Choosing the right hydraulic adapters ensures your system operates safely, efficiently, and without leaks. You need to match the adapter to your system’s pressure, fluid, thread type, and material requirements. Sunhy, a leading manufacturer, produces adapters that play a critical role in maintaining performance and reliability.
Industry studies show that high-quality fittings:
- Prevent leaks and fluid loss
- Increase durability and system longevity
- Reduce maintenance costs and downtime
System Compatibility and Selection Criteria
Pressure and Fluid Requirements
You must match hydraulic adapters to your system’s pressure requirements and fluid type to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Start by identifying the maximum operating pressure in your hydraulic system. Select adapters and hydraulic fittings that can handle these pressure requirements without risk of failure. If you choose an adapter with a lower pressure rating than your system, you risk leaks or catastrophic failure.
Next, consider the type of hydraulic fluid in use. Different fluids can affect the selection criteria for both adapter materials and sealing mechanisms. For example, some fluids may degrade certain O-ring materials, leading to leaks or system breakdowns.
Tip: Always check both the pressure rating and fluid compatibility before making your final selection.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Pressure | The pressure applied to the O-ring during compression is critical; excessive pressure can lead to failure. |
| Temperature | Temperature fluctuations affect O-ring performance; materials must maintain elasticity under varying conditions. |
| Fluid Compatibility | O-rings must be compatible with hydraulic fluids to prevent degradation and ensure long-term performance. |
- Using incompatible O-ring materials can cause chemical degradation, resulting in leaks and system failures.
- Temperature extremes can cause O-rings to lose elasticity, leading to seal failure and safety hazards.
- Selecting the right O-ring material is crucial for maintaining hydraulic system integrity and preventing costly repairs.
Temperature and Environment
You need to select hydraulic adapters that withstand the temperature range and environmental conditions of your application.
Temperature swings can impact the performance of both the adapter and its seals. Standard hydraulic hoses typically operate between -40°F (-40°C) and +212°F (+100°C). Specialty hoses can handle even wider ranges, from -55°F (-48°C) to +300°F (+149°C). Choose materials and seals that maintain their properties within your system’s temperature range.
| Type of Hose | Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Standard Hydraulic Hose | -40°F (-40°C) to +212°F (+100°C) |
| Specialty Hydraulic Hose | -55°F (-48°C) to +300°F (+149°C) |
Environmental factors such as humidity and dust also influence your selection criteria. High humidity can accelerate corrosion, especially in carbon steel. Dust can wear down protective coatings, reducing the lifespan of your hydraulic adapters.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Hydraulic Adapter Materials |
|---|---|
| Humidity | Creates an ideal environment for corrosion, leading to material degradation and potential leaks. |
| Dust | Abrasive particles wear down protective coatings, compromising the integrity of the materials. |
Note: For most systems, carbon steel with Buna-N seals works well. For higher temperatures, consider upgrading to Viton seals for better performance.
Chemical Compatibility
You must ensure chemical compatibility between the hydraulic fluid, adapter material, and sealing mechanisms to prevent premature failure.
Not all materials resist every chemical. Some hydraulic fluids can react with certain metals or elastomers, causing swelling, cracking, or loss of strength. Always review the chemical compatibility of your chosen materials as part of your selection criteria.
Industry standards help you verify compatibility:
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM D1414 | Standard test method for rubber property testing. |
| ASTM D471 | Standard test method for rubber property testing in various fluids. |
| ASTM D4289 | Guide for testing elastomer compatibility with hydraulic fluids. |
| ASTM D6546 | Guide for testing elastomer compatibility with hydraulic fluids. |
| ASTM D2240 | Standard test method for rubber hardness. |
Tip: Always consult manufacturer data sheets and industry standards to confirm compatibility before installation.
By following these selection criteria, you ensure system compatibility, prevent leaks, and extend the life of your hydraulic adapters.
Types of Hydraulic Adapters and Fittings
Common Hydraulic Adapter Types
You need to choose the right type of hydraulic adapter for your system’s requirements.
