316 stainless steel usually offers the best protection for corrosive service because it resists damage in salt-rich and chemical-heavy environments. Choosing the right grade matters because almost one-third of industrial failures result from selecting the wrong stainless steel for corrosive service. Refineries, water treatment plants, and petrochemical facilities often face pitting and crevice corrosion from high chloride levels and humid climates. Sunhy’s expertise in manufacturing Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings helps ensure reliable performance in these demanding settings.
304 vs 316 vs Duplex: Quick Comparison Table
Corrosion Resistance and Applications
316 and Duplex stainless steels provide the highest corrosion resistance for demanding environments.
304 stainless steel works well in mild environments, such as food processing or indoor water systems. 316 stainless steel resists damage from chemicals and saltwater, making it suitable for marine, chemical, and water treatment applications. Duplex stainless steel offers excellent protection against pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride-rich settings like oil and gas or chemical processing. Sunhy’s Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings use advanced solution annealing and strict quality control to maximize corrosion resistance for each grade.
| Property | 304 | 316/L | Duplex 2205 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Better (Mo addition) | Excellent |
| Typical Applications | Food, water | Marine, chemical | Oil & gas, harsh chemicals |
Strength and Durability
Duplex stainless steel delivers the highest strength and durability.
304 and 316 stainless steels have similar mechanical properties, with yield strengths around 205 MPa and tensile strengths near 515 MPa. Duplex stainless steel stands out with yield strengths above 450 MPa and tensile strengths above 620 MPa. This extra strength allows for thinner walls and longer service life in tough environments. Sunhy’s manufacturing methods, such as Cold Mandrel Forming and Hydroforming, ensure consistent wall thickness and reliable performance for all Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings.
| Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | ≥515 | ≥205 |
| 316 | ≥515 | ≥205 |
| Duplex 2205 | ≥620 | ≥450 |
Cost Considerations
304 stainless steel offers the lowest initial cost, while Duplex provides better long-term value in harsh conditions.
304 stainless steel is the most affordable option. 316 costs about 20–30% more due to added molybdenum. Duplex stainless steel has the highest upfront cost, but its durability and reduced maintenance often lower total lifecycle expenses. Sunhy’s Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings meet international standards, ensuring that customers get reliable products that justify their investment.
| Grade | Price Range (per foot) | Cost Difference |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | $3–$8 | Most affordable |
| 316 | $8–$30+ | 20–30% higher than 304 |
| Duplex | Highest | Offsets with durability |
Tip: For environments with high chloride or temperature, Duplex stainless steel often saves money over time due to fewer replacements and repairs.
Pitting Resistance & Chloride Environments (PREN Overview)
Stainless steels in chloride service usually fail by pitting and crevice corrosion rather than by uniform thinning.
PREN (Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number) is a practical way to compare how well different grades resist this type of attack: higher PREN values generally mean better protection in chloride-rich environments. In practice, 304 sits in the lower PREN range, 316/316L is higher thanks to its molybdenum content, and duplex grades such as SAF 2205 are higher again. This explains why 304 tends to pit first, 316 survives longer, and duplex stainless steels are chosen for the harshest duties. Sunhy designs Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings around these differences to deliver reliable performance in aggressive service.
For quick grade selection in chloride environments, you can use the following guidelines:
- Mild corrosion, low chlorides (indoor service water, slightly saline condensate, general utility lines) – 304 may be acceptable if budget is tight and temperatures stay moderate.
- Chloride-containing water, outdoor or marine exposure (cooling water with chlorides, coastal installations, washdown areas, many water-treatment lines) – 316 is usually the default choice.
- Severe chlorides with high pressure and/or high temperature (offshore seawater lines, high-salinity brines, aggressive chemical processing) – duplex stainless steel should be considered.
| Steel Type | PREN Values |
|---|---|
| 304 | 17.5–20.8 |
| 316/316L | 23.1–28.5 |
| SAF 2205 | 30.8–38.1 |
Note: Always check PREN values when choosing fittings for saltwater or chemical-rich systems.
Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings: Grade Breakdown
304 Stainless Steel: Uses and Limits
304 stainless steel is best for mild environments but has clear limits in high-chloride or polluted areas.
304 Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings perform well in clean water systems, food processing, and indoor plumbing, where corrosion conditions are relatively light and temperatures are moderate. It is a sensible choice for indoor, general industrial water and utility lines when budgets are tight.
However, 304 has relatively low pitting resistance to chlorides. In seawater, brine, coastal atmospheres, or heavily polluted environments, 304 fittings are prone to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially at welds and gasketed joints, so it is not recommended for long-term service in those systems.
Sunhy manufactures these fittings using advanced CNC machining and solution annealing at 1040°C to restore a clean grain structure and maximize corrosion resistance.
Common certifications include:
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Effective quality management processes |
| ANSI | Compliance with national standards |
| ASME | Adherence to engineering standards |
304 stainless steel can corrode in high-salt environments, such as coastal regions or polluted areas. Improper cleaning can also cause rust.
Sunhy provides inspection certificates and Mill Test Reports to guarantee product quality.
316 Stainless Steel: Enhanced Corrosion Protection
316 stainless steel offers superior protection against chemicals and saltwater and is the default “go-to” grade for many corrosive services.
316 Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings typically contain around 2% molybdenum, which increases resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride-bearing environments. For cooling water circuits, coastal installations, washdown areas, and many water-treatment or chemical-processing lines, 316 provides a robust balance of performance and cost.
Even so, 316 is not invincible: in hot, stagnant seawater or very high-salinity brines it can still suffer pitting and stress corrosion cracking over time, in which case duplex or higher-alloy grades should be evaluated.
The alloy composition comparison:
| Alloy | Chromium | Nickel | Molybdenum | Corrosion Resistance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 18% | 8% | 0% | Moderate resistance, susceptible to pitting in chloride environments |
| 316 | 16% | 10% | 2% | Enhanced resistance, ideal for chloride-rich environments |
- Marine components
- Chemical processing equipment
- Medical devices
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Outdoor electrical enclosures
- Food processing in saline environments
Duplex Stainless Steel: High Performance in Harsh Environments
Duplex stainless steel delivers the highest strength and corrosion resistance for extreme conditions where 316 is no longer sufficient.
Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings feature a dual-phase austenitic–ferritic structure, providing roughly twice the yield strength of standard austenitic grades together with excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking and chloride-induced pitting. This makes duplex an excellent choice for offshore seawater systems, high-pressure desalination plants, and aggressive chemical or brine services where failure would be very costly or unsafe.
These advantages come with trade-offs: duplex alloys are more expensive per kilogram and require qualified welding procedures to preserve toughness and corrosion resistance. For mild or moderate service they may be unnecessary, but in truly harsh environments they often deliver the lowest lifecycle cost.
Duplex stainless steel delivers the highest strength and corrosion resistance for extreme conditions.
Duplex Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings feature a dual-phase structure, providing twice the yield strength of standard grades and excellent resistance to stress corrosion cracking.
Key advantages:
- Yield strength of about 450 MPa
- Tensile strength from 620 to 850 MPa
- Toughness in cold environments
| Property | Duplex Stainless Steel | Traditional Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 450 | 225 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 620 – 850 | 505 |
| Resistance to SCC | Excellent | Poor above 60°C |
| Operational Lifespan | >2x longer | Standard lifespan |
| PREN Value | Higher (DSS 2205/2507) | Lower |
Duplex stainless steel resists pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, making it ideal for oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings: Practical Selection Guide
Assessing Environmental and Chemical Exposure
The best way to select stainless steel pipe fittings for corrosive service is to match the grade to the specific chemicals and environmental conditions present.
