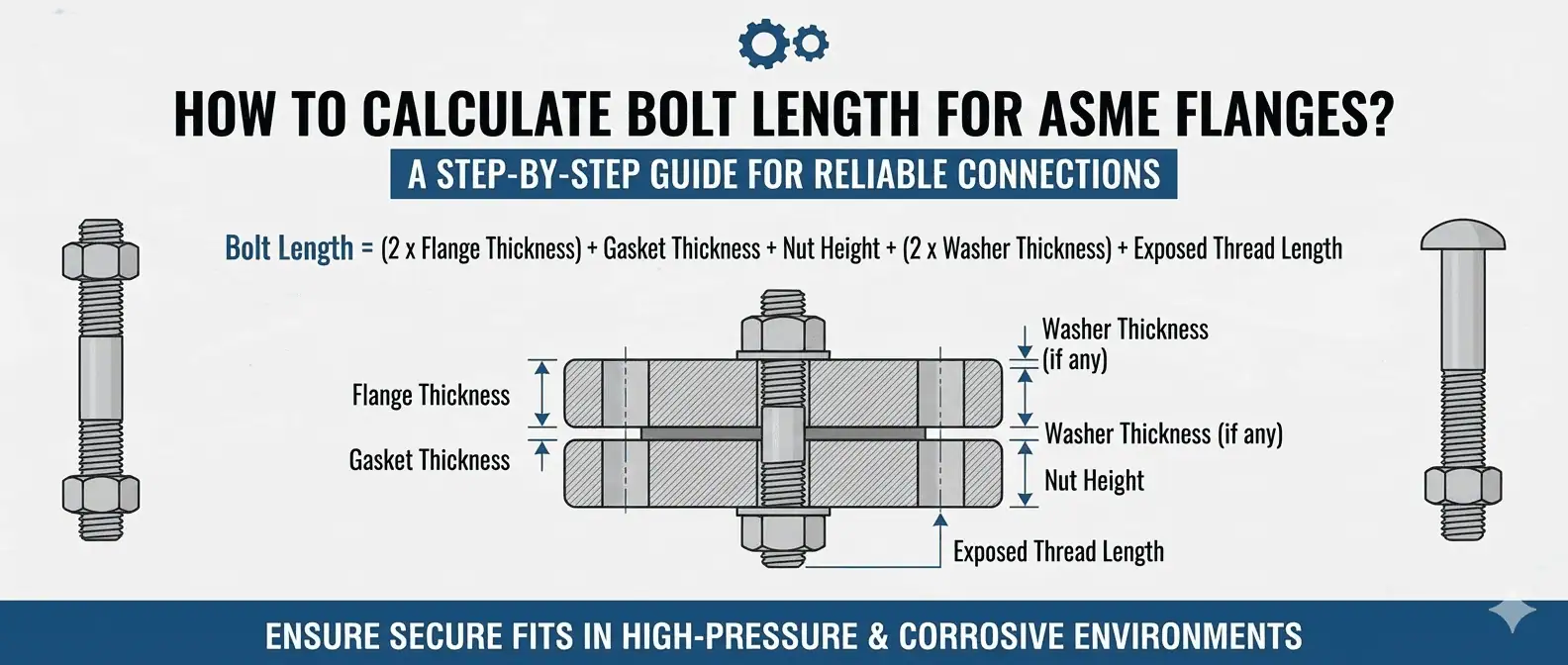
Accurate bolt length calculation is essential for reliable connections in industrial piping systems.
You need to ensure a secure fit when working with ASME flanges, especially in high-pressure or corrosive environments. Sunhy Stainless Steel Flanges offer precision machining and consistent thickness, which helps you select the correct bolt length every time. Following the standard for flange installation reduces the risk of leaks and equipment failure.
- Choose the right bolt length to match your flange and gasket.
- Trust quality products for optimal performance and safety.
- Rely on proven standards to guide your decisions.
