive chemicals.
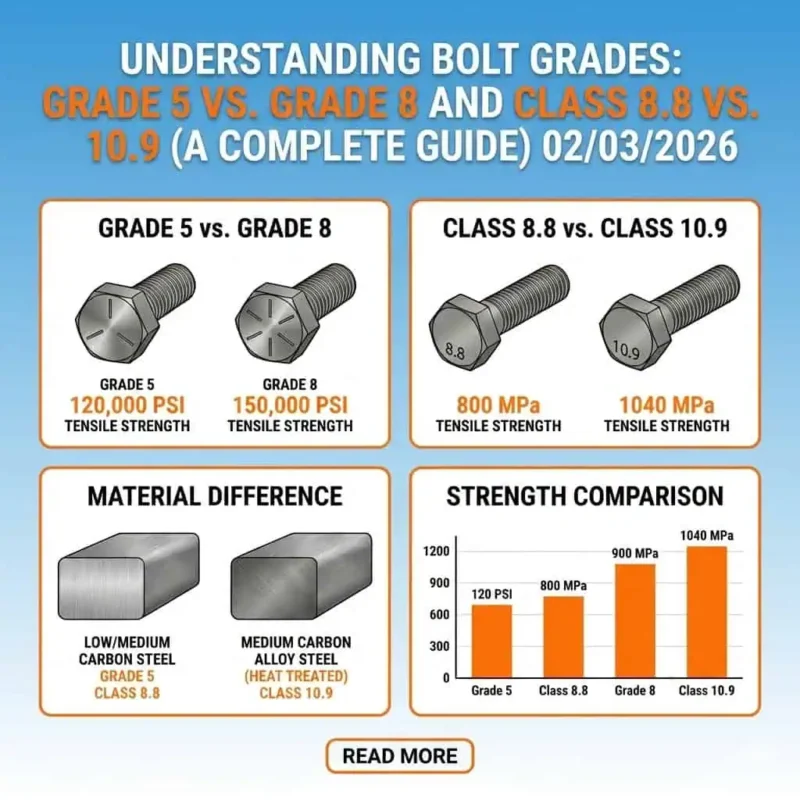
| Bolt Type | Strength Class | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN 933 | 8.8 | 800 | 640 | 93 |
| DIN 933 | 10.9 | 1000 | 900 | 130 |
| DIN 931 | 8.8 | 800 | 640 | 93 |
| DIN 931 | 10.9 | 1000 | 900 | 130 |

Sunhy Industrial Fasteners Advantages
Sunhy delivers industrial fasteners with superior quality, traceability, and customization for every application.
Sunhy’s catalog includes fasteners in sizes from M3 to M64, with options for stainless steel, carbon steel, and specialty alloys. The company maintains strict quality control with ISO 9001 traceability and inspection records for each batch. Engineers rely on Sunhy for fasteners that meet audit and compliance requirements. Sunhy supports custom and OEM fasteners, providing made-to-print solutions for unique projects. The company’s advanced testing facilities ensure every stainless fastener meets dimensional and mechanical standards.
- Wide selection of stainless, carbon, and alloy fasteners
- Lot traceability and inspection records for compliance
- Custom and OEM fasteners for specialized needs
- Quick dispatch of over 1,500 catalog SKUs
Ordering and Compliance Tips
Procurement teams should verify material, strength class, and certification when ordering hex bolts for critical projects.
Sunhy recommends checking stainless steel grades, strength ratings, and inspection documentation before placing orders. Engineers should match fasteners to the application’s load and environmental requirements. For custom builds, Sunhy’s application engineering team assists with design and specification. Fasteners with proper markings and traceability simplify audits and ensure safety in regulated industries.
Tip: Always request inspection records and lot traceability for stainless fasteners used in pressure equipment or structural assemblies.
DIN 931 bolts feature a partial thread for enhanced shear strength, while DIN 933 bolts offer full threading for superior grip and flexibility. Selecting the correct hex bolt ensures safety and reliable performance in industrial settings.
- DIN 931 bolts excel in high-strength applications such as bridges and machinery.
- DIN 933 bolts provide secure fastening in automotive and assembly tasks.
- Materials include carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel with various finishes.
For best results, consult dimension charts, verify material certifications, and partner with ISO 9001-certified suppliers like Sunhy.
FAQ
What is the main difference between DIN 931 and DIN 933 hex bolts?
DIN 931 bolts have a partially threaded shank; DIN 933 bolts are fully threaded.
The unthreaded shank on DIN 931 bolts increases shear strength. DIN 933 bolts provide full thread engagement for clamping and tensioning.
Can DIN 931 and DIN 933 bolts be used interchangeably?
Not always.
Engineers select DIN 931 for shear strength and alignment. DIN 933 suits tension and clamping. Always check application requirements before substituting one for the other.
What materials are available for DIN 931 and DIN 933 bolts?
Manufacturers offer carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel.
Sunhy also supplies advanced alloys like Duplex 2205, Titanium Grade 5, and Inconel 625 for demanding environments.
Are DIN and ISO hex bolts compatible?
Often, but not always.
Most dimensions match, but small differences—such as width across flats—may affect fit. Always verify specifications before mixing DIN and ISO bolts.
How can buyers ensure fastener quality and compliance?
Request inspection records and lot traceability.
Choose suppliers like Sunhy that provide ISO 9001 certification, material documentation, and batch inspection reports for every order.