Sunhy offers a wide range of hydraulic adapters to match different thread types and applications. Each type serves a specific purpose and ensures compatibility with your hydraulic fittings.
| Adapter Style | Description | Typical Pressure Rating | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
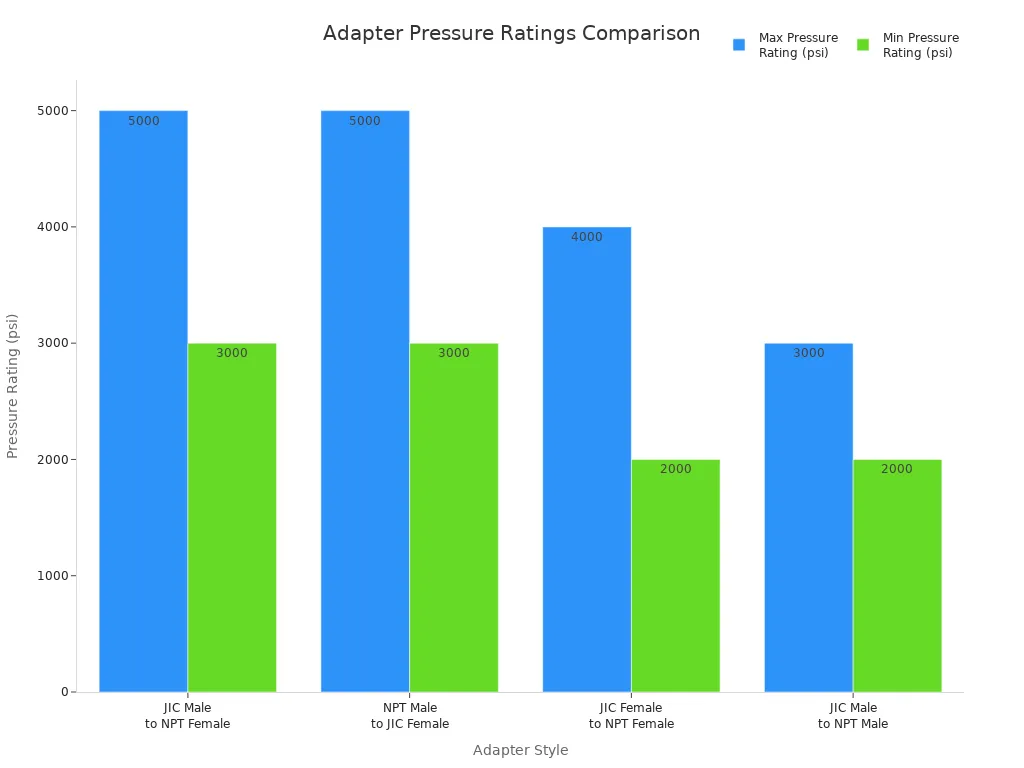
| JIC Male to NPT Female | JIC male flare on one end, NPT female taper on the other; often includes an internal O-ring for added sealing | 3,000–5,000 psi | Carbon steel, 316 SS, brass |
| NPT Male to JIC Female | NPT male taper with JIC female flare port; may include bonded seal washer to protect flare integrity | 3,000–5,000 psi | Carbon steel, 316 SS, brass |
| JIC Female to NPT Female | Bulkhead or run-through adapter combining JIC female flare and NPT female threads in one body for panel or manifold mounting | 2,000–4,000 psi | Carbon steel, brass |
| JIC Male to NPT Male | Less common; requires sealant on NPT threads and torque control to avoid over-stress on JIC flare face | 2,000–3,000 psi | Stainless steel, brass |
You will find NPT/NPTF, ORFS, JIC, BSP, and DIN adapters in Sunhy’s product line. These adapters support a wide range of hydraulic fittings and help you connect hoses, tubes, and components with different thread standards.
Hydraulic Fittings and Hose Connections
You must select the correct hydraulic fittings to ensure leak-free and secure hose connections.
