The main difference between BSP vs NPT stainless fittings lies in their thread design and sealing method.
BSP threads use a 55-degree Whitworth flank angle, while NPT threads use a 60-degree flank angle and a defined taper. In the field, those two details decide whether you get full flank contact (stable make-up) or a leak path that only “looks tight.”
- BSP fittings may be parallel (BSPP) or tapered (BSPT) and often seal with a washer, bonded seal, or O-ring (especially BSPP).
- NPT fittings are tapered and typically require a sealant (PTFE tape, PTFE-free tape, or anaerobic sealant) to block the spiral leak path.
- BSP is common in Europe, Asia, and Australia; NPT is the default in North America.
- Mixing BSP and NPT can give only a few turns of engagement and can damage threads before you notice the leak.
Correct identification is a safety step, not a paperwork step. If you are standardizing a plant or building a BOM, lock down the thread standard first, then select material grade (304/316/316L) and the fitting product standard (for example, forged threaded fittings are commonly specified under ASME B16.11 for ratings/dimensions). If you need both BSP and NPT options across regions, you can cross-check Sunhy’s related technical guides here: Technical Guides.
| Quick Field Check | BSP (BSPP/BSPT) | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Thread angle | 55° Whitworth profile | 60° profile |
| Parallel vs taper | BSPP = parallel, BSPT = taper | Tapered |
| Typical sealing location | BSPP often seals at face with washer/O-ring; BSPT seals on threads (often with jointing medium) | Seals on threads; sealant commonly used to block spiral leak path |
| Standards you’ll see on specs | ISO 7-1 (taper), ISO 228-1 (parallel) | ASME B1.20.1 |
What Are BSP Stainless Fittings?
BSP Definition
BSP stainless fittings use the British Standard Pipe thread family (Whitworth form) to connect pipes and equipment in many industries. In engineering documentation, “BSP” is usually clarified as either BSPP (parallel) or BSPT (taper). If the joint is intended to be pressure-tight on the threads, BSPT commonly aligns with ISO 7-1. If the threads are primarily for mechanical assembly and the seal is made elsewhere (for example, by an O-ring/washer at the face), BSPP commonly aligns with ISO 228-1.
Engineer’s note: many leaks blamed on “bad machining” are actually a mismatch between thread type and where the seal is supposed to happen. A parallel thread with no face seal hardware will leak even if threads are perfect.
BSP Thread Characteristics
BSP threads stand out because of their Whitworth 55° profile and how the joint is sealed. You will see two main types: BSPP (Parallel) and BSPT (Tapered). The table below compares what matters for sealing and inspection (not sales descriptors):
| Feature | BSPP (Parallel) | BSPT (Tapered) |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Shape | Parallel (no taper) | Tapered (interference make-up) |
| Typical Designation | “G” thread on drawings/specs (common ISO usage) | “R/Rp/Rc” family on drawings/specs (common ISO usage) |
| Where the Seal Is Made | Usually at the face with O-ring, bonded seal, washer, or gasket (depends on port design) | On the threads by interference; in practice a jointing medium is often used to ensure pressure-tightness |
| What Actually Limits Pressure | Not the thread name alone. Pressure capability is governed by the fitting design (wall thickness, end form), material, temperature, and the governing product standard/specification. | |
| Best For | Serviceable connections where repeat assembly matters and face sealing is controlled | General utility/process joints where tapered thread practice is established and sealant control is acceptable |
BSP threads use a 55-degree angle (Whitworth form). BSPP relies on controlled face sealing hardware; BSPT relies on controlled make-up and typically uses a jointing medium to block the spiral leak path and reduce galling risk during assembly/disassembly.
Engineering example (selection mistake → leak): a maintenance team replaced a leaking BSPP female port connection using an NPT male “because it matched nominal size.” The fitting engaged only a few turns and felt tight, but hydrotest seepage started at low pressure. Root cause was mismatched pitch/angle and wrong sealing concept (thread seal attempted where the design required a face seal). Corrective action: confirm BSPP with a gauge, install the correct BSPP male + bonded seal/washer at the face, then re-test.