ASME Flanges Bolt Length Formula
Stud Bolt Theoretical Length Explained
You calculate stud bolt theoretical length for ASME flanges using a standard formula from ASME B16.5. This formula helps you determine the correct length for a secure and leak-free connection. The formula considers all the essential components that make up the total length needed for proper installation.
Tip: Always use the correct formula to avoid underestimating or overestimating the required bolt length.
Here is the standard formula for stud bolt theoretical length:
| Component | Description | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| L | Theoretical length of stud bolt | L = 2 (s + n + h + rf) + g |
| s | Free threads (1/3 times bolt diameter) | s = 1/3 * bolt diameter |
| n | Nut height (equals nominal bolt diameter) | n = nominal bolt diameter |
| h | Flange thickness | h = flange thickness |
| rf | Height of raised face | rf = height of raised face |
| g | Gasket thickness | g = gasket thickness |
You need to add up the thickness of the flange, the gasket, the nut height, the raised face, and the free threads. Multiply the sum of these by two (for both sides), then add the gasket thickness. This ensures the bolt will fit through both flanges, secure the nuts, and allow for proper thread engagement.
Note: International standards may require you to adjust the length if you use different flange types or thicker gaskets. Always check the specific requirements for your application.
Required Measurements and Tools
You must measure each component accurately to calculate the correct bolt length. Use the right tools and follow best practices to ensure precision.
Here are the key variables and their units:
| Variable | Unit |
|---|---|
| Flange Thickness | mm |
| Gasket Thickness | mm |
| Nut Thickness | mm |
| Protrusion Allowance | mm |
You will need these tools:
- Caliper or micrometer for measuring thickness
- Steel ruler or tape measure for overall length
- Thread gauge for bolt diameter
Sunhy Stainless Steel Flanges are manufactured with tight tolerances, which helps you achieve accurate bolt length selection. The table below shows typical tolerances for Sunhy flanges:
| Dimension | Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Outside Diameter (O.D. ≤ 24″) | +0.125″, -0.0625″ |
| Outside Diameter (O.D. > 24″) | +0.125″, -0.125″ |
| Inside Diameter (I.D. ≤ 10″) | +0.03125″, -0″ |
| Inside Diameter (I.D. > 10″) | +0.0625″, -0″ |
| Contact Face Diameter | +0.0156″, -0.0156″ |
| Bolt Hole Diameter | +0.03125″, -0.03125″ |
| Bolt Circle Diameter | +0.0625″, -0.0625″ |
| Bolt Hole Spacing | +0.03125″, -0.03125″ |
| Thickness (Nominal size ≤ 18″) | +0.125″, -0″ |
| Thickness (Nominal size > 18″) | +0.1875″, -0″ |
You can trust these tolerances to help you select the right bolt for your flange. This reduces the risk of leaks and ensures a reliable seal in your piping system.
Bolt Length Factors
Flange and Gasket Thickness
Flange and gasket thickness directly determine the grip length needed for your bolt.
You must measure both the flange and gasket thickness to calculate the correct bolt length. The grip length is the distance from the middle of one nut to the middle of the other nut. This measurement ensures the bolt stretches across both flanges and the gasket, creating a tight seal.
- Thicker flanges require longer bolts to maintain proper engagement.
- Gasket thickness adds to the total length needed for a secure fit.
- Shorter bolts may not provide enough stretch, which can lead to unreliable connections.
- A length-to-diameter ratio of 5:1 is recommended for optimal performance.
- Longer bolts maintain load better under deflection, reducing the risk of leaks.
Sunhy flanges feature precision machining, so you can trust the flange thickness to remain consistent across all products. This consistency helps you select the right bolt length every time.
Nut Height and Washer Allowance
Nut height and washer allowance are essential parts of the total assembly height in bolt length calculations.
You must include the nut height, which usually matches the nominal bolt diameter, as specified by ASME B16.5. Washers, if used, add extra thickness and must be measured as well.