Hydraulic fittings come in many shapes and serve different functions in your system.
- Straight fittings connect two hoses or tubes in a straight line.
- Elbow fittings change the direction of a hose or tube by 90 degrees.
- Tee fittings branch a hose or tube into two directions.
- Cross fittings connect four hoses or tubes in a cross pattern.
- Union fittings allow you to connect and disconnect hoses or tubes without tools.
- Adapter fittings connect hoses or tubes with different sizes or thread types.
- Bulkhead fittings connect a hose or tube to a panel or bulkhead.
When you buy hydraulic fittings, always check the pressure rating, thread type, and compatibility with your hydraulic fluid.
Follow installation best practices to prevent leaks and reduce downtime.
Material Options and Durability
You should choose the right material for your hydraulic adapters and fittings based on your system’s environment and pressure needs.
Material selection affects durability, corrosion resistance, and performance.
| Material | Corrosion Resistance Rating | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Moderate | Agricultural, industrial, construction sectors |
| Stainless Steel | High | Highly corrosive environments |
| Brass | Moderate | Smaller compression and threaded fittings |
| Aluminum | Good | Low density, low pressure applications |
- Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and works well in harsh environments.
- Carbon steel provides strength for high-pressure systems but needs protective coatings in corrosive settings.
- Brass suits low-pressure, non-corrosive environments and is compatible with certain fluids.
For installation best practices, always match the material to your application and fluid type.
This step helps you avoid premature failure and ensures long-term reliability when you buy hydraulic fittings.
Thread Identification and Connection Standards
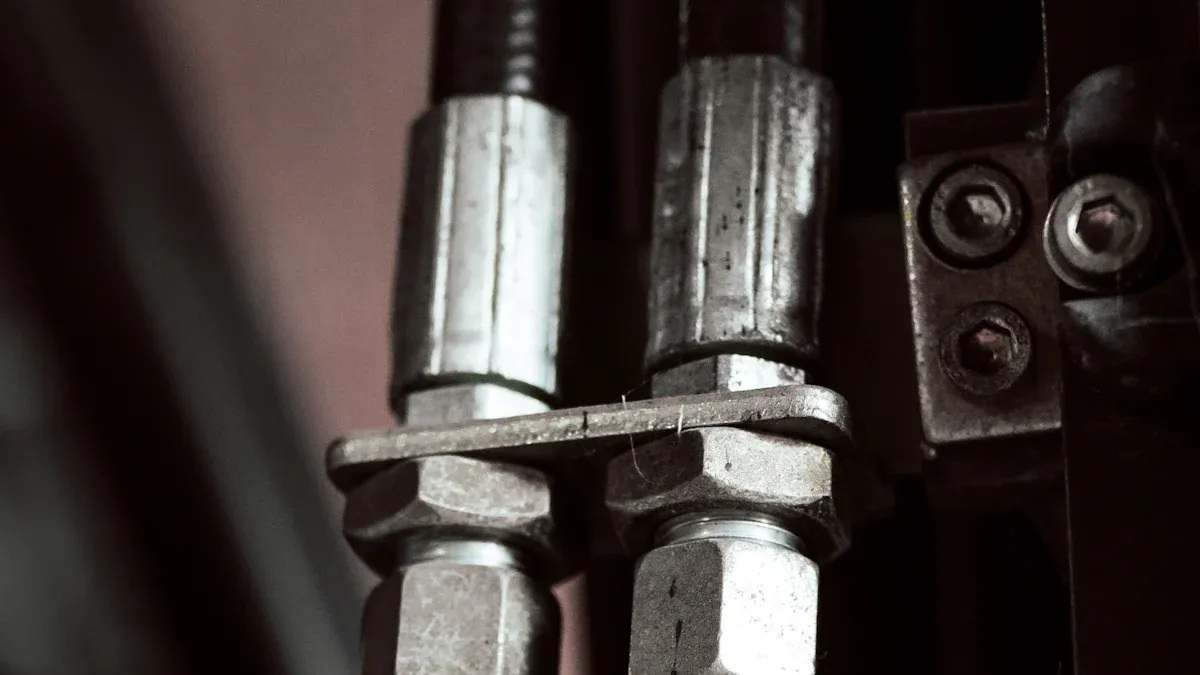

Measuring and Identifying Threads
You must accurately identify thread types to ensure a secure connection and prevent costly mistakes.