BSP Applications
You will find BSP stainless fittings in applications where Whitworth pipe threads are the established regional standard. Stainless (typically 304/316/316L) is selected for corrosion control, hygiene, or external environmental exposure. Common use cases include:
| Industry | Application Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Used on utility and compatible chemical services where corrosion resistance and cleanability matter; verify media compatibility, temperature, and any chloride exposure risk before choosing 304 vs 316. |
| Water & Wastewater Management | Common in regional standards; maintenance teams often prefer serviceable joints where sealing elements can be replaced on scheduled inspection. |
| Oil, Gas, and Petrochemicals | Used in auxiliary systems and some regional builds; pressure/temperature limits come from the component standard and piping code, not the “BSP” label. |
| Food, Beverage & Pharmaceuticals | Selected when corrosion resistance and cleaning regimes require stainless; avoid dead-legs and ensure sealing materials match CIP/SIP temperatures and chemicals. |
Tip from field practice: when a site has mixed equipment origins (EU + US skids), thread identification must be done at the connection point, not assumed from the vendor nameplate.
Identifying BSP Threads
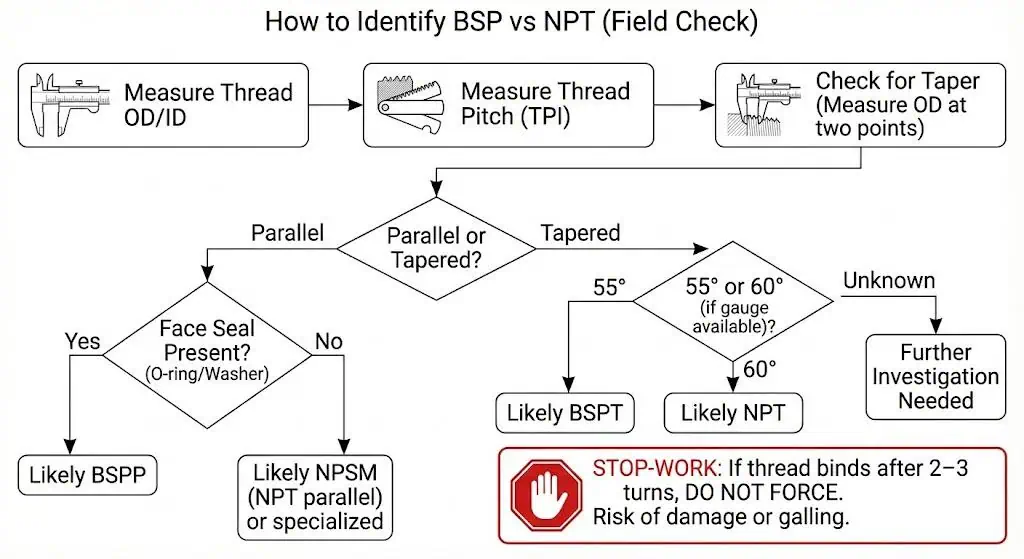
Tip: Identification is faster when you standardize the toolbox: calipers + pitch gauge set (BSP/NPT) + a simple “go/no-go” habit (do not force threads that bind early).
- Measure the male OD (or female ID carefully) with calipers and compare to a reference chart for BSP sizes.
- Use a thread pitch gauge to confirm TPI; do not “eyeball” 18 vs 19 TPI.
- Check taper: measure OD near the first thread and near the last thread; a meaningful change indicates taper.
- Confirm sealing concept: BSPP joints often have a sealing face/shoulder intended for a washer/O-ring; BSPT relies on thread interference.
- If you have access to gauges, verify flank angle (55° vs 60°) rather than guessing from nominal size.
Engineering example (wrong diagnosis → repeat leak): a technician kept re-wrapping PTFE tape on a BSPP connection that leaked at the face. The tape never solved it because the design needed a face seal (bonded seal/washer) and the sealing surface had a scratch. Fix: replace the sealing washer and dress/replace the mating face; then assemble with controlled torque and recheck.
What Are NPT Stainless Fittings?
NPT Definition
NPT stainless fittings use the National Pipe Thread Tapered system, widely specified in North America for threaded pipe joints. In specifications, NPT geometry and gauging are commonly referenced to ASME B1.20.1. NPT is a tapered thread form; the taper and 60° flank geometry create interference as the joint is made up. In practice, most NPT assemblies still use sealant to block the spiral leak path and to reduce thread galling during assembly.
