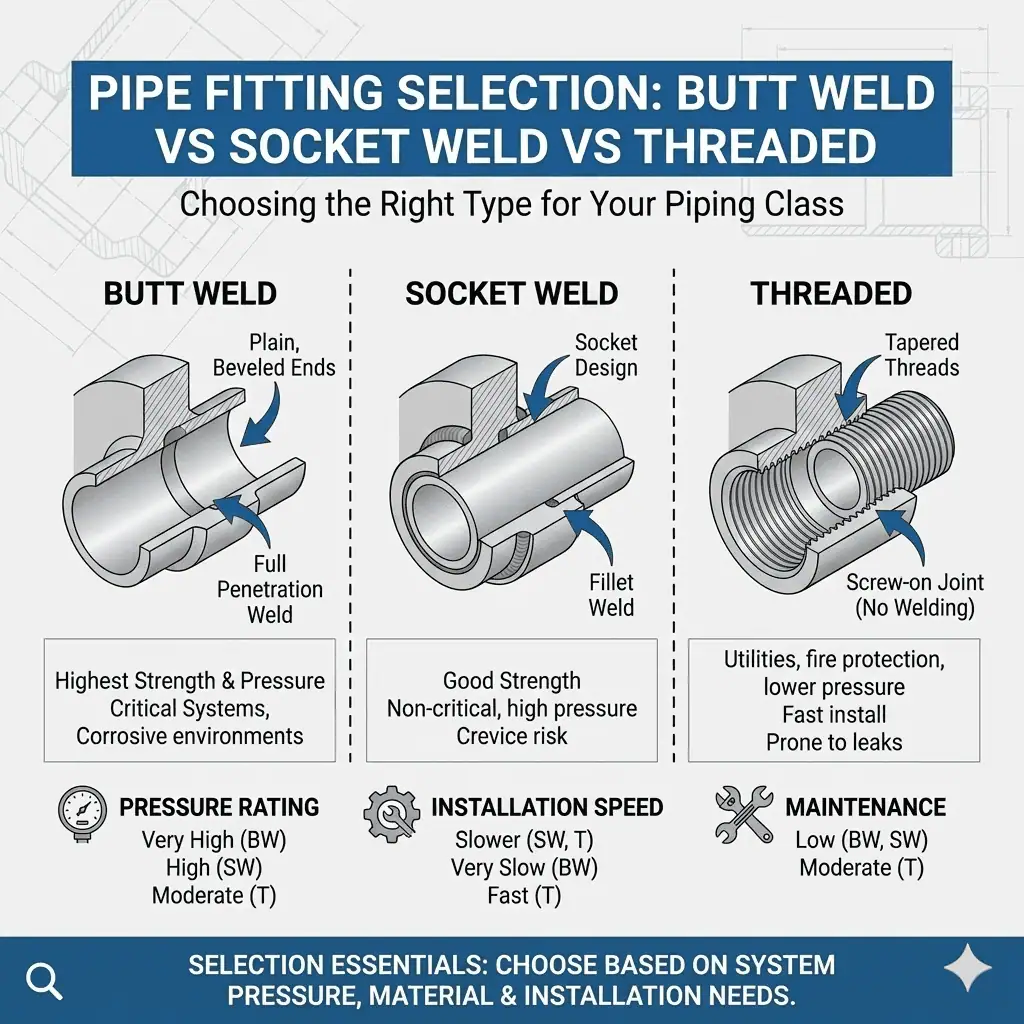
Engineers should select butt weld, socket weld, or threaded pipe fittings based on system pressure, material quality, and installation needs.
- Sunhy’s stainless steel fittings deliver exceptional durability for demanding environments.
- Quality, corrosion resistance, and precise manufacturing ensure reliable performance in industrial applications.
- The right pipe fittings minimize leaks and support long-term operation.
Butt Weld Fittings Overview
What Are Butt Weld Fittings?
Butt weld fittings are pipe fittings joined by welding the ends together to create a strong, leak-proof connection.
Manufacturers produce these fittings using processes such as raw material preparation, welding and forming, and finishing the welding edges. They often use stainless steel grades like 316/316L, duplex stainless steel, and nickel alloys. The production involves heating raw stainless steel to high temperatures, forming through seamless or welded methods, and ensuring compliance with wall thickness and size specifications. These weld fittings provide a continuous metal structure, which supports high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Advantages of Butt Weld Fittings
Butt weld fittings offer superior strength, durability, and optimal flow characteristics for industrial pipe systems.