Correct thread identification is essential for hydraulic hose fittings. Many thread types look similar, which can lead to errors and system failures. Use the right tools and follow these steps:
- Use calipers to measure the outside and inside diameters of the threads.
- Use a thread pitch gauge to determine the number of threads per inch.
- Use a flare angle gauge or protractor to measure the fitting angle.
Failing to identify threads correctly can cause mismatched connections, downtime, and even safety hazards. Always double-check your measurements before selecting an adapter.
Regional and Global Standards
You need to match your hydraulic adapter to the correct regional or global thread standard for a precision and leak-proof system.
Hydraulic systems use a variety of thread standards, depending on the region and application. The table below highlights key differences:
| Thread Type | Region | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BSPT | Global (outside NA) | Similar to NPT but with a different thread angle; seals on flanks. |
| JIC | Global | Straight threads with a 37° flare for metal-to-metal seal. |
| ORFS | Global | O-ring compressed against flat face; excellent for high-pressure applications. |
| Metric | Europe, Asia | Parallel threads with 24° cone or O-ring boss seals. |
Sealing methods, torque requirements, and pressure ratings can vary between standards. International standards organizations, such as SAE and ISO, regulate these differences to ensure compatibility:
| Standard | Description | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| SAE J514 | Defines design, dimensions, and performance for hydraulic fittings. | Threaded connections |
| SAE J516 | Outlines requirements for hydraulic hose fittings. | Hose-to-component connections |
| ISO 9974 | Specifies requirements for ports and stud ends in hydraulic systems. | Fluid power connections |
Ensuring Leak-Proof Connections
You must use the proper sealing mechanism to achieve a leak-proof and secure connection, especially in high-pressure applications.
The right seal prevents leaks and maintains system integrity. Common sealing mechanisms include:
| Sealing Mechanism | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| ORFS Fittings | Flat sealing surface compresses an O-ring for a tight seal. | Highly effective in high-pressure applications. |
| O-ring Seals | Elastomer rings provide a barrier against leakage. | Effective in low to medium-pressure systems. |
| Threaded Seals | Relies on tightness of threads, often with tapered threads. | Can leak if not installed properly. |
- O-ring seals are the most common for hydraulic hose fittings.
- Always select O-rings based on fluid type, temperature, and pressure.
- Proper installation is critical for a leak-proof connection.
When you follow these steps, you reduce the risk of malfunctions and ensure your hydraulic system operates safely and efficiently.
Application-Specific Needs and Maintenance
Vibration and Corrosion Resistance
You must select hydraulic adapters designed for high-vibration and corrosive environments to ensure long-term reliability.
Adapters and reducers in high-vibration settings require careful evaluation of material compatibility, pressure ratings, and fit. O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings work best in these conditions. They deliver leak-free reliability and meet modern industrial standards.
Corrosion-resistant coatings protect adapters from chemical attacks and environmental wear. These coatings act as barriers, preventing stress concentration and galvanic corrosion. You should prioritize these features for marine or chemical processing applications.
- ORFS fittings provide superior performance in high-vibration environments.
- Corrosion-resistant coatings extend service life in harsh conditions.
- Stainless steel and coated carbon steel offer strong protection against rust and chemical exposure.
Installation and Troubleshooting Tips
You need to follow proper installation steps and troubleshoot issues to prevent hydraulic adapter failure.