Engineers must identify the type of fluid or gas flowing through the system, the presence of chlorides, acids, or alkalis, and the likelihood of exposure to humidity or saltwater. Each corrosion type affects fittings differently. For example, pitting corrosion often occurs in chloride-rich environments, while uniform corrosion appears in acidic conditions. Sunhy’s stainless steel fittings resist many forms of corrosion due to their advanced solution annealing and strict quality control.
| Corrosion Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Corrosion | Even surface attack, common in acids |
| Pitting Corrosion | Localized pits, often from chlorides |
| Crevice Corrosion | In gaps or stagnant areas, under gaskets |
| Stress Corrosion Cracking | Sudden failure from stress and corrosive media |
| Galvanic Corrosion | Between dissimilar metals in electrolytes |
Tip: Always check the chemical compatibility of the fitting alloy with the process media. Grades like 316 and Duplex excel in saline or aggressive chemical environments.
Temperature, Pressure, and Mechanical Needs
Selecting the right grade depends on the system’s operating temperature, pressure, and mechanical requirements.
High temperatures and pressures demand fittings with superior strength and toughness. Duplex stainless steel offers the highest yield and tensile strength, making it ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature systems. Type 316 stainless steel performs well in marine and chemical processing environments due to its molybdenum content. Sunhy’s manufacturing processes, such as Cold Mandrel Forming, ensure fittings maintain their integrity under stress.
| Material Grade | Max Operating Temp (°C) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 925 | ≥205 | General plumbing, HVAC |
| 316/L | 925 | ≥205 | Marine, pharmaceutical |
| Duplex 2205 | 870 | ≥450 | Oil & gas, water treatment |
- Strength: Withstands stress without deforming.
- Ductility: Changes shape without breaking.
- Toughness: Absorbs energy before fracturing.
Note: For systems with frequent temperature changes or high mechanical loads, Duplex stainless steel provides extra safety and longevity.
Budget and Lifecycle Value
Investing in higher-grade stainless steel pipe fittings often results in lower total costs over the system’s lifetime.
Initial budget constraints may lead some projects to choose lower-cost options like 304 stainless steel. However, maintenance and replacement costs for less durable materials can quickly surpass initial savings. Stainless steel pipe fittings, especially those made by Sunhy, offer long-term durability and reliability, reducing downtime and replacement expenses.
- Stainless steel pipes can last over 100 years with proper care.
- High-quality fittings minimize leaks and failures.
- Cheaper alternatives may require frequent repairs, increasing total cost.
| Grade | Initial Cost | Maintenance Cost | Expected Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | Low | Moderate | 50+ years |
| 316 | Medium | Low | 70+ years |
| Duplex | High | Very Low | 100+ years |
Case Study: A food processing plant in Southeast Asia found that stainless steel pipe fittings provided a more hygienic and durable solution than copper, with long-term savings realized within seven years.
Quick Grade Selection Checklist
Use this checklist to quickly determine the best stainless steel grade for your application.
- Identify the media type (fluid or gas).
- Check for chlorides, acids, or alkalis in the environment.
- Determine required pressure and temperature ratings.
- Assess mechanical stress and load conditions.
- Confirm material compatibility with pipes and service conditions.
- Review regulatory certifications (ASME, ASTM, ISO).
- Calculate total lifecycle cost, not just initial price.
| Grade | Key Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 304/304L | General corrosion resistance | Food, beverage, general process |
| 316/316L | Enhanced chemical & salt resistance | Marine, pharmaceutical, sanitary |
| 2205 Duplex | High strength, pitting resistance | Oil & gas, water treatment |
Sunhy’s stainless steel fittings meet ASME and ISO standards, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments.