Engineers value these fittings for their metallurgical bonding, which delivers excellent structural integrity. The smooth internal profile reduces turbulence and pressure drops, supporting efficient flow. Long-term durability and resistance to environmental factors make them suitable for harsh environments. Industries such as petrochemical, oil and gas, and water treatment rely on butt weld fittings for their versatility and reliability.
Tip: Selecting butt weld fittings ensures minimal leakage and supports seamless operation in demanding conditions.
Disadvantages of Butt Weld Fittings
Butt weld fittings require skilled installation and may present challenges during inspection and modification.
The welding process demands expertise and specialized equipment. Common failure modes include blowholes, cracks, and untight welds, which can occur if the welding is not performed correctly. These issues may be difficult to detect without thorough inspection. Modifying butt weld fittings after installation is also challenging, often requiring additional welding and testing.
| Failure Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Blowholes | Gas trapped between weld gaps, difficult to detect without inspection. |
| Cracks | Caused by low-melting-point iron sulfide and hydrogen in steel. |
| Untight welds | Gaps between steel plates leading to potential leakage. |
Applications for Butt Weld Fittings
Butt weld fittings are ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive industrial environments.
Engineers use these pipe fittings in sectors such as oil and gas, petrochemical, power generation, and water treatment. Facilities like wastewater treatment plants, alcohol production sites, and chemical factories also prefer butt weld fittings for their robust performance. These fittings withstand demanding conditions and provide reliable connections for critical pipe systems.
Socket Welding Fittings Explained
What Are Socket Welding Fittings?
Socket welding fittings connect pipes by inserting the pipe end into a recessed socket and joining them with a fillet weld.
Manufacturers design these fittings with precision-machined ends to ensure tight, uniform welds. The pipe end fits into the socket, leaving a small expansion gap that helps distribute stress and minimize fatigue. This method creates a strong, leak-proof unit ideal for systems that demand reliability and longevity.
- Precision-machined ends for secure welds
- Pipe inserted into recessed socket
- Expansion gap for stress distribution
- Metallurgically bonded joint through fillet weld
Advantages of Socket Welding Fittings
Socket weld fittings offer strong, leak-proof connections and simplify installation for small-diameter pipe systems.
Engineers choose these fittings for their high mechanical strength and long-term leak resistance. The design absorbs stress and vibrations, making them suitable for demanding environments. Their compact size fits well in systems with limited space, and the installation process is straightforward, reducing errors and saving time.
- Leak-proof connection for critical pipe fittings
- High strength and durability under pressure and temperature
- Easy installation process
- Efficient for small-diameter pipes
- Resistance to stress and vibration
- Eliminates threading issues
- Cost-effective due to reduced maintenance
Disadvantages of Socket Welding Fittings
Socket weld fittings require high-quality welding and may present challenges in inspection and corrosion resistance.
The reliability of these weld fittings depends on the skill of the welder. Poor welding can cause defects such as porosity, cracks, or incomplete fusion, which weaken the joint. Metal corrosion can occur in harsh environments, especially under high pressure. The abrupt transition between the pipe and the flange creates stress concentration, increasing the risk of fatigue failure. Inspecting socket weld joints is difficult because they are often hidden, making it hard to detect defects or corrosion.
Note: Socket weld joints may not provide the same integrity as butt weld or threaded joints in high-pressure situations.
Applications for Socket Welding Fittings
Socket welding fittings serve critical roles in industries that require reliable, high-pressure pipe connections.
These fittings are common in oil and gas, petrochemical, power generation, chemical processing, and water treatment facilities. Engineers use them in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, aerospace applications, and cryogenic systems where reliability and leak resistance are essential.
| Industry | Application Description |
|---|---|
| Petrochemical | Systems handling high-temperature, corrosive fluids |
| Oil and Gas | Transportation and processing of hydrocarbons |
| Power Generation | Steam pipelines and feedwater systems |
| Chemical Processing Plants | Equipment exposed to corrosive fluids |
| Water Treatment Facilities | High-pressure water and filtration pipelines |
| Hydraulic/Pneumatic Systems | Junctions for high-pressure liquid movement |
| Aerospace | Systems under critical pressures |
| Cryogenic Systems | Low-temperature piping |
Threaded Pipe Fittings Guide
What Are Threaded Pipe Fittings?