Engineer’s note: NPTF (“Dryseal”) exists for applications designed to seal by thread deformation with tighter tolerances, but many industrial sites still standardize on sealant-controlled NPT practice to reduce variability and to improve serviceability.
NPT Thread Characteristics
NPT threads have a 60-degree profile and a defined taper (commonly described as 1 in 16). That taper means the male OD increases along the thread length, creating interference and flank contact as you tighten. Sealant is commonly used because the thread geometry still creates a helical leakage path unless it is blocked.
| Feature | NPT Threads |
|---|---|
| Thread Angle | 60 degrees |
| Thread Type | Tapered (interference fit) |
| Typical Taper Description | Commonly expressed as 1 in 16 (check spec/gauging requirements for acceptance) |
| Sealing Method (field practice) | Thread interference + sealant to block spiral leak path |
| Standard Reference | ASME B1.20.1 (geometry & gauging) |
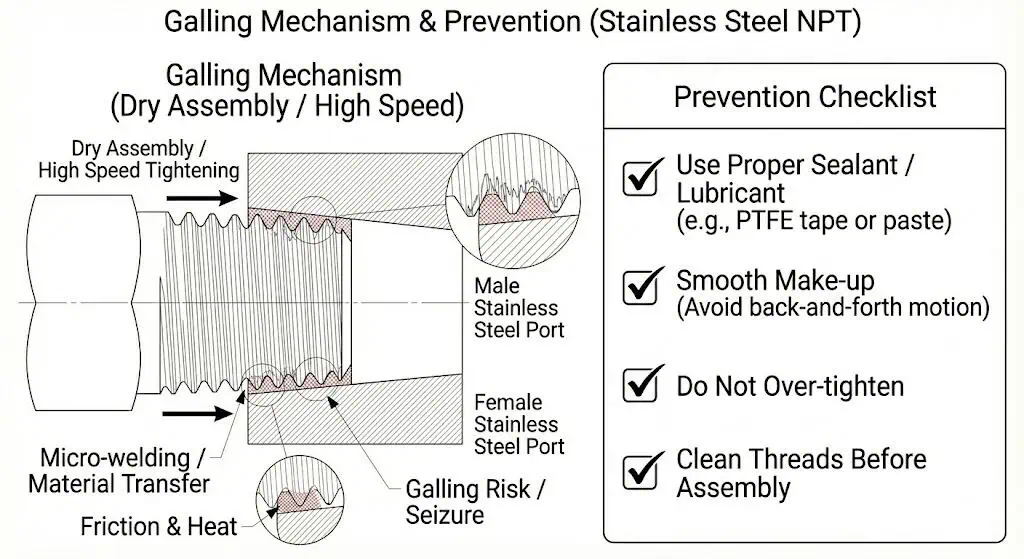
| Common Failure Mode in Stainless | Galling/seizing if assembled dry or too fast; use appropriate sealant/lubrication and controlled make-up |
Engineering example (galling → forced rework): a 316 stainless NPT nipple was installed dry into a 316 stainless body and tightened rapidly with a long wrench. Threads galled (“cold-welded”), the joint seized, and removal destroyed both parts. Prevention: use an appropriate thread sealant/lubricant and assemble smoothly (no back-and-forth), then pressure-test and mark the joint as accepted.
NPT Applications
NPT stainless fittings are common in systems that need corrosion resistance and a serviceable threaded joint. Typical application areas include:
- Plumbing and HVAC (site standardization is common—verify thread type across imported equipment)
- Construction and utility skids
- Marine and coastal service (material selection and crevice corrosion controls matter)
- Agriculture and general industrial utilities
- Food and beverage utilities (verify cleaning chemicals/temperatures and sealing material compatibility)
- Oil and gas auxiliary and instrumentation services (spec-driven selection is typical)
- Manufacturing and maintenance-friendly piping modifications
Important: “stainless” does not automatically mean “chemical-proof.” Selection still depends on media, temperature, chlorides, cleaning chemistry, and whether the connection will be disassembled regularly.
Identifying NPT Threads
You can identify NPT threads by measuring pitch (TPI), major diameter, and confirming taper. A tapered NPT male will show a measurable OD increase from the first to the last engaged threads.
