The main difference between UNC and UNF fittings lies in their thread pitch—UNC has a coarser pitch, while UNF uses a finer one. Choosing the correct fitting type is critical for ensuring safety and optimal performance in demanding environments. For example, unc vs unf fittings affect how well your connections handle stress and vibration:
| Thread Type | Strength | Application Environment |
|---|---|---|
| UNC | High strength due to coarse pitch | Heavy-duty, high-stress uses |
| UNF | Superior grip and stability | Vibration-prone, precision systems |
Sunhy’s stainless steel fittings deliver reliable connections for both thread types, supporting your operations in any application. If your project uses threaded process connections (e.g., tapered pipe threads), compare against NPT/BSPT selection guidance before you finalize procurement.
UNC vs UNF Fittings Overview
What Are UNC Fittings?
UNC fittings use a coarse thread pitch for general-purpose fastening.
You will find that UNC stands for Unified National Coarse. This thread type is part of the unified thread standard, which sets the rules for thread dimensions and profiles. UNC threads have fewer threads per inch, making them easier to manufacture and more resistant to dirt and damage. The coarse pitch allows for quick assembly and disassembly, which is useful in many industrial settings.
- Common materials for UNC fittings include:
- Steel for strength and versatility
- Stainless steel for corrosion resistance
- Aluminum for lightweight needs
- Brass for machinability and corrosion resistance
You can see the typical thread dimensions for UNC fittings in the table below:
| Nominal Diameter | Major Diameter (in) | TPI | Pitch (in) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #12 | 0.216 | 32 | 0.031 |
| 1⁄4″ | 0.25 | 32 | 0.031 |
| 5⁄16″ | 0.3125 | 32 | 0.031 |
| 3⁄8″ | 0.375 | 32 | 0.031 |
| 7⁄16″ | 0.4375 | 28 | 0.036 |
| 1⁄2″ | 0.5 | 28 | 0.036 |
| 9⁄16″ | 0.5625 | 24 | 0.042 |
| 5⁄8″ | 0.625 | 24 | 0.042 |
| 3⁄4″ | 0.75 | 20 | 0.050 |
| 7⁄8″ | 0.875 | 20 | 0.050 |
| 1″ | 1 | 20 | 0.050 |
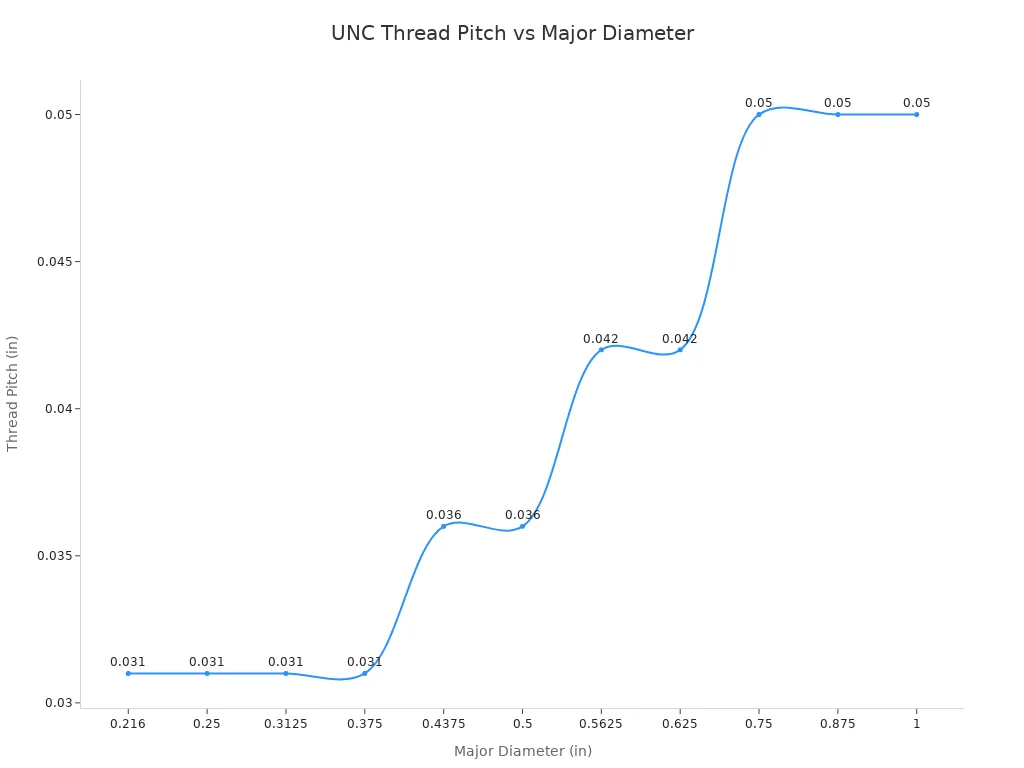
UNC threads follow the unified thread standard, which ensures compatibility and reliability across industries. For critical applications, verify pitch/diameter using a calibrated gauge set and the applicable thread standard before installation.