Threaded pipe fittings use screw threads to connect pipes and components, providing a simple and effective joining method for many systems.
These fittings feature internal or external threads that match standard thread types. The most common thread standards include NPT, BSP, Metric, SAE, and JIS. Each type offers unique sealing characteristics and regional compatibility.
| Thread Type | Description | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPT | Tapered thread, U.S. standard | 60-degree thread angle, seals through taper | Gas, liquid, and oil piping in North America |
| BSP | British Standard Pipe thread | 55-degree thread angle; BSPT seals through taper, BSPP uses washers/O-rings | Piping in Europe, Asia, Australia |
| Metric | Metric system threads | 60-degree thread angle, uses washers/O-rings | Engineering, machinery, global use |
| SAE | Automotive standard | 45-degree angle, straight threads need O-rings | Hydraulic, automotive, refrigeration |
| JIS | Japanese standard | 55-degree thread angle, seals through taper or sealing elements | Japanese piping systems |
Advantages of Threaded Pipe Fittings
Threaded pipe fittings offer quick installation, cost savings, and flexibility for low-pressure systems.
These fittings do not require welding, making them ideal for projects needing fast assembly or frequent maintenance. They suit a wide range of materials and sizes, and users can reuse them in other systems.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Easy Installation and Removal | Quick setup without advanced tools, suitable for flexible projects. |
| Cost-Effective Solution | Lower cost than weld fittings, less preparation needed. |
| Flexibility in Maintenance | Simple disassembly for repairs or replacements. |
| Leak-Proof Connections | Reliable joints with sealing tape or compound. |
| Compatibility with Materials | Available in many materials for diverse environments. |
| Wide Range of Sizes | Fits various pipe sizes and project needs. |
| Reusability | Can be reused, supporting sustainability and cost savings. |
Disadvantages of Threaded Pipe Fittings
Threaded pipe fittings are prone to leakage, alignment issues, and damage under rapid temperature or pressure changes.
Industrial reports highlight risks such as coupling fractures and joint separation. Over-tightening may cause cracks, and rapid fluctuations in temperature or pressure often lead to leaks. Alignment challenges can complicate installation, especially in complex pipe systems. These vulnerabilities require careful consideration when selecting fittings for critical applications.
Note: Threaded fittings may need emergency response protocols if rapid leakage or joint failure occurs.
Applications for Threaded Pipe Fittings
Threaded pipe fittings serve general-purpose piping, especially in oil & gas, HVAC, and chemical processing plants.
They are widely used where versatility and cost-effectiveness matter. In chemical plants, threaded connections handle routine fluid transfer and utility lines. Other connection types, such as tri-clamp or DIN, suit hygienic or standardized environments.
| Type of Connection | Application Scenario |
|---|---|
| Threaded | General applications in oil & gas, HVAC, chemical processing |
| Tri-Clamp | Food, beverage, pharmaceutical industries |
| DIN | Chemical and pharmaceutical plants |
| Flanged | Power plants, petrochemical facilities |
| Welded | Nuclear, chemical, high-pressure steam systems |
Threaded pipe fittings also appear in water treatment, fire protection, and low-pressure utility lines. Stainless steel, carbon steel, copper, and non-metallic materials enhance corrosion resistance. Coatings such as paints and epoxies further protect fittings in aggressive environments.
Comparing Pipe Fittings Types
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Butt weld fittings provide the highest pressure and temperature ratings, making them the best choice for demanding industrial systems.
Welded fittings create a permanent, robust connection that withstands high-pressure gas and fluid applications. This strength is essential in oil and gas pipelines, where preventing leaks is critical. Socket weld fittings also offer strong performance, with standard pressure ratings of 3000, 6000, and 9000 lbs. Threaded fittings have lower ratings, typically 2000, 3000, and 6000 lbs, and suit low- to medium-pressure systems. Selecting the right fitting depends on the system’s maximum pressure and temperature, as well as the type of fluid or gas being transported.
| Fitting Type | Pressure Rating (lbs) |
|---|---|
| Socket Weld | 3000, 6000, 9000 |
| Threaded | 2000, 3000, 6000 |
Choosing the correct fitting ensures safety, efficiency, and durability in every pipe system.