- Determine whether the fitting is male or female; identify the sealing concept of the port you are connecting to.
- Use a thread gauge to measure thread spacing (TPI) and compare to an NPT reference.
- Measure OD at two points along the thread to confirm taper (do not force a “near match”).
- Visually inspect for taper and for any shoulder/face-seal features (NPT typically seals on threads, not on a flat face).
- If you see an O-ring at the face/shoulder of a parallel-thread port, treat it as a strong signal the joint is not relying on NPT-style thread sealing.
Tip: If a “1/4” thread only runs in 2–3 turns and stops abruptly, stop. That symptom matches common common BSP/NPT mismatch behavior and usually ends in damaged threads.
Engineering example (inspection catch → avoided downtime): during commissioning, a leak was spotted at a compressed air manifold. The fitter had used an NPT male into a BSPP female port. A quick pitch gauge check confirmed mismatch before threads were stripped. Corrective action: install the correct thread adapter (BSPP↔NPT) and seal using the method required by each side (face seal on BSPP side, sealant-controlled tapered thread on NPT side), then soap-test.
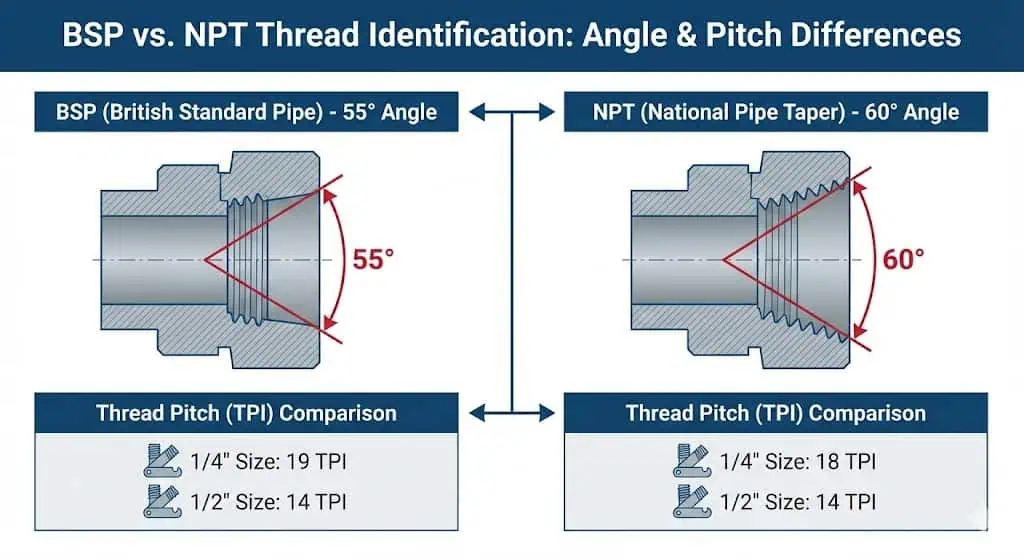
BSP vs NPT Stainless Fittings: Key Differences
Thread Angle and Profile

The main difference between BSP vs NPT stainless fittings lies in the thread angle and profile.
NPT uses a 60-degree flank angle and a defined taper; BSP uses a 55-degree Whitworth profile and exists in both parallel (BSPP) and tapered (BSPT) forms. In practice, this changes flank contact, how quickly interference builds, and whether the joint was designed to seal on threads or at a face/seal element.
- NPT: 60-degree thread angle, tapered profile; commonly referenced to ASME B1.20.1
- BSP: 55-degree Whitworth profile; BSPT commonly aligns with ISO 7-1, BSPP commonly aligns with ISO 228-1
Tip: Do not rely on nominal size marks alone. Confirm angle + pitch + taper, then confirm where the seal is intended to occur.