- Nut height ensures full thread engagement for strength and safety.
- ASME B16.5 provides clear guidelines for nut dimensions.
- Washers protect the flange surface and distribute load evenly.
- Always add washer thickness to your calculation if washers are used.
Tip: Double-check nut and washer sizes before finalizing your bolt length to avoid assembly issues.
Additional Allowances
Additional allowances account for protrusion and environmental factors that affect bolt length selection.
You should allow for a small protrusion of the bolt beyond the nut, which ensures full thread engagement and makes future maintenance easier. Environmental conditions, such as high temperature or pressure, can also influence your choice.
- Allow for bolt protrusion, typically 1-2 threads beyond the nut.
- Consider the effects of temperature and pressure on the assembly.
- At elevated temperatures, bolts and flanges may relax, reducing bolt load and risking leaks.
- Always check the flange size, material, and bolt diameter to ensure compatibility.
The precision machining of Sunhy flanges supports consistent bolt length requirements. You can see how this precision impacts your assembly in the table below:
| Evidence Description | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Correct flange dimensions and pressure class | Precision ensures safety and efficiency, supporting reliable bolt length selection. |
| Standardized ANSI flange dimensions | Consistent dimensions help you achieve uniform bolt lengths. |
| Proper bolt hole spacing and number | Stability and load distribution support consistent bolt length. |
| Accurate NPS, O.D., I.D., bolt circle, thickness, and face type | These measurements are critical for a secure connection and correct bolt length. |
By understanding each factor—flange thickness, gasket thickness, nut height, washer allowance, and additional allowances—you can confidently select the right bolt length for your ASME flange assembly.
Calculation Example for ASME Flanges
Sample Values and Step-by-Step Calculation
You can calculate the correct bolt length for your flange assembly by following a clear process.
Let’s use a practical example with Sunhy Stainless Steel Flanges:
Given:
- Flange thickness: 24 mm (each flange)
- Gasket thickness: 3 mm
- Nut height: 20 mm (per nut)
- Washer thickness: 2 mm (per washer, 2 washers)
- Required protrusion: 6 mm
Step-by-step calculation:
- Add up the thicknesses:
- Two flanges: 24 mm × 2 = 48 mm
- Gasket: 3 mm
- Two nuts: 20 mm × 2 = 40 mm
- Two washers: 2 mm × 2 = 4 mm
- Protrusion: 6 mm
- Total bolt length:
- 48 mm (flanges)
- 3 mm (gasket)
- 40 mm (nuts)
- 4 mm (washers)
- 6 mm (protrusion)
- Total: 101 mm
You should round up to the next commercially available bolt length.
If 105 mm is available, select that size for your assembly.
Tip: Always double-check each measurement before finalizing your selection.
Using ASME B16.5 Tables and Rules of Thumb
You can use ASME B16.5 tables to find recommended bolt lengths for standard flange sizes.
These tables list the correct bolt length for each flange class and size, making your selection easier.
You can also use the 5:1 rule of thumb for stud length.
This rule states that the stud bolt should be five times the diameter of the bolt. For example, if your bolt diameter is 20 mm, the recommended length is 100 mm. Longer bolts maintain joint integrity better because they require more deflection to lose load. Shorter bolts can lose load quickly and may not hold the flange securely.
Summary Table:
| Flange Size | Bolt Diameter | 5:1 Rule Length | ASME Table Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2″ | 16 mm | 80 mm | 80 mm |
| 3″ | 20 mm | 100 mm | 100 mm |
| 4″ | 22 mm | 110 mm | 110 mm |
You should always compare your calculated value with the ASME B16.5 table and select the greater length if in doubt.
This ensures a safe and reliable flange connection.
Measuring and Avoiding Mistakes
Measuring Stud Bolts and Hex Bolts
You must measure bolts accurately to ensure a safe and reliable flange connection.