Common installation errors can lead to leaks and system breakdowns. The table below highlights frequent mistakes and their impact:
| Common Installation Errors | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improper Sizing | Mismatched sizes cause leaks and failures. Accurate dimensions are essential. |
| Neglecting Material Compatibility | Incompatible materials result in corrosion and operational failure. |
| Ignoring Pressure Ratings | Exceeding ratings leads to blowouts and system damage. |
| Overlooking Environmental Factors | Environmental stress causes premature wear or failure. |
| Failing To Consider Thread Compatibility | Mismatched threads create leaks and damage components. |
To diagnose leaks or pressure drops, use these steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check for fluid drips and damage.
- Pressure Testing: Test for pressure stability and identify leaks.
- Documenting Results: Record pressure levels and corrective actions.
- Tightening or Replacing Fittings: Adjust or replace damaged parts.
- Resealing Threaded Connections: Apply sealants for proper sealing.
- Retesting After Repairs: Confirm repairs resolved leaks.
Inspect O-rings and seals for wear. Ensure proper alignment and fitment. Maintain cleanliness to avoid contamination.
Fluid compatibility is critical during installation to prevent leaks and ensure system integrity.
Custom Solutions for Unique Systems
You should consider custom hydraulic adapter solutions for non-standard or legacy systems to achieve optimal performance.
Custom solutions provide a precise fit for unique requirements. You can optimize flow rates, pressure levels, and system size. These adapters use rugged materials for reliability in harsh conditions.
Custom designs offer energy-efficient components, minimize heat generation, and include advanced safety features. Maintenance becomes easier, reducing downtime and long-term costs.
Consult Sunhy for tailored solutions when your system needs specialized adapters or unique configurations.
- Custom adapters ensure compatibility with legacy equipment.
- Compact and lightweight designs save space.
- Enhanced safety and efficiency improve overall system performance.
You must follow a precise selection process to ensure your hydraulic couplers deliver safe and reliable performance.
Start by matching fluid compatibility, thread types, and environmental resistance. Use identification tools to verify the types of hydraulic couplers and quick-connect adapters in your system. Consult Sunhy for expert advice on selection and installation. Prioritize manufacturers with ISO certifications for quality assurance.
- Confirm material resistance to hydraulic fluid.
- Match thread types and dimensions to prevent leaks.
- Consider corrosion and vibration resistance.
- Adhere to ISO, SAE, and DIN standards.
| Certification | Region | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Global | Quality assurance |
| CE Marking | Europe | Regulatory compliance |
You improve system reliability and efficiency when you select the right hydraulic couplers and fittings.
FAQ
What factors should you consider when selecting a hydraulic adapter?
You must consider pressure rating, fluid compatibility, thread type, and material.
Check each specification to match your system. Review manufacturer data sheets for pressure and fluid compatibility. Confirm thread type and choose materials that resist corrosion and wear.
How do you identify the correct thread type for your hydraulic system?
You should measure thread diameter and pitch using calipers and gauges.
Compare your measurements to standard charts. Identify if the thread is metric, NPT, BSP, or JIC. Use manufacturer guides for accurate identification.
| Tool | Use |
|---|---|
| Caliper | Measures thread diameter |
| Pitch Gauge | Counts threads per inch |
| Chart | Matches thread standards |
Which material works best for hydraulic adapters in corrosive environments?
Stainless steel offers the highest corrosion resistance.
Choose stainless steel for marine, chemical, or outdoor applications. Brass and coated carbon steel work for moderate conditions. Always match material to your environment.
Tip: Stainless steel adapters last longer in harsh settings.
How do you prevent leaks in hydraulic connections?
You must use the correct sealing mechanism and install adapters properly.
Select O-ring face seals or ORFS fittings for high-pressure systems. Inspect seals for damage. Tighten connections to manufacturer specifications.
- Use O-rings compatible with your fluid.
- Check for proper alignment.
- Avoid over-tightening.
When should you request a custom hydraulic adapter solution?
You should request a custom solution for non-standard or legacy systems.
Custom adapters fit unique configurations, optimize flow, and improve safety. Contact Sunhy for expert advice and tailored designs.