Sealing Methods
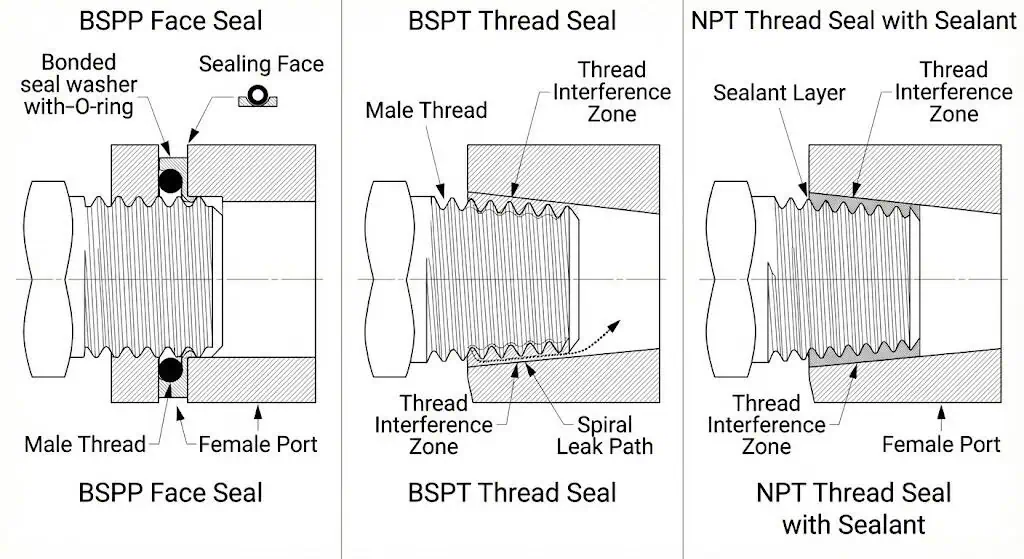
BSP vs NPT stainless fittings use different sealing methods to prevent leaks.
NPT joints typically use thread interference and a sealant to block the spiral leak path. BSPP joints typically seal at the face (washer/O-ring/bonded seal). BSPT joints seal by tapered thread interference, and jointing medium is commonly used for pressure-tightness and to reduce galling risk.
- NPT: thread interference + sealant control is common practice
- BSP (BSPT): tapered thread interference; jointing medium often used depending on service and site practice
- BSP (BSPP): face seal (gasket/washer/O-ring/bonded seal) is usually the primary sealing mechanism
Engineering example (sealant misuse → recurring seepage): a BSPP connection was repeatedly reassembled with more PTFE tape after minor seepage. The tape changed nothing because the leak path was at the face seal, not through the threads. Correct fix was replacing the washer/O-ring and verifying the sealing surface finish/condition.
Compatibility Issues
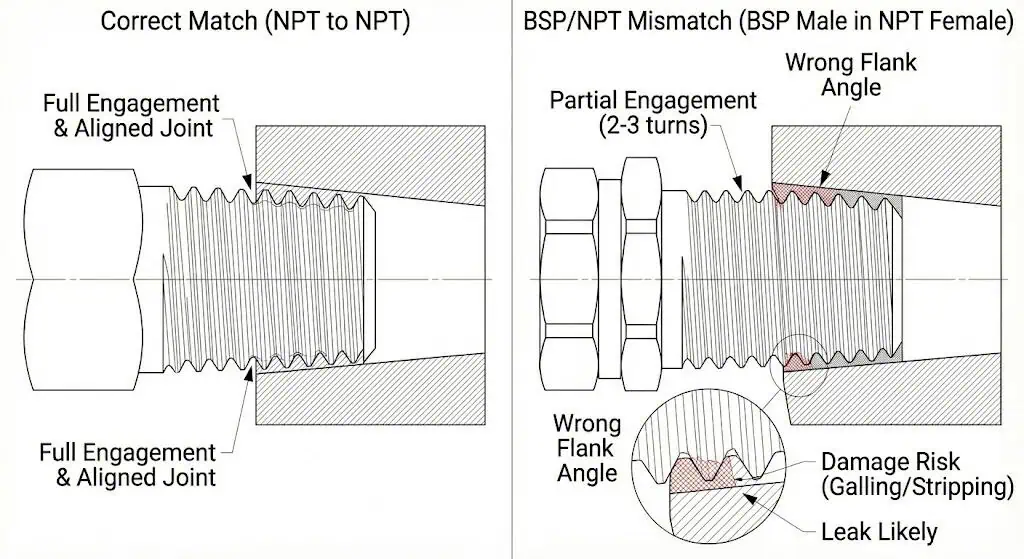
BSP vs NPT stainless fittings are not compatible with each other, and mixing them causes serious problems.
