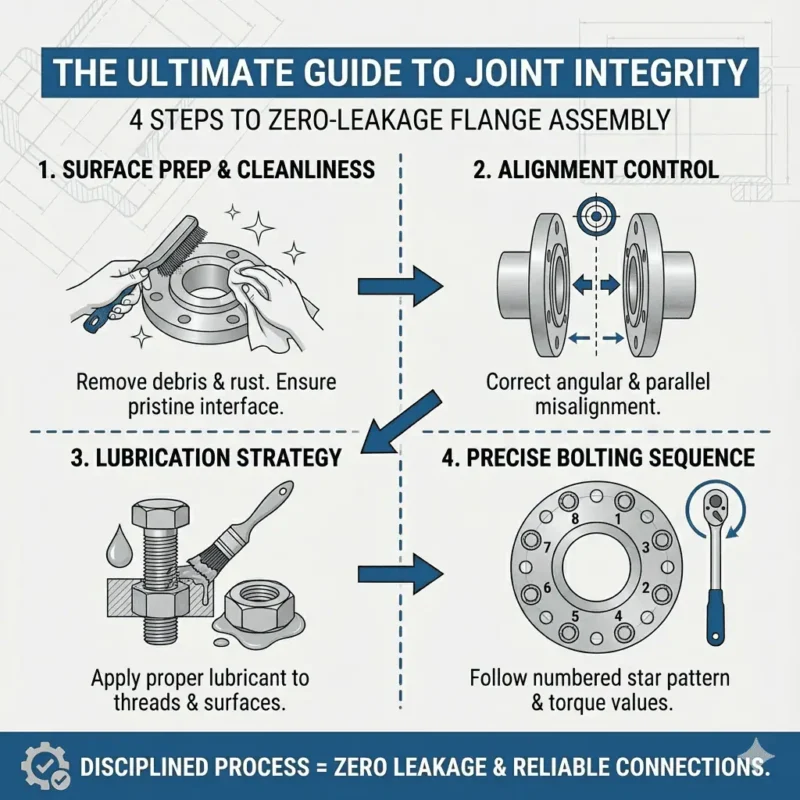
You need to understand the differences between jis vs ansi vs din flanges to achieve reliable project results. International standards guide the design and quality of industrial piping, helping you avoid costly mistakes and ensure safety.
- ANSI standards improve compatibility and safety in global piping projects.
- DIN standards support quality assurance and compliance, leading to successful installations.
- JIS standards make international trade easier by setting clear technical requirements.
Sunhy supplies stainless steel flanges for demanding environments, offering precision and reliability for a wide range of applications.
JIS vs ANSI vs DIN: Key Differences
Understanding the key differences between jis vs ansi vs din flanges helps you select the right product for your project. Each standard has unique design features, pressure ratings, dimensional rules, material specifications, and typical applications.
Design Features Compared
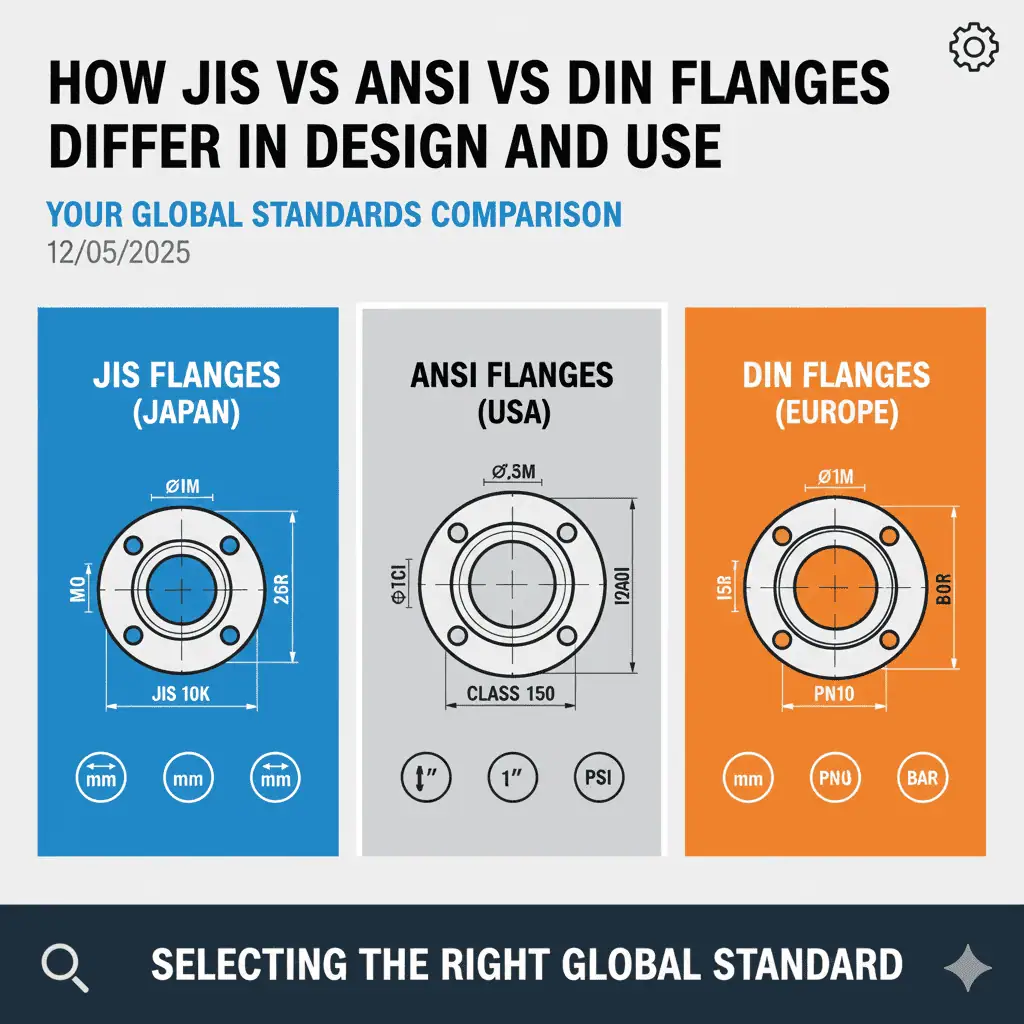
ANSI flanges are generally larger and thicker, JIS flanges are more compact, and DIN flanges use metric units.
| Flange Type | Nominal Size | Bolt Holes | Bolt Circle (mm) | Pressure Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIS 10K | 100A (4”) | 8 | 175 | 10K |
| ANSI Class 150 | 4” | 8 | 190 | 150 psi |
| DIN PN16 | DN100 | 8 | 180 | 16 bar |
- ANSI flanges follow ASME B16.5 standards and feature standardized bolt hole patterns.
- JIS flange designs are more compact, which saves space in installations.
- DIN flanges use metric sizing and focus on precision.
Tip: You should check the bolt circle and hole pattern before mixing standards in a piping system.
Pressure Ratings Overview
JIS, ANSI, and DIN flanges use different pressure rating systems, which affect their suitability for various environments.
| Standard | Pressure Ratings | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ANSI | 150, 300, 600, 900 | Classes used in the US for various applications |
| DIN | PN10, PN16, PN25 | Pressure Nominal values used in Europe |
| JIS | 10K, 16K, 20K | Kilo units used in Japan for flange ratings |
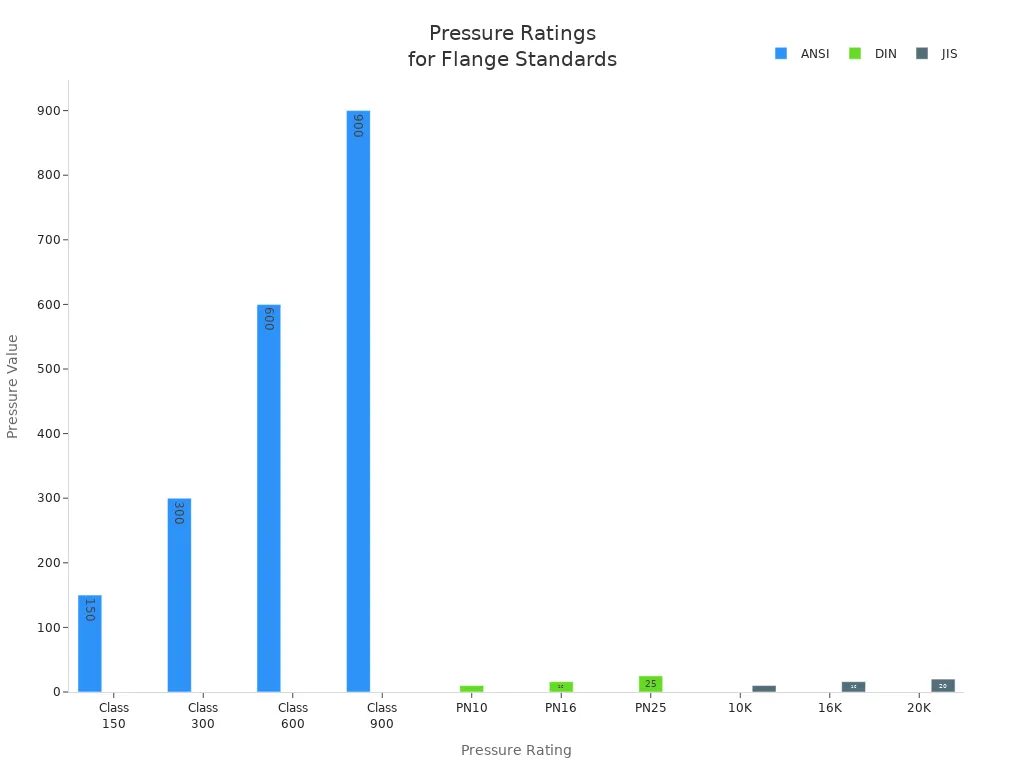
- JIS uses ‘K’ (kilogram per square centimeter).
- ANSI uses ‘Class’ (based on psi).
- DIN uses ‘PN’ (bar rating).
Dimensional Standards
ANSI flanges are typically thicker and larger than JIS flange and DIN flanges for the same nominal size.
| Feature | JIS Flanges | ANSI Flanges |
|---|---|---|
| Bolt Hole Patterns | Unique to JIS | Standardized per ASME |
| Flange Face | Compact | Thicker, larger |
Both JIS and DIN flanges often have unthreaded female ports with bolt holes at the corners. ANSI flanges follow a different pattern, which means you need to check compatibility before installation.
Material Specifications
JIS, ANSI, and DIN standards specify different material grades for flanges, which impact durability and corrosion resistance.
- JIS uses Japanese grades like SS400 and SUS304.
- ANSI specifies ASTM or ASME grades such as A105 and A182 F304.
- DIN uses EN grades like C22.8 and 1.4301.
| Material Type | Specification | Application Description |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A105 | Used for ambient and higher temperatures |
| Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 | Ideal for corrosive and high-temperature environments |
| Low-Temperature Carbon Steel | ASTM A350 | Needed for low-temperature applications |
| Alloy Steel | ASTM A182 F11, F22 | Used in power generation and refineries |
Note: Sunhy manufactures flanges from dual-certified 316/316L stainless steel forgings. This process ensures high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. You benefit from strict testing protocols and precision machining, which guarantee reliability in demanding environments.
Typical Applications
You will find ANSI flanges mostly in the Americas, JIS flange in Asia, and DIN flanges in Europe.
- ANSI flanges suit oil & gas, chemical, and power generation projects in the US.
- JIS flange is common in Japanese industrial plants and marine systems.
- DIN flanges are preferred in European chemical, water treatment, and manufacturing industries.
You should match the flange standard to your project’s location and regulatory requirements for best results.
JIS Flange, ANSI Flange, and DIN Flange Overviews
JIS Standard and Usage
JIS flange follows the Japanese Industrial Standards and is widely used in Asia.
You see the JIS standard in many Japanese factories, shipyards, and water treatment plants. JIS flange offers a compact design, which helps you save space in tight installations. You often choose this flange for projects in Japan or regions that follow Japanese engineering practices.
- JIS flange sizes range from 5K to 40K pressure classes.
- You find these flanges in marine, chemical, and industrial piping systems.
- JIS flanges use metric dimensions, making it easy to match with Japanese equipment.
Tip: When you work on international projects, check if the piping system requires JIS flange to ensure proper fit and compliance.
ANSI Flange in the Americas
ANSI flange is the standard in North and South America for industrial piping.
You rely on ANSI flange for oil and gas, chemical, and power generation projects. ANSI flange follows ASME and ANSI B16.5 standards, which set strict rules for dimensions and pressure ratings. You often select this flange for high-pressure and large-diameter applications.
- ANSI flange pressure classes range from 150 to 2500.
- You see these flanges in refineries, pipelines, and energy plants.
- ANSI flange uses inch-based sizing, which matches American equipment.
Note: You should always confirm the pressure class and face type when selecting ANSI flange for your project.
DIN Flange in Europe
DIN flange is the preferred choice in Europe and regions that use metric standards.
You find DIN flange in water treatment, chemical processing, and manufacturing plants. DIN flange follows EN 1092-1 and DIN standards, which use PN ratings for pressure. You select this flange for projects that require precise metric dimensions and European compliance.
- DIN flange pressure ratings include PN6, PN10, PN16, PN40, and PN100.
- You see DIN flange in European industrial and municipal systems.
- DIN flange offers a wide range of face types and bolt patterns.
Tip: When you work in Europe, choose DIN flange to meet local regulations and ensure compatibility.
Sunhy’s Global Flange Solutions
You can rely on Sunhy to supply all three types of flanges for your global projects. Sunhy manufactures flanges that meet JIS, ANSI, and DIN standards, as well as large diameter and high-pressure requirements. If you need a custom flange, you can submit your drawings for a tailored solution.
| Flange Standard | Specifications |
|---|---|
| JIS | JIS B22205K, 10K, 20K, 30K, 40K |
| ANSI | ASME / ANSI B16.5 Class 150–2500 (RF, FF, RTJ) |
| DIN | EN 1092-1 / DIN PN6, PN10, PN16, PN40, PN100 |
| Large Diameter | ASME B16.47 Series A/Large diameter flanges >24″ |
| High Pressure | API 6A 6B & 6BX for wellhead & subsea |
| Custom Flanges | Custom / Non-Standard Need customization? Submit drawings |
Sunhy helps you meet project requirements anywhere in the world with reliable flanges and expert support.
Dimensional Comparison of Flanges
Bolt Patterns and Sizes
Bolt patterns and sizes differ significantly among JIS, ANSI, and DIN flanges, which affects installation and compatibility.
You notice that ANSI flanges use standardized bolt hole patterns based on class and nominal size. DIN flanges feature metric-based bolt circles and hole arrangements, which suit European systems. JIS flanges have unique bolt hole patterns and nominal sizes designed for the Asian market. These differences mean you must check bolt alignment before connecting flanges from different standards.
| Feature | ANSI Flanges | DIN Flanges | JIS Flanges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | Varies based on class | Different dimensions and bolt patterns | Different nominal sizes and bolt hole patterns |
| Pressure Ratings | Class system (e.g., Class 150) | Nominal pressure (PN) in bars | Nominal pressure (PN) in kg/cm² |
| Market Focus | American market | European market | Asian market |
Tip: Always match bolt patterns to avoid leaks or misalignment in your piping system.
Face Types and Thickness
Face types and thicknesses vary by standard, influencing sealing performance and mechanical strength.
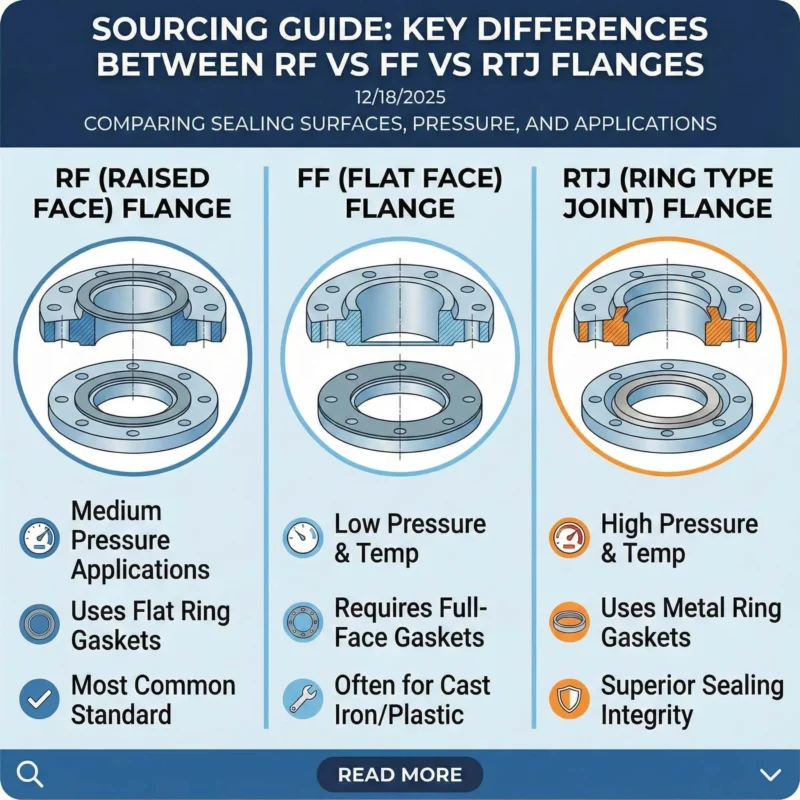
You find that ANSI flanges often have thicker profiles and offer raised face (RF), flat face (FF), and ring-type joint (RTJ) options. DIN flanges provide a range of face types, including flat face and raised face, with thicknesses set by pressure rating. JIS flanges usually feature compact faces and moderate thickness, which help save space in installations. When you select a flange, consider the face type and thickness to ensure a proper seal and structural integrity.
- ANSI: Raised face, flat face, ring-type joint; thicker profiles.
- DIN: Flat face, raised face; thickness varies by PN rating.
- JIS: Compact face; moderate thickness for space-saving design.
Note: Proper face selection improves gasket seating and prevents leaks.
Size Ranges
Size ranges for flanges depend on the standard, which impacts your project’s design flexibility.
You see that JIS flanges cover pressure capacities from 5K to 63K, suitable for mechanical and industrial applications. ANSI flanges range from Class 150 to Class 2500, supporting a wide spectrum of pressure and temperature needs. DIN flanges span PN6 to PN400, with nominal pressure ratings that indicate maximum allowable pressure at 20°C for water systems.
| Standard | Size Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| JIS | 5K to 63K | Pressure capacity in kg/cm², with specific ratings for mechanical applications. |
| ANSI | Class 150 to Class 2500 | Pressure-temperature ratings and structural integrity classifications. |
| DIN | PN6 to PN400 | Nominal pressure system indicating maximum allowable pressure in bar at 20°C for water applications. |
You should always review flange dimensions and pressure ratings to ensure compatibility with your system requirements.
Choosing the right size range helps you achieve safe and efficient operation in your piping network.
Pressure Ratings and Classes in JIS, ANSI, DIN
JIS Pressure Classes
JIS pressure classes use a “K” rating system, which stands for kilograms per square centimeter.
You see these ratings as 2K, 5K, 10K, 16K, 20K, 30K, 40K, and 63K. JIS flange ratings help you select the right product for Japanese and Asian piping systems. These ratings show the maximum pressure the flange can handle. You should always check the pressure class before installation to ensure safety.
| Standard | Pressure Class Designations |
|---|---|
| JIS | 2K, 5K, 10K, 16K, 20K, 30K, 40K, 63K |
Tip: JIS pressure classes are ideal for compact systems and moderate pressure environments.
ANSI Pressure Classes
ANSI pressure classes use a “LB” or “Class” system, which is based on pounds per square inch (psi).
You find ansi flange ratings as 150LB, 300LB, 600LB, 900LB, 1500LB, and 2500LB. These classes are designed for high-pressure applications. You rely on ANSI standards for oil and gas, chemical, and power generation projects in the Americas.
- ANSI flanges are specifically designed for high-pressure applications, with pressure classes ranging from Class 150 to Class 2500, ensuring safety and reliability in systems.
- The choice of flange standard is crucial in high-pressure environments, as it affects compatibility and performance.
| Standard | Pressure Class Designations |
|---|---|
| ANSI | 150LB, 300LB, 600LB, 900LB, 1500LB, 2500LB |
Note: Always confirm the pressure class to match your system’s requirements.
DIN Pressure Classes
DIN pressure classes use a “PN” system, which stands for “Pressure Nominal” and is measured in bars.
You see DIN ratings as PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, PN63, PN100, and PN160. These ratings are common in European industries. You select DIN flanges for water treatment, power generation, and industrial applications.
| Pressure Class | Applications |
|---|---|
| DIN PN6 | Oil and gas, Petrochemicals |
| DIN PN10 | Water Treatment and Desalination |
| DIN PN16 | Power Generation |
| DIN PN25 | Mining Industry |
| DIN PN40 | Various industrial applications |
| Standard | Pressure Class Designations |
|---|---|
| DIN | PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, PN63, PN100, PN160 |
You should choose DIN pressure classes for systems that require metric sizing and European compliance.
Material and Quality Standards
Common Materials Used
You find stainless steel, carbon steel, and nickel alloys as the most common materials for flanges in JIS, ANSI, and DIN standards.
| Material Type | Corrosion Resistance Description |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Outstanding corrosion resistance, especially grades 304 and 316, ideal for harsh environments. |
| Nickel Alloys | Extraordinary resistance to extreme heat and severe corrosion, suitable for specialized applications. |
Stainless steel gives you excellent protection against rust and chemicals. Nickel alloys work best in extreme conditions. You choose the material based on your project’s environment and safety needs.
Sunhy’s Stainless Steel Advantages
You benefit from Sunhy’s dual-certified 316/316L stainless steel flanges because they offer superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength compared to standard materials.
Sunhy’s flanges meet pressure-temperature ratings for class 150 and class 300. The higher strength of SS 316 ensures durability and reliability in tough environments. You can trust these flanges for long-term performance.
Note: Sunhy uses advanced forging and testing protocols to guarantee quality.
- Sunhy employs electric and vacuum furnaces to smelt stainless steel.
- You get flanges with proper heat treatment cycles and strict temperature controls.
- Each batch undergoes tension tests to verify mechanical properties.
- Ultrasonic inspections check hollow forgings for hidden flaws.
- Sunhy follows international standards like ASTM to ensure chemical composition and mechanical properties meet requirements.
You receive flanges that pass rigorous inspections and meet global standards for safety and reliability.
Regional and Industry Applications
Geographic Distribution
You find JIS, ANSI, and DIN flange standards used in different regions, which shapes global supply chains and project planning.
The choice of flange standard depends on local engineering practices and regulations. You see JIS flanges most often in Japan and Southeast Asia. ANSI standards dominate in the United States, but you also encounter them in the Middle East and parts of Asia. DIN and EN standards appear frequently in Europe, and you notice their presence growing in the Middle East and Asia as well.
Here is a summary of where each standard is most common:
| Flange Standard | Common Regions | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| JIS B2220 | Japan, Southeast Asia | Metric dimensions, used in shipbuilding and waterworks |
| ANSI/ASME | US, Middle East, Asia | Imperial units, various pressure ratings |
| DIN/EN 1092-1 | Europe, Middle East, Asia | Metric units, gradually replaced by EN standards |
Tip: You should always check the regional standard before ordering flanges for international projects. This helps you avoid delays and ensures compatibility.
Industry-Specific Uses
You see each flange standard preferred in specific industries because of local requirements and technical advantages.
- JIS flanges support shipbuilding, waterworks, and chemical plants in Asia. You often choose these for compact installations and metric-based systems.
- ANSI flanges serve oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing in the Americas. You rely on these for high-pressure and large-diameter pipelines.
- DIN flanges fit European water treatment, manufacturing, and energy sectors. You select these for projects that require metric sizing and strict compliance.
Note: You improve project efficiency when you match the flange standard to the industry and region. This reduces the risk of mismatched parts and costly modifications.
You can work with suppliers like Sunhy to source the right flange for your application, whether you need JIS for a shipyard in Japan or DIN for a water plant in Germany.
Compatibility and Conversion Issues
Interchangeability Challenges
You cannot directly interchange JIS, ANSI, and DIN flanges because their dimensions, bolt patterns, and pressure ratings differ.
When you try to connect flanges from different standards, you often face these problems:
- Bolt Hole Misalignment: The bolt circle diameter and the number of bolt holes usually do not match.
- Different Pressure Ratings: Each standard uses its own system, so pressure classes may not align.
- Varying Face Types: Raised face, flat face, and ring-type joint faces may not seal properly if mixed.
- Metric vs. Imperial Sizes: JIS and DIN use metric units, while ANSI uses inches.
| Issue | JIS | ANSI | DIN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bolt Pattern | Unique | Standardized | Metric-based |
| Pressure Rating System | “K” (kg/cm²) | “Class” (psi) | “PN” (bar) |
| Sizing System | Metric | Imperial | Metric |
Tip: Always check the flange drawing and standard before attempting to connect different types. This helps you avoid leaks and costly rework.
Adapting Between Standards
You can adapt between JIS, ANSI, and DIN flanges by using special adapters, custom flanges, or conversion gaskets.
If your project requires joining different standards, you have several options:
- Use Flange Adapters: These components bridge the gap between two standards. You select the adapter based on the flange types you need to connect.
- Order Custom Flanges: Manufacturers like Sunhy can produce custom flanges that match both standards’ bolt patterns and pressure ratings.
- Install Conversion Gaskets: Special gaskets help seal between mismatched faces, but you must ensure pressure compatibility.
Note: You should always consult with your engineering team or supplier before mixing standards. This ensures safety and compliance with regulations.
By understanding these challenges and solutions, you make better decisions and keep your piping systems safe and reliable.
Choosing the Right Flange
Project Requirements
You should always match the flange standard to your project’s pressure, temperature, and compatibility needs.
When you start choosing the right flange, consider these factors:
- Pressure rating required for your system
- Temperature range of the application
- Material compatibility with the fluid or gas
- Regional standards and regulations
- Space constraints and installation environment
You can improve reliability by selecting flanges that meet your system’s exact specifications. If your project has unique requirements, you can consult Sunhy’s engineering team for custom solutions.
Tip: Review your project drawings and technical data before making a final selection.
Compliance and Certification
You must verify that your flanges meet the necessary compliance and certification standards for your industry.
Here is a comparison of compliance focus for each standard:
| Standard | Description | Compliance Focus |
|---|---|---|
| ANSI | Governs dimensions and pressure ratings for flanges in piping systems. | Ensures a common approach across industries. |
| DIN | German standards for flanges, widely used in Europe. | Focuses on compatibility and reliability in various applications. |
| JIS | Japanese standards for flanges, ensuring compatibility in Japan. | Emphasizes reliability and application-specific requirements. |
You should check for certifications such as ASTM, EN, or JIS marks. This helps you meet local and international regulations and ensures safety.
Note: Sunhy provides flanges with full traceability and certification to support compliance in regulated industries.
Cost and Availability
You need to balance cost and availability when selecting flanges for your project.
The global pipe flange market continues to grow, driven by infrastructure investment and energy sector development. You see strong demand in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East. Supply chain disruptions and fluctuating raw material prices can affect availability and cost. You should plan ahead and work with reliable suppliers to avoid delays.
You can request quotes from Sunhy for standard and custom flanges. This helps you manage your budget and timeline.
Tip: Early planning and supplier consultation help you secure the right products at the best price.
You ensure long-term reliability and safety when you choose the correct flange standard for your project. Adhering to JIS, ANSI, or DIN standards helps you avoid safety hazards and supports easier maintenance. Regional norms and project requirements guide your decision, as shown below:
| Flange Standard | Primary Regions of Use |
|---|---|
| ASME/ANSI | North America, Asia, S. America |
| EN/DIN | Europe, Commonwealth nations |
| JIS | Japan, S. Korea, SE Asia |
Sunhy’s commitment to quality and customer support gives you confidence in every flange selection. For complex projects, you benefit from expert advice and thorough resources to make the right choice.
FAQ
What is the main difference between JIS, ANSI, and DIN flanges?
JIS uses metric sizing and compact design. ANSI uses imperial units and thicker profiles. DIN follows European metric standards.
| Standard | Sizing System | Region |
|---|---|---|
| JIS | Metric | Asia |
| ANSI | Imperial | Americas |
| DIN | Metric | Europe |
Can you mix JIS, ANSI, and DIN flanges in one piping system?
You cannot mix these flanges directly because bolt patterns, pressure ratings, and face types differ.
Use adapters or custom flanges if you need to connect different standards.
How do you choose the right flange for your project?
You match the flange standard to your project’s pressure, temperature, and regional requirements.
- Check pressure rating
- Confirm material compatibility
- Review local regulations
- Consult with Sunhy for custom solutions
What materials does Sunhy use for stainless steel flanges?
You get flanges made from dual-certified 316/316L stainless steel forgings.
This material offers high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength for demanding environments.
Where can you use JIS, ANSI, and DIN flanges?
You use JIS in Asia, ANSI in the Americas, and DIN in Europe.
| Flange Type | Common Region | Typical Industry |
|---|---|---|
| JIS | Asia | Shipbuilding, Water |
| ANSI | Americas | Oil & Gas, Power |
| DIN | Europe | Chemical, Water |