Inspectability/NDT
Butt weld fittings require advanced non-destructive testing (NDT), while socket weld and threaded fittings allow for easier visual inspection.
Critical infrastructure projects often demand thorough inspection of welds to guarantee integrity. Butt weld joints typically undergo radiographic or ultrasonic testing to detect internal flaws. Socket weld fittings can be inspected visually, which simplifies quality checks. Threaded fittings also allow for straightforward visual inspection, but may not reveal hidden defects.
Common NDT methods include:
- Radiographic Testing (RT): Detects internal discontinuities using X-rays or gamma rays.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Identifies internal defects with high-frequency sound waves.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): Reveals surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT): Highlights surface cracks and imperfections.
Butt welds often require more rigorous inspection protocols to ensure long-term reliability.
Installation and Maintenance
Threaded fittings offer the simplest installation and maintenance, while butt weld and socket weld fittings require skilled labor and specialized tools.
Threaded connections assemble quickly without welding, making them ideal for projects needing frequent disassembly or repair. Socket weld fittings need precise alignment and welding, but their compact design suits tight spaces. Butt weld fittings demand the highest skill level for installation, as proper weld preparation and execution are critical for leak-free performance.
| Issue | Identification Methods | Root Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaks | Visual inspection, pressure testing | Improper installation, material incompatibility | Tighten connections, replace damaged fittings, apply sealants |
| Corrosion | Visual check, material analysis | Environmental factors, inadequate material selection | Use corrosion-resistant materials, apply protective coatings |
| Pressure Drops | Flow monitoring, pressure gauge readings | Blockages, improper sizing | Clean and flush system, redesign system to minimize losses |
Regular inspection and proper installation extend the service life of all pipe fittings.
Cost and Supply Chain Considerations
Threaded fittings generally cost less and offer easier sourcing, while butt weld fittings require higher investment in labor and quality control.
Butt weld fittings involve labor-intensive processes, including precise alignment and high-quality welding. Socket weld fittings reduce labor costs but still need skilled welders. Threaded fittings minimize labor and equipment expenses, making them attractive for budget-sensitive projects.
| Fitting Type | Cost Influencing Factors |
|---|---|
| Threaded Fittings | Specialized equipment, skilled labor, thread size, pitch, material used |
| Butt Weld Fittings | Labor-intensive, precise alignment, welding techniques, size, thickness, weld quality |
| Socket Weld Fittings | Less labor-intensive, size, thickness, socket design, welding process |
Supply chain factors also play a role:
- Supplier evaluation, including certifications and manufacturing capabilities
- Logistics expertise, affecting shipping and delivery times
- Compliance with international trade regulations
- Adoption of technology in procurement for efficiency and transparency
Sunhy’s integrated manufacturing and rigorous verification process help simplify procurement and ensure consistent quality.
Corrosion Resistance and Material Quality
Material quality and corrosion resistance determine the long-term reliability of pipe fittings in harsh environments.
Stainless steel, duplex, and super duplex materials provide high to very high corrosion resistance and strength. These materials suit general, offshore, and extreme applications. Inconel, Monel, and titanium offer specialized performance for high-temperature, seawater, or aerospace systems.
| Material Type | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Application Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High | High | General use |
| Duplex | Very High | High | Offshore applications |
| Super Duplex | Very High | Very High | Extreme conditions |
| Inconel/Incoloy | High | High | High-temperature systems |
| Monel | High | Moderate | Seawater applications |
| Titanium | Very High | High | Aerospace and marine |
Sunhy’s fittings undergo solution annealing at 1040°C and rapid water quenching, restoring grain structure and enhancing resistance to intergranular corrosion. The 3-Point Verification Process ensures every fitting meets strict quality standards before delivery.
Selecting the right material and manufacturer ensures durability, safety, and operational certainty for every pipe system.
Selection Guide for Pipe Connection Types
Decision Checklist
Engineers should use a structured checklist to select the right pipe connection type for their system.
A practical checklist helps engineers and buyers match the correct fittings to their project requirements. Sunhy’s product range covers all major connection types, supporting diverse industrial needs.