Start by using the right tools for each dimension. Calipers help you measure the outer diameter and thickness. Tape measures work well for larger flanges. Specialty flange measuring tools give you precise readings for inside diameter, outside diameter, and bolt hole diameter.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Calipers | Measure outer diameter, inner diameter, flange thickness, and bolt hole diameter. |
| Tape measures | Measure outside diameter and bolt hole diameter on larger flanges. |
| Flange measuring tools | Provide accurate readings of ID, OD, and bolt hole for flange assemblies. |
Follow these steps to measure stud bolts and hex bolts:
- Measure the head height to match ASME standards.
- Check the width across flats for proper fit.
- Confirm the body diameter for correct tolerance.
- Measure the total bolt length from end to end.
- Verify thread lengths for effective fastening.
| Dimension Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Head Height | Must comply with ASME standards for proper height measurement. |
| Width Across Flats | Required for proper fit and compatibility. |
| Body Diameter | Ensures the bolt fits within specified tolerances. |
| Bolt Length Tolerances | Adhere to ASME standards for installation and performance. |
| Thread Lengths | Necessary for effective fastening. |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Follow ASME guidelines for quality and safety. |
Common Errors in Bolt Length Selection
You can avoid mistakes by following ASME standards and Sunhy’s quality assurance processes.
Many errors happen when you skip steps or use incorrect measurements. You should always reference the correct standard for threaded fasteners and bolt tolerances. Citing ASME B18.2.1 for dimensions helps you stay compliant and reduces errors. Incorporate these standards into your engineering drawings to maintain consistent quality.
Common mistakes include:
- Using the wrong bolt length for the flange thickness.
- Ignoring washer or nut height in calculations.
- Overlooking the need for bolt protrusion.
- Failing to check dimensional tolerances.
- Not verifying thread engagement.
You can reduce mistakes by ensuring proper training for all personnel.
Training levels range from on-boarding for new staff to specialist and inspector training for advanced roles.
| Training Level | Description |
|---|---|
| On-Boarding Training | Minimum for staff working on bolted flange joint applications. |
| Bolting Trainee | Recommended for assembly personnel. |
| Bolting Specialist | Required for project managers in specific environments. |
| Inspector Training | Essential for inspection contractors. |
Tip: Always double-check your measurements and refer to ASME tables before finalizing bolt length selection.
You ensure accuracy and compliance by following these key steps for bolt length calculation:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Measure flange, gasket, nut, and washer thickness. |
| 2 | Add allowances for bolt protrusion. |
| 3 | Check ASME B16.5 tables for standard sizes. |
| 4 | Confirm bolt extends fully through the nut as required by ASME codes. |
You improve safety and performance by using a checklist and consulting ASME standards.
- Proper bolt length supports effective sealing and flange stiffness.
- Correct installation helps prevent leaks and warping.
Accurate bolt preload keeps your flange assembly reliable over time. Sunhy Stainless Steel Flanges deliver consistent quality, making your installation safe and durable.
FAQ
How do you choose the correct bolt length for asme flanges?
You add up the thickness of both flanges, the gasket, nuts, washers, and required protrusion.
- Measure each part.
- Use the ASME B16.5 formula.
- Round up to the next available bolt length.
What tools help you measure flange and bolt dimensions?
You use calipers, tape measures, and thread gauges for accurate measurements.
- Calipers: flange thickness, bolt diameter.
- Tape measure: overall length.
- Thread gauge: thread size.
Why is bolt protrusion important in flange assembly?
You need bolt protrusion for full thread engagement and easier maintenance.
- Prevents nuts from loosening.
- Allows for future adjustments.
- Meets ASME standards.
Can you use washers with every flange connection?
You can use washers if required by your application or standards.
- Washers protect flange surfaces.
- Distribute load evenly.
- Add to total bolt length.
What happens if you use the wrong bolt length?
You risk leaks, joint failure, and unsafe connections.
- Too short: poor engagement, leaks.
- Too long: assembly issues, wasted material.
- Always check measurements and standards.