Flowchart: Step-by-Step Selection Guide
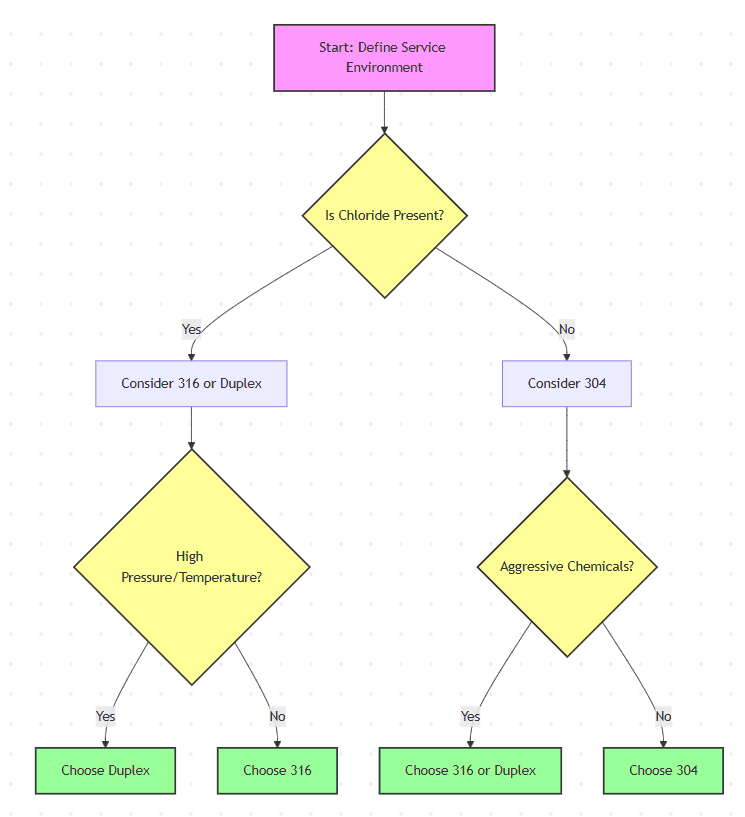
Sunhy’s product catalog covers all major grades and connection types, including butt-weld, threaded, and flanged fittings. Their rigorous testing protocols guarantee operational certainty for every project.
Common Mistakes When Choosing Stainless Steels for Corrosive Service
Over-relying on 304 in chloride-rich environments
304 stainless steel often fails in chloride-rich environments due to its limited resistance to pitting and stress corrosion cracking.
Engineers sometimes choose 304 for its affordability, but this grade cannot withstand high chloride levels found in marine or chemical settings. Chloride ions attack the passive film on 304, causing rapid degradation and localized damage.
| Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) | Chloride ions break down the protective layer, leading to sudden structural failures. |
| Pitting Corrosion | Chloride accumulation causes small, deep pits that weaken the fitting over time. |
| Passive Film Degradation | The breakdown of the surface layer increases the risk of corrosion and leaks. |
Tip: Always select 316 or Duplex stainless steel for environments with high chloride exposure.
Ignoring weld corrosion and heat-affected zones
Neglecting weld quality and heat-affected zones can lead to premature failure of stainless steel fittings.
Welding introduces heat that changes the metal’s structure, making it more vulnerable to corrosion. Distortion during welding can also occur if workers use excessive amperage or improper techniques.
- Stainless steel flanges may distort during welding because of high expansion rates.
- Minimal amperage helps reduce distortion while maintaining weld integrity.
- Pollutants like iron filings and grease can contaminate the surface, increasing corrosion risk.
| Common Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Distortion During Welding | Poor technique causes shape changes, affecting fit and performance. |
| Surface Contamination | Pollutants introduced during fabrication reduce corrosion resistance. |
Regular cleaning and proper welding procedures help maintain the integrity of stainless steel fittings.
Choosing only by price, not lifecycle cost
Selecting fittings based only on initial price often leads to higher long-term expenses and safety risks.
Low-cost options like 304 may seem attractive, but frequent replacements and maintenance increase total costs. Neglecting safety protocols can result in accidents, as highlighted by OSHA statistics.
- Regular cleaning prevents contamination and extends service life.