- Compatibility of pipe materials
Select fittings that match the pipe material to prevent galvanic corrosion or mechanical failure. - Ratings for temperature and pressure
Confirm that the connection type meets or exceeds system pressure and temperature demands. - Dimensions and size
Verify that fittings fit the pipe diameter and wall thickness specified in the design. - Environmental factors & corrosion resistance
Choose fittings with corrosion-resistant materials for harsh or corrosive environments. - Budget and longevity
Balance initial cost with expected service life and maintenance frequency. - Maintenance and accessibility
Consider how easily the system can be inspected, repaired, or replaced. - Specific application requirements
Match fittings to the fluid type, flow rate, and any regulatory standards.
Tip: Sunhy’s stainless steel fittings offer high corrosion resistance and durability, making them suitable for critical applications.
Common Mistakes
Selecting the wrong connection type or installing fittings incorrectly can compromise system integrity and safety.
Engineers sometimes overlook failure modes or installation errors, which can lead to leaks, corrosion, or mechanical breakdowns. Understanding these risks helps prevent costly mistakes.
| Fitting Type | Common Mistakes |
|---|---|
| Threaded | Overtightening, vibration loosening, corrosion, galling |
| Socket Weld | Poor welding, insufficient penetration, thermal cracking |
| Butt Weld | N/A |
- Using the wrong connection can compromise the entire system’s integrity.
- Ignoring environmental factors may result in premature corrosion or failure.
- Failing to match pressure ratings can cause leaks or ruptures.
- Overlooking accessibility complicates maintenance and increases downtime.
Note: Proper training and adherence to standards reduce the risk of installation errors.
Example Scenarios
Engineers should match connection types to specific scenarios for optimal performance and reliability.
- High-pressure steam line in a power plant
Butt weld fittings provide the strength and leak resistance needed for high-pressure, high-temperature service. - Chemical transfer in a corrosive environment
Stainless steel socket weld fittings resist corrosion and simplify installation in compact spaces. - Utility water line in a commercial building
Threaded fittings allow quick assembly and easy maintenance for low-pressure systems. - Offshore oil platform
Duplex stainless steel butt weld fittings withstand harsh marine conditions and support long-term operation.
Engineers can consult Sunhy’s catalog to select fittings tailored to their application, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Engineers should select pipe fittings based on system pressure, material quality, and installation needs.
Butt weld fittings suit high-pressure and high-temperature systems. Socket weld fittings work well for compact, high-pressure applications. Threaded fittings offer quick installation for low-pressure lines. Sunhy’s advanced manufacturing and strict quality checks ensure reliable performance.
- Butt weld: Best for strength and durability
- Socket weld: Ideal for small, high-pressure systems
- Threaded: Fast assembly for maintenanceConsult industry standards and experts for complex projects.
FAQ
What is the best fitting for high-pressure pipelines?
Butt weld fittings provide the strongest solution for high-pressure pipelines.
They create a durable welded fitting that withstands extreme pressure and temperature. Engineers rely on these connections for critical systems where safety and reliability matter most.
How do I ensure a leak-resistant fit in my piping system?
Proper installation and material selection guarantee a leak-resistant fit.
Engineers should choose fittings that match the pipe material and use correct assembly techniques. Regular inspection and maintenance help prevent leaks in industrial applications.
Which fitting type works best in corrosive environments?
Stainless steel butt weld and socket weld fittings perform best in corrosive environments.
These fittings resist chemical attack and maintain integrity over time. Sunhy’s solution annealing process enhances corrosion resistance for long-term reliability.
Can threaded fittings handle frequent maintenance?
Threaded fittings allow easy disassembly for frequent maintenance.
They suit systems that require regular inspection or replacement. Quick installation and removal make them ideal for utility lines and low-pressure applications.
How do I choose between butt weld, socket weld, and threaded fittings?
Engineers should match fitting type to system pressure, environment, and maintenance needs.
Use this table for quick reference:
| Fitting Type | Best Use Case | Maintenance | Pressure Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Butt Weld | High-pressure pipelines | Low | High |
| Socket Weld | Compact, corrosive systems | Medium | Medium-High |
| Threaded | Utility, frequent service | High | Low-Medium |