What Are UNF Fittings?
UNF fittings use a fine thread pitch for precision and vibration resistance.
UNF stands for Unified National Fine. This thread type also belongs to the unified thread standard. UNF threads have more threads per inch, which gives you a tighter fit and greater holding power. You will often use UNF fittings in applications where you need high strength and resistance to vibration.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Thread Pitch | The pitch is the distance between thread peaks, typically expressed as threads per inch (TPI). |
| Thread Profile | UTS threads have a symmetric V-shaped profile with a 60° angle between the flanks. |
| Dimensional Standards | Each thread is defined by its major diameter and pitch, with specific values differing from ISO. |
The unified thread standard for UNF fittings helps you achieve consistent performance in demanding environments. If vibration is present, confirm engagement length and consider anti-galling measures for stainless-on-stainless pairs.
Historical Note:
The unified thread standard, including both UNC and UNF, became widely adopted after the American Standards Association reorganized into ANSI in 1958. This move helped unify thread types across North America and improved compatibility in manufacturing.
| Year | Event Description |
|---|---|
| 1957 | Launch of Sputnik triggers a focus on technological competitiveness in the U.S. |
| 1958 | American Standards Association reorganized into ANSI, leading to the establishment of UNC and UNF standards. |
| Post-WWII | Adoption of metric standards and establishment of UNTS for global uniformity in manufacturing. |
Difference Between UNC and UNF
Thread Pitch and Profile
UNC threads have a coarser thread pitch, while UNF threads use a finer thread pitch.
You will notice the difference between unc and unf in the number of threads per inch. UNC threads have fewer threads per inch, which means the threads are spaced farther apart. UNF threads have more threads per inch, so the threads are closer together. This difference in thread pitch affects how the threads engage and how much load-bearing capacity each type provides.
| Thread Type | Thread Pitch Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| UNC | Coarser pitch, fewer threads/inch | Universal, high load-bearing capacity |
| UNF | Finer pitch, more threads/inch | Precision, sealing, better load-bearing capacity |
UNC threads tolerate imperfections and work well in softer materials. UNF threads provide better engagement and strength in high-precision applications. The thread profile for both types follows the unified thread standard, but the spacing and engagement differ. You should always match the correct thread pitch to your application to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Application and Strength
UNC threads excel in heavy-duty applications, while UNF threads are best for precision and vibration resistance.
You will find unc vs unf fittings in different environments based on their load-bearing capacity and performance needs. UNC threads are ideal for machinery, construction, and equipment that require quick assembly and disassembly. They handle high torque and impact forces, making them suitable for frequent use and heavy loads. UNF threads, on the other hand, are perfect for applications that demand tight seals and resistance to vibration, such as instrumentation, automotive, and aerospace systems.
- UNC threads:
- Maintain strength in softer materials.
- Resist wear during frequent assembly and disassembly.
- Allow faster installation due to fewer turns.
- Provide reliable load-bearing capacity in universal applications.
- UNF threads:
- Offer superior holding power in high-precision environments.
- Deliver better sealing and resistance to loosening from vibration.
- Require more turns for assembly, which increases engagement.
- Excel in applications where tight tolerances and high load-bearing capacity are critical.
Sunhy’s stainless steel fittings support both unc and unf threads, ensuring you get the right performance and load-bearing capacity for your specific applications. You can rely on Sunhy’s advanced manufacturing and quality control to minimize risks like cross-threading, over-tightening, and leakage. For precision systems, review instrumentation fittings & valves options to keep thread class, finish, and material pairing consistent.
Identification and Interchangeability
You can identify UNC and UNF threads by measuring diameter and counting threads per inch; they are not interchangeable.
To distinguish between unc and unf threads, follow these steps:
- Measure the outer diameter of the fitting using calipers.
- Count the number of threads in a one-inch section.
- Use a thread gauge to match the thread type.
- Refer to a screw thread chart for quick comparison.