The angles differ and many sizes differ in pitch. A common symptom is “it tightens for only a couple of turns,” which feels like progress until the threads are damaged. Once stainless threads gall or deform, the port may be scrap.
- Mixing BSP and NPT threads can result in:
- Leaks from incomplete flank contact and an unblocked spiral leak path
- Damaged threads (stripping or galling), especially in stainless-to-stainless joints
- False “tight” feel after only a few turns of engagement
- Rework and downtime (port replacement, re-tapping, or manifold scrap)
Note: If you must transition between standards, use a designed adapter (BSP↔NPT) and seal each side using the correct method for that side.
Geographic Use
You will find that BSP vs NPT stainless fittings are used in different regions due to historical standards.
For global projects, the practical rule is simple: match what the mating equipment/ports are actually built to, then control adapters and spares so maintenance does not “make it fit” on night shift.
| Region | Fitting Type | Practical Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Europe | BSPP/BSPT | Common on EU-built equipment; confirm whether the port is face-seal (parallel) or thread-seal (taper). |
| Commonwealth Nations | BSPP/BSPT | Legacy Whitworth practice is common; mixed fleets still require verification. |
| Southeast Asia | BSPP/BSPT | Often BSP on imported equipment; projects with US skids may bring NPT into the same plant. |
| North America | NPT | Most utility/process threaded joints are NPT by default; imported equipment may still use BSP. |
| Middle East | BSP/NPT | Both appear depending on EPC origin; adapters and thread gauges should be standard site tooling. |
You should always check the standard used at the connection point before selecting fittings. This prevents the most expensive “small leak” you can buy: repeated rework on damaged ports.
Choosing the Right Stainless Fitting
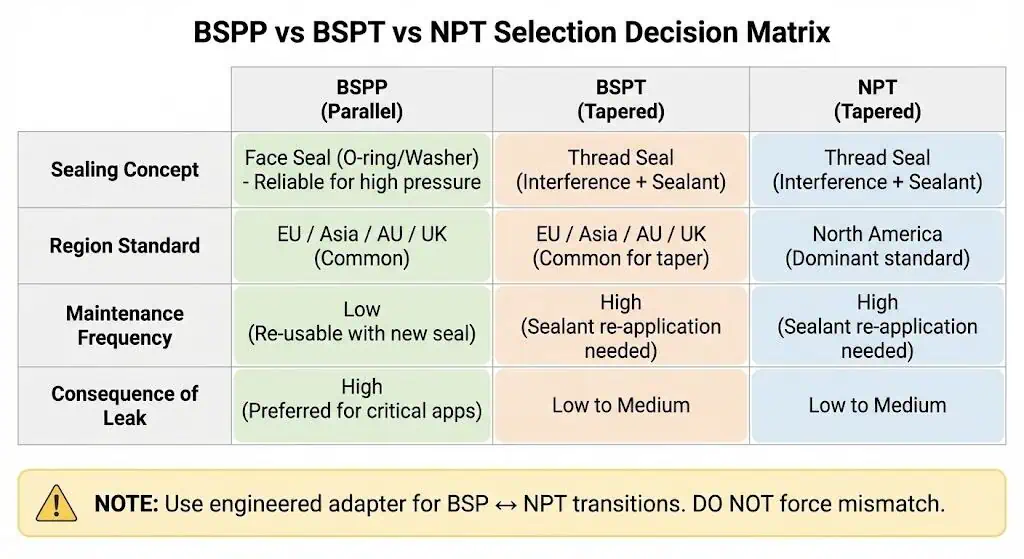
Selection Factors
Choose stainless fittings based on the thread standard at the mating port, the sealing concept, and the governing product standard—then confirm material/service compatibility.
When selecting between BSP and NPT, focus on what you can measure and what you can verify on drawings and inspection reports:
- Thread Standard at the Port: Verify with gauge + spec: ISO 7-1 / ISO 228-1 vs ASME B1.20.1. Do not assume from nominal size.
- Sealing Concept: Is the joint designed to seal on threads (taper) or at a face/washer/O-ring (parallel)? Select fitting + seal hardware accordingly.
- Product Standard / Rating Basis: For threaded forged fittings, ratings/dimensions are often tied to standards such as ASME B16.11. Do not infer pressure rating from “BSP vs NPT” alone.