- High-quality fittings reduce downtime and improve safety.
- Lifecycle cost analysis ensures better value and reliability.
| Common Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Safety Issues | Ignoring safety protocols can cause accidents and system failures. |
| Lack of Cleanliness | Failing to clean fittings leads to contamination and corrosion. |
Consider both initial investment and long-term performance when choosing stainless steel pipe fittings.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Oil & Gas Applications
Stainless steel pipe fittings provide reliable performance and safety in oil and gas operations because they resist corrosion and withstand high pressure.
Oil and gas facilities often face harsh conditions, including exposure to saltwater, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. Sunhy’s fittings have proven effective in offshore platforms and refineries. Their solution annealing process at 1040°C and rapid water quenching restore the material’s grain structure, which increases resistance to intergranular corrosion. Sunhy also uses hydrostatic and pneumatic testing to ensure every fitting meets strict safety standards.
- Offshore rigs use duplex stainless steel fittings to prevent pitting and crevice corrosion from seawater.
- Refineries select 316 stainless steel for pipelines that carry aggressive chemicals.
- Sunhy’s fittings maintain structural integrity during pressure surges and temperature swings.
Sunhy’s rigorous testing protocols help reduce the risk of leaks and unplanned shutdowns, protecting both equipment and workers.
Chemical Processing and Water Treatment
Sunhy’s stainless steel pipe fittings improve efficiency and safety in chemical plants and water treatment facilities by offering long-lasting corrosion resistance and hygienic properties.
Chemical processing plants handle acids, alkalis, and solvents that can quickly damage ordinary materials. Water treatment systems require fittings that do not contaminate potable water or promote bacteria growth. Sunhy’s products meet these needs through advanced manufacturing and strict quality control.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Corrosion resistance | Stainless steel has a low corrosion rate, leading to no internal deposits that impede flow. |
| Longevity | The lifespan exceeds 50 years, reducing the need for replacements and maintenance costs. |
| Strength and durability | High tensile strength and ductility allow for easier installation and resistance to erosion. |
| Hygienic properties | Less susceptible to bacteria growth and does not require toxic coatings, making it safe for potable water. |
| Eco-friendliness | 100% recyclable and produced with a cleaner process, making it a greener choice. |
| Versatility | Suitable for various water types and conditions, ensuring performance without compromising quality. |
Operators in chemical plants report fewer shutdowns and lower maintenance costs after switching to Sunhy’s fittings. Water utilities choose these fittings for their safety and long service life, ensuring clean water delivery to communities.
316 and Duplex stainless steel pipe fittings offer the best protection for corrosive service.
Engineers should match the grade to the environment and application.
- 304 suits mild, indoor, or food-grade systems.
- 316 resists chemicals and saltwater in marine or pharmaceutical settings.
- Duplex provides high strength and durability for oil, gas, and harsh chemical plants.
Choosing a trusted supplier like Sunhy ensures quality, safety, and long-term value.
FAQ
What is the main difference between 304, 316, and Duplex stainless steel fittings?
304 suits mild environments. 316 resists chemicals and saltwater. Duplex offers the highest strength and corrosion resistance.
| Grade | Best Use |
|---|---|
| 304 | Food, water, indoor |
| 316 | Marine, chemical |
| Duplex | Oil & gas, harsh chemicals |
How do engineers choose the right grade for corrosive service?
Engineers match the grade to the chemicals, temperature, and pressure in the system.
- Identify the fluid or gas
- Check for chlorides or acids
- Review pressure and temperature needs
- Select the grade with suitable resistance
Are Sunhy’s stainless steel fittings certified for industrial use?
Sunhy’s fittings meet ASME, ASTM, and ISO standards.
These certifications ensure safety, reliability, and quality for industrial applications.
Can stainless steel fittings be used for drinking water systems?
316 and Duplex stainless steel fittings work well for drinking water systems.
They resist corrosion, do not leach harmful substances, and maintain water purity.