These methods are reliable when you use clean threads and quality tools. The difference between unc and unf becomes clear when you compare the thread pitch and count. UNC threads will have fewer threads per inch than UNF threads of the same diameter.
Important engineering note: UNC/UNF are straight (non-tapered) machine screw threads. In fluid systems, “tightening the threads” is not a sealing method by itself—sealing is typically achieved by an O-ring, gasket, bonded seal, or a separate metal-to-metal seat. If your connection is intended to seal on the threads (tapered pipe thread), use the correct pipe-thread standard and fitting style (e.g., NPT/BSPT). See NPT/BSPT threaded tees & elbows and compare against NPT identification guidance (OD + TPI) before substitution.
| Fitting Type | Interchangeable | Risks of Incorrect Substitution |
|---|---|---|
| UNC & UNF | No | Leaks, system failures, reduced load-bearing capacity |
Never substitute unc vs unf fittings in critical systems. Incorrect substitution can lead to leaks, system failures, and loss of load-bearing capacity. Sunhy’s stainless steel fittings are engineered for precise compatibility, so you can trust every connection in your system. For thread-type cross-checks and related standards, you can also browse Sunhy technical guides.
Tip: Always verify the thread type before installation to ensure safety and optimal performance.
How to Identify UNF and UNC Threads
You can accurately identify unc threads and unf threads by using specialized measurement tools and following a systematic approach.
Correct identification ensures you select the right fitting for your application, especially in precision machinery where thread compatibility is critical.
Step-by-Step Identification Process
- Clean the Threads
Always start by cleaning the threads. Remove dust, oil, or debris to prevent inaccurate measurements. - Measure Thread Pitch
Use a thread pitch gauge. Align the gauge with the threads to determine if you have unc threads or unf threads. Unc threads have fewer threads per inch, while unf threads have more. - Check Thread Diameter
Use a thread caliper to measure the major and minor diameters. This helps confirm if the fitting matches unc or unf standards. - Verify with Go/No-Go Gauges
For internal threads, use go/no-go thread plug gauges. For external threads, use go/no-go thread ring gauges. The correct gauge should fit smoothly, while the no-go gauge should not.
Tip: Always use calibrated and unworn tools for the most reliable results.
Common Identification Errors and How to Avoid Them
- Incorrect Gauge Selection:
Choose the correct gauge for unc or unf threads. Using the wrong one leads to misidentification. - Not Accounting for Wear:
Inspect threads for wear or damage, especially in older fittings. Worn threads can give false readings. - Measuring Contaminated Threads:
Clean all threads before measuring. Contaminants can affect accuracy. - Ignoring Temperature Variations:
Measure threads in a stable temperature environment. Temperature changes can alter thread dimensions. - Using Worn or Inaccurate Tools:
Regularly check your tools for wear and calibration to maintain measurement accuracy.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Thread Pitch Gauge | Measures pitch for unc threads and unf threads |
| Thread Caliper | Measures major/minor diameters of threads |
| Go/No-Go Plug Gauge | Checks internal unc and unf threads |
| Go/No-Go Ring Gauge | Checks external unc and unf threads |
By following these steps, you ensure every unc and unf fitting in your system matches the required specifications.
This process helps you avoid leaks, system failures, and costly downtime, especially in demanding environments where unc threads and unf threads play a vital role.
Choosing the Right Fitting
Factors to Consider
You must match the fitting to your application for safe and reliable performance.
When you compare unc vs unf fittings, you need to look at several important factors. Each type of thread works best in specific situations. Here is how to choose unc and unf threads for your needs:
- Application Type: Use unc threads for general applications. Choose unf threads for high-precision and high-strength applications.
- Strength Needs: Unf threads give you higher strength and better vibration resistance. Unc threads work well when you need quick assembly and disassembly.
- Accuracy Requirements: Unf threads provide better matching and stability in high-accuracy applications.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider corrosion, vibration, and pressure. Unf threads excel in controlled environments and where tight tolerances matter. Unc threads handle rougher conditions and frequent maintenance.
- Cost and Maintenance: Unc fittings cost less and are easier to assemble. Unf fittings cost more but offer better sealing and stability.
Tip: Always follow manufacturer instructions and inspect threads regularly to prevent cross-threading and over-tightening.