- Material & Media Compatibility: 304 vs 316/316L depends on chlorides, temperature, cleaning chemicals, and corrosion mechanism (pitting/crevice/SCC). Confirm with project materials specs.
- Assembly Controls: Stainless tapered threads are prone to galling if assembled dry or too fast. Plan sealant/lubrication and a controlled make-up method.
Tip: If your site sees both BSP and NPT, standardize three things: (1) thread gauge kits, (2) approved adapters, (3) approved sealant/lubricant for stainless service.
Application Considerations
Match the fitting to the application’s actual demands: media, temperature, maintenance frequency, and the failure consequence.
- High-consequence services: Prefer designs that reduce assembly variability (controlled face seals, verified adapters, documented torque/make-up practice).
- Water and utilities: BSPP face-seal joints can be maintenance-friendly when washers/O-rings are controlled and sealing faces are protected.
- Chemical processing: Confirm stainless grade and sealing material compatibility with the chemical and temperature range; thread form does not solve corrosion.
- Frequent disassembly: Choose sealing concepts that are repeatable; manage galling risk with approved sealant/lubrication and clean threads.
| Decision Point | NPT (typical practice) | BSP (typical practice) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary seal location | Threads + sealant control | BSPP: face seal; BSPT: threads (often with jointing medium) |
| Common pitfall | Dry assembly → galling; over-tightening | BSPP assembled without correct washer/O-ring; BSPT/NPT mixed by “feel” |
Note: Precision machining helps, but it cannot compensate for a wrong thread standard or a missing sealing element.
Maintenance and Longevity
Fitting life is mainly controlled by correct identification, correct sealing method, and controlled assembly.
Field maintenance practices that consistently reduce leaks and thread damage:
- Clean threads before assembly: debris and metal fines increase galling risk and damage flank contact.
- Use an approved sealant/lubricant strategy: tapered threads commonly use PTFE tape / PTFE-free tape / anaerobic sealant to block the leak path and reduce galling risk.
- Avoid over-tightening: once stainless threads start to gall, the joint may seize and require destructive removal.
- Inspect sealing faces on BSPP joints: a scratched face or hardened washer/O-ring can create repeat leaks even if threads are correct.
- Standardize adapters: where BSP↔NPT transitions are unavoidable, treat adapters as engineered components with controlled spares and inspection.
Tip: If a joint will be opened often, document the seal method (what sealant, what washer/O-ring) on the maintenance job plan. Repeatability beats “tribal knowledge.”
Sunhy delivers stainless fittings engineered for controlled assembly and documented standards.
If your project spans regions, you can specify NPT (ASME B1.20.1) or BSP (ISO 7-1 / ISO 228-1) on drawings and purchase documents, then validate incoming threads with gauges. For related threaded product families, see: Threaded Couplings & Sockets and Stainless Steel Threaded Flanges.
Common Mistakes and Best Practices
Installation Errors
The most common installation errors with BSP and NPT stainless fittings include damaged threads, wrong sealing method, and uncontrolled over-tightening.
These errors are usually preventable with gauges, seal hardware control, and a stop-work rule when engagement feels abnormal.
| Installation Error | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Stripped or Galled Threads | Loss of flank contact → leaks, seized joints, and damaged ports (often scrap on stainless manifolds). |
| Distorted Fittings / Misalignment | Non-uniform contact or side loading → face seal damage (BSPP) or uneven thread interference (tapered joints). |
| Over-tightening | Thread deformation, galling, cracked components, and poor repeatability on reassembly. |
| BSPP assembled without washer/O-ring/bonded seal | Leaks at the face; repeated rework if technicians keep adding tape to threads instead of fixing the seal hardware. |
| Mixing BSP and NPT “because it threads in” | Few-turn engagement, false tight feel, damaged threads, and persistent leakage. |
Tip: A good rule: if engagement is less than expected or binding starts early, stop and verify standard—do not “power through” stainless threads.
Inspection Tips
Inspection is how you make threaded joints predictable.
A practical inspection routine for BSP/NPT in stainless service:
- Verify thread type with gauges (angle/pitch/taper) before assembly; do not rely on packaging labels.
- Inspect male/female threads for burrs, dents, and contamination; clean before applying sealant.
- For BSPP, inspect the sealing face/shoulder and replace sealing elements (washer/O-ring) on any sign of hardening, cuts, or flattening.
- Assemble using a controlled method (steady make-up, no repeated back-and-forth) to reduce galling risk.
- Leak-test the joint using an appropriate method for the service (soap solution for gas utilities, pressure hold for liquids) and record acceptance.
Note: “It didn’t leak during startup” is not a test method. Threads that are mismatched may pass briefly and then leak after vibration/thermal cycling.
Training and Safety
Training should focus on measurable checks, not just “tighten until it feels right.”
Key training protocols that reduce leaks and thread damage:
- Use thread identification standards and guides (pitch gauges, taper verification, and “stop-work” criteria when engagement is abnormal).
- Understand where the seal is made (threads vs face seal) and stock the correct sealing elements for BSPP joints.
- Apply sealants correctly for tapered threads and control contamination (avoid excess tape strings entering the system).
🛠️ Well-trained technicians prevent the most expensive failure mode in threaded joints: damaged ports that force replacement of manifolds, valves, or skids.
BSP and NPT stainless fittings differ in thread angle, sealing method, and compatibility.
The simplified comparison below is a reminder—your acceptance should still be based on measured pitch/taper and the correct seal concept:
| Feature | NPT Threads | BSP Threads |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Angle | 60 degrees | 55 degrees |
| Sealing Method | Threads + sealant control (typical practice) | BSPP: face seal; BSPT: tapered thread interference (often with jointing medium) |
| Compatibility | Not compatible with BSP | Not compatible with NPT |
Choosing the right fitting protects your system from leaks and failures. Verify thread type with gauges, confirm sealing concept, and standardize adapters where cross-standard transitions are unavoidable. For thread-standard references, see ASME B1.20.1, ISO 7-1, and ISO 228-1.
FAQ
What is the main difference between BSP and NPT stainless fittings?
BSP uses a 55-degree Whitworth profile (BSPP parallel or BSPT taper). NPT uses a 60-degree profile and a defined taper.
More importantly, many BSPP joints are designed to seal at the face with a washer/O-ring, while NPT joints typically seal on the threads with sealant control. The correct answer on site is the one you can measure: pitch + taper + where the seal is intended to happen.
Tip: If your thread gauge kit does not include both BSP and NPT leaves, upgrade the kit—this is one of the fastest ROI tools in maintenance.
Can you connect BSP and NPT fittings together?
You should not connect BSP and NPT directly.
Even when a fitting seems to start threading, mismatch in angle and often pitch leads to partial engagement, leaks, and thread damage (especially in stainless). If you must transition, use a designed adapter (BSP↔NPT) and seal each side using the correct method for that side (face seal vs tapered-thread sealant practice).
- BSP: 55-degree profile (BSPP parallel or BSPT taper)
- NPT: 60-degree profile with taper
How do you identify BSP and NPT threads?
Use calipers + a pitch gauge set, confirm taper, then confirm sealing concept.
BSP is 55° Whitworth form and can be parallel (BSPP) or tapered (BSPT). NPT is 60° and tapered. A quick safety rule: if a “match” binds after only a couple of turns, stop and verify—do not force stainless threads.
| Feature | BSP | NPT |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | 55 degrees | 60 degrees |
| Profile | Parallel/Taper | Tapered |
| What to measure | OD/ID + TPI + taper check + face-seal features | OD/ID + TPI + taper check |
Which industries use stainless steel BSP and NPT fittings?
BSP appears commonly where Whitworth pipe thread practice is regional standard; NPT dominates most North American threaded pipe joints.
Across both, stainless is selected for corrosion control, hygiene, or external environment. Always verify the port standard on equipment (EU/US skids in the same plant are common).
- BSP: chemical, water/wastewater, food/utilities in many regions
- NPT: utilities, construction/industrial skids, oil & gas auxiliary/instrumentation in North America
Why should you choose Sunhy stainless steel fittings?
You can specify NPT or BSP thread standards and match stainless grade to your service conditions.
For engineering control, focus on thread standard (ASME/ISO reference), incoming inspection (gauging), and documented sealing practice. Sunhy supports NPT and BSP options and provides product families suited to threaded joint applications.