Environmental and Cost Comparison Table
| Factor | Unf Threads | Unc Threads |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Suitable for tight tolerances and exact alignment | Good for general alignment |
| Temperature | Works well in controlled environments | Handles wider temperature changes |
| Pressure | Excels in structural integrity and precision | Reliable for universal applications |
| Chemical Exposure | Best in minimal chemical exposure | Often made from corrosion-resistant materials |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher due to fine pitch | Generally less expensive |
| Ease of Assembly | More complex assembly | Easier to assemble and disassemble |
| Maintenance | More challenging, risk of cross-threading | Easier, faster, ideal for frequent maintenance |
Regular maintenance and inspection help you avoid downtime and keep your system running smoothly.
Sunhy Stainless Steel Fittings for UNC and UNF
You can trust Sunhy to deliver top-quality fittings for both unc and unf threads in all applications.
Sunhy offers a wide range of stainless steel fittings designed for unc vs unf fittings. You get products that meet strict international standards and perform reliably in demanding environments.
- Sunhy uses advanced CNC machining for precise unc and unf threads.
- Each fitting passes rigorous quality checks, including high-pressure leak tests.
- You can choose from compression fittings, adapters, hose end fittings, and more for any application.
- Sunhy’s fittings resist corrosion and withstand high pressure, making them ideal for oil & gas, chemical processing, and instrumentation applications.
- The product line covers both standard and custom sizes, so you always find the right fit.
Note: Sunhy’s expertise ensures you get the right fitting for your application, whether you need unc threads for easy maintenance or unf threads for high-precision performance.
When you need to know how to choose unc and unf threads, rely on Sunhy’s experience and product range. You get safe, leak-free connections and long-lasting performance in every installation.
UNC vs UNF Fittings Table
Quick Comparison Table
You need a quick way to compare unc threads and unf threads.
This table highlights the main differences between unc and unf fittings so you can choose the right threads for your application.
| Feature | UNC Threads | UNF Threads |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Pitch | Coarse pitch, fewer threads per distance | Fine pitch, more threads per distance |
| Strength | Lower strength in tension and shear | Higher strength in tension and shear |
| Cross-threading Risk | Less likely | More likely |
| Assembly Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Typical Applications | Mass production, general use | High-strength, precision, vibration resistance |
| Material Compatibility | Softer materials | Harder materials |
You can see that unc threads have a coarse pitch and work well for general use.
Unc threads allow for quick assembly and resist cross-threading. You often use unc in mass production or when you need to work with softer materials.
Unf threads have a fine pitch and provide higher strength.
Unf threads excel in applications where you need precision and vibration resistance. You find unf in automotive, aerospace, and instrumentation systems.
Tip: Always match the threads to your application for the best performance and safety.
You may also want to compare the actual dimensions of unc and unf threads.
The following table shows common thread designations, their type, threads per inch, and basic diameters:
| Thread Designation | UNF / UNC | Threads per Inch | Basic Major Diameter (External Threads) | Basic Minor Diameter (Internal Threads) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-80 | UNF | 80 | 0.060 | 0.047 |
| 1-64 | UNC | 64 | 0.073 | 0.056 |
| 2-56 | UNC | 56 | 0.086 | 0.067 |
| 2-64 | UNF | 64 | 0.086 | 0.069 |
| 4-40 | UNC | 40 | 0.112 | 0.085 |
| 5-40 | UNC | 40 | 0.125 | 0.098 |
| 5-44 | UNF | 44 | 0.125 | 0.100 |
| 6-32 | UNC | 32 | 0.136 | 0.104 |
| 6-40 | UNF | 40 | 0.136 | 0.111 |
| 8-32 | UNC | 32 | 0.164 | 0.130 |
| 8-36 | UNF | 36 | 0.164 | 0.134 |
| 10-24 | UNC | 24 | 0.190 | 0.145 |
| 10-32 | UNF | 32 | 0.190 | 0.156 |
| 1/4-20 | UNC | 20 | 0.250 | 0.196 |
| 1/4-28 | UNF | 28 | 0.250 | 0.211 |
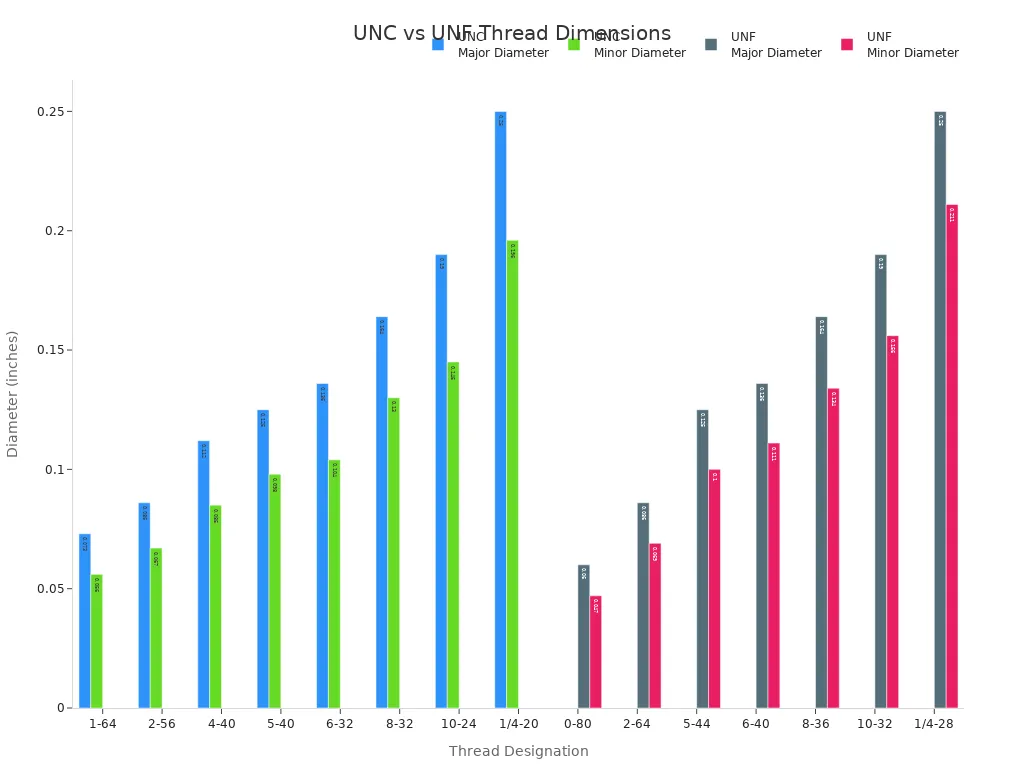
You can use this chart to visualize the differences in thread dimensions.
Unc threads and unf threads have different pitches and diameters, so you must always check the specifications before selecting fittings.
Summary List:
- Unc threads: Coarse, quick to assemble, best for general use.
- Unf threads: Fine, strong, best for precision and vibration resistance.
- Always match unc or unf to your system requirements.
UNC threads offer strength and easy assembly, while UNF threads provide precision and vibration resistance.
You must always match unc vs unf fittings to your application for safety and reliability. When you select between unc and unf, keep these points in mind:
- UNC threads deliver durability and quick installation.
- UNF threads excel in high-precision and vibration-prone environments.
- Material compatibility and industry standards matter for both thread types.
- Manufacturing costs and assembly complexity differ.
Choosing the wrong threads can cause leaks, failures, or downtime. Always consult the quick comparison table and selection tips before making a decision.
| Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| System Failure | Incorrect threads may lead to leaks or loss of strength. |
| Costly Downtime | Mismatched threads can halt operations unexpectedly. |
You can trust Sunhy stainless steel fittings for both unc and unf threads. Review the tables and tips above to ensure the best results for your next project. If your assembly includes flanged joints, review threaded flanges requirements to keep thread type, facing, and tightening practice aligned.
FAQ
What is the main difference between UNC and UNF threads?
UNC threads have a coarse pitch; UNF threads have a fine pitch.
You will notice UNC threads have fewer threads per inch, making them better for quick assembly. UNF threads have more threads per inch, providing greater strength and vibration resistance.
Can you use UNC and UNF fittings interchangeably?
No, you cannot use UNC and UNF fittings interchangeably.
Each thread type has a unique pitch and profile. Mixing them can cause leaks, system failures, or damage to your equipment.
Where do you typically use UNF fittings?
You use UNF fittings in precision and vibration-prone environments.
Common applications include automotive, aerospace, and instrumentation systems. UNF threads provide a tight seal and resist loosening from vibration.
How do you identify UNC and UNF threads?
You identify UNC and UNF threads by measuring thread pitch and diameter.
Use a thread pitch gauge and calipers. UNC threads have fewer threads per inch than UNF threads of the same diameter.
Why choose Sunhy stainless steel fittings for UNC and UNF applications?
Sunhy fittings offer precision, durability, and certified quality.
You benefit from advanced CNC machining, rigorous testing, and corrosion-resistant materials. Sunhy ensures reliable performance for both UNC and